Abstract
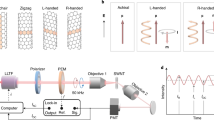
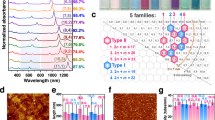
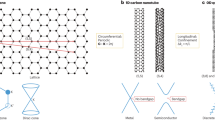
The optical, electrical and mechanical properties of single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWNTs) are largely determined by their structures, and bulk availability of uniform materials is vital for extending their technological applications1. Since they were first prepared2,3, much effort has been directed toward selective synthesis and separation of SWNTs with specific structures. As-prepared samples of chiral SWNTs contain equal amounts of left- and right-handed helical structures4, but little attention has been paid to the separation of these non-superimposable mirror image forms, known as optical isomers. Here, we show that optically active SWNT samples can be obtained by preferentially extracting either right- or left-handed SWNTs from a commercial sample. Chiral ‘gable-type’ diporphyrin molecules bind with different affinities to the left- and right-handed helical nanotube isomers to form complexes with unequal stabilities that can be readily separated. Significantly, the diporphyrins can be liberated from the complexes afterwards, to provide optically enriched SWNTs.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baughman, R. H., Zakhidov, A. A. & de Heer, W. A. Carbon nanotubes—the route toward applications. Science 297, 787–792 (2002).
Iijima, S. & Ichihashi, T. Single-shell carbon nanotubes of 1-nm diameter. Nature 363, 603–605 (1993).
Bethune, D. S. et al. Cobalt-catalysed growth of carbon nanotubes with single-atomic-layer walls. Nature 363, 605–607 (1993).
Dukovic, G. et al. Racemic single-walled carbon nanotubes exhibit circular dichroism when wrapped with DNA. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128, 9004–9005 (2006).
Bachilo, S. M. et al. Narrow (n,m)-distribution of single-walled carbon nanotubes grown using a solid supported catalyst. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 125, 11186–11187 (2003).
Collins, P. G., Arnold, M. S. & Avouris, P. Engineering carbon nanotubes and nanotube circuits using electrical breakdown. Science 292, 706–709 (2001).
Krupke, R., Hennrich, F., Löhneysen, H. V. & Kappes, M. M. Separation of metallic from semiconducting single-walled carbon nanotubes. Science 301, 344–347 (2003).
Strano, M. S. et al. Electronic structure control of single-walled carbon nanotube functionalization. Science 301, 1519–1522 (2003).
Zheng, M. et al. DNA-assisted dispersion and separation of carbon nanotubes. Nature Mater. 2, 338–342 (2003).
Li, H. et al. Selective interactions of porphyrins with semiconducting single-walled carbon nanotubes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126, 1014–1015 (2004).
Arnold, M. S., Green, A. A., Hulvat, J. F., Stupp, S. I. & Hersam, M. C. Sorting carbon nanotubes by electronic structure using density differentiation. Nature Nanotech. 1, 60–65 (2006).
Maeda, Y. et al. Dispersion and separation of small-diameter single-walled carbon nanotubes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128, 12239–12242 (2006).
Zheng, M. et al. Structure-based carbon nanotube sorting by sequence-dependent DNA assembly. Science 302, 1545–1548 (2003).
Duesberg, G. S., Muster, J., Krstic, V., Burghard, M. & Roth, S. Chromatographic size separation of single-walled carbon nanotubes. Appl. Phys. A 67, 117–119 (1998).
Chattopadhyay, D., Lastella, S., Kim, S. & Papadimitrakopoulos, F. Length separation of zwitterion-functionalized single wall carbon nanotubes by GPC. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124, 728–729 (2002).
Duesberg, G. S. et al. Chromatography of carbon nanotubes. Synth. Metals 103, 2484–2485 (1999).
Farkas, E., Anderson, M. E., Chen, Z. & Rinzler, A. G. Length sorting cut single wall carbon nanotubes by high performance liquid chromatography. Chem. Phys. Lett. 363, 111–116 (2002).
Heller, D. A. et al. Concomitant length and diameter separation of single-walled carbon nanotubes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126, 14567–14573 (2004).
Wildöer, J. W. G., Venema, L. C., Rinzler, A. G., Smalley, R. E. & Dekker, C. Electronic structure of atomically resolved carbon nanotubes. Nature 391, 59–62 (1998).
Odom, T. W., Huang, J.-L., Kim, P. & Lieber, C. M. Atomic structure and electronic properties of single-walled carbon nanotubes. Nature 391, 62–64 (1998).
Liu, Z. et al. Determination of optical isomers for left-handed or right-handed chiral double-wall carbon nanotubes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 187406 (2005).
Hashimoto, A. et al. Atomic correlation between adjacent graphene layers in double-wall carbon nanotubes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 045504 (2005).
Meyer, R. R. et al. A composite method for the determination of the chirality of single walled carbon nanotubes. J. Microsc. 212, 152–157 (2003).
Tasaki, S., Maekawa, K. & Yamabe, T. π-band contribution to the optical properties of carbon nanotubes: effects of chirality. Phys. Rev. B 57, 9301–9318 (1998).
Ivchenko, E. L. & Spivak, B. Chirality effects in carbon nanotubes. Phys. Rev. B 66, 155404 (2002).
Samsonidze, G. G. et al. Interband optical transitions in left- and right-handed single-walled carbon nanotubes. Phys. Rev. B 69, 205402 (2004).
Sánchez-Castillo, A., Román-Velazquez, C. E. & Noguez, C. Optical circular dichroism of single-wall carbon nanotubes. Phys. Rev. B 73, 045401 (2006).
Bachilo, S. M. et al. Structure-assigned optical spectra of single-walled carbon nanotubes. Science 298, 2361–2366 (2002).
Borovkov, V. V., Hembury, G. A. & Inoue, Y. Origin, control, and application of supramolecular chirogenesis in bisporphyrin-based systems. Acc. Chem. Res. 37, 449–459 (2004).
Weisman, R. B. & Bachilo, S. M. Dependence of optical transition energies on structure for single-walled carbon-nanotubes in aqueous suspension: an empirical Kataura plot. Nano. Lett. 3, 1235–1238 (2003).
Acknowledgements
We thank Y. Kawai (Nagahama Institute of Bio-Science and Technology) for allowing us to use the CD spectropolarimeter, Y. Nakata and I. Hamagami (Horiba) for taking photoluminescence spectra, T. Mori (Osaka University) for helpful suggestions for CD of SWNTs, N. Yoshimoto, T. Itabashi, S. Yamada (Hitachi) and A. Toshimitsu (Kyoto University) for their encouragement, and M. Uchida (Osaka Prefecture University) for proof-reading the manuscript. This work was financially supported by Integrative Industry-Academia Partnership including Kyoto University, NTT, Pioneer, Hitachi, Mitsubishi Chemical and Rohm.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
X.P., N.K. and A.O. conceived and designed the experiments. T.K. and S.A. provided suggestions on the experiments. X.P. performed most of the experiments and analyses. T. S. contributed to solubilization of SWNTs. X.P. and S.B. carried out the theoretical calculations. N.K. and A.O. co-wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary methods (PDF 5306 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, X., Komatsu, N., Bhattacharya, S. et al. Optically active single-walled carbon nanotubes. Nature Nanotech 2, 361–365 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2007.142
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2007.142
This article is cited by
-
Spiral effect of helical carbon nanorods boosting electrocatalysis of oxygen reduction reaction
Science China Materials (2022)
-
Complete structural characterization of single carbon nanotubes by Rayleigh scattering circular dichroism
Nature Nanotechnology (2021)
-
Water-mediated deracemization of a bisporphyrin helicate assisted by diastereoselective encapsulation of chiral guests
Nature Communications (2019)
-
Reconfigurable chiroptical nanocomposites with chirality transfer from the macro- to the nanoscale
Nature Materials (2016)
-
Experimental determination of excitonic band structures of single-walled carbon nanotubes using circular dichroism spectra
Nature Communications (2016)