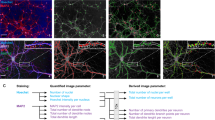
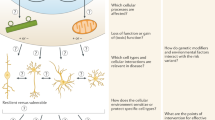
Abstract
Proteomics is complementary to genomic approaches anchored in DNA and RNA. Global characterization of proteins is providing new insights into general biological structures as well as synapses, receptor complexes and other neuronal and glial features. Current challenges for proteomics of the nervous system include problems relating to sample preparation, brain complexity, limited databases and informatics tools. The combination of proteomics with other global functional genomic approaches at the levels of genome and transcriptome, together with network biology, will provide important bridges between genes, physiology and pathology.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Ivelisse Robles
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Phizicky, E., Bastiaens, P.I., Zhu, H., Snyder, M. & Fields, S. Protein analysis on a proteomic scale. Nature 422, 208– 215 (2003).
Aebersold, R. & Mann, M. Mass spectrometry–based proteomics. Nature 422, 198– 207 (2003).
Tyers, M. & Mann, M. From genomics to proteomics. Nature 422, 193– 197 (2003).
Patterson, S.D. & Aebersold, R.H. Proteomics: the first decade and beyond. Nat. Genet. 33 (Suppl.) 311– 323 (2003).
Kitano, H. Computational systems biology. Nature 420, 206– 210 (2002).
Herbert, B.R. et al. What place for polyacrylamide in proteomics? Trends Biotechnol. 19, S3– S9 (2001).
Romijn, E.P., Krijgsveld, J. & Heck, A.J. Recent liquid chromatographic-(tandem) mass spectrometric applications in proteomics. J. Chromatogr. A. 1000, 589– 608 (2003).
Washburn, M.P., Wolters, D. & Yates, J.R., III . Large-scale analysis of the yeast proteome by multidimensional protein identification technology. Nat. Biotechnol. 19, 242– 247 (2001).
Florens, L. et al. A proteomic view of the Plasmodium falciparum life cycle. Nature 419, 520– 526 (2002).
Gygi, S.P. et al. Quantitative analysis of complex protein mixtures using isotope-coded affinity tags. Nat. Biotechnol. 17, 994– 999 (1999).
Olsen, J.V. et al. HysTag—a novel proteomic quantification tool applied to differential display analysis of membrane proteins from distinct areas of mouse brain. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 3, 82– 92 (2003).
Lubec, G., Krapfenbauer, K. & Fountoulakis, M. Proteomics in brain research: potentials and limitations. Prog. Neurobiol. 69, 193– 211 (2003).
Mann, M. & Jensen, O.N. Proteomic analysis of post-translational modifications. Nat. Biotechnol. 21, 255– 261 (2003).
Wells, L. et al. Mapping sites of O-GlcNAc modification using affinity tags for serine and threonine post-translational modifications. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 1, 791– 804 (2002).
Soreghan, B.A., Yang, F., Thomas, S.N., Hsu, J. & Yang, A.J. High-throughput proteomic-based identification of oxidatively induced protein carbonylation in mouse brain. Pharm. Res. 20, 1713– 1720 (2003).
Schweitzer, B. & Kingsmore, S.F. Measuring proteins on microarrays. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 13, 14– 19 (2002).
Zhu, H. et al. Global analysis of protein activities using proteome chips. Science 293, 2101– 2105 (2001).
Hudson, J.R. Jr. et al. The complete set of predicted genes from Saccharomyces cerevisiae in a readily usable form. Genome Res. 7, 1169– 1173 (1997).
Reboul, J. et al. C. elegans ORFeome version 1.1: experimental verification of the genome annotation and resource for proteome-scale protein expression. Nat. Genet. 34, 35– 41 (2003).
Stapleton, M. et al. The Drosophila gene collection: identification of putative full-length cDNAs for 70% of D. melanogaster genes. Genome Res. 12, 1294– 1300 (2002).
Martin, K. et al. Strategies and solid-phase formats for the analysis of protein and peptide phosphorylation employing a novel fluorescent phosphorylation sensor dye. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen. 6, 331– 339 (2003).
Rodriguez, M., Li, S.S., Harper, J.W. & Songyang, Z. An oriented peptide array library (OPAL) strategy to study protein-protein interactions. J. Biol. Chem. 279 8802– 8807 (2003).
Nedelkov, D. & Nelson, R.W. Surface plasmon resonance mass spectrometry: recent progress and outlooks. Trends Biotechnol. 21, 301– 305 (2003).
Klose, J. et al. Genetic analysis of the mouse brain proteome. Nat. Genet. 30, 385– 393 (2002).
Fountoulakis, M., Juranville, J.F., Dierssen, M. & Lubec, G. Proteomic analysis of the fetal brain. Proteomics 2, 1547– 1576 (2002).
Kidd, D., Liu, Y. & Cravatt, B.F. Profiling serine hydrolase activities in complex proteomes. Biochemistry 40, 4005– 4015 (2001).
Ohtsuka, T. et al. Cast: a novel protein of the cytomatrix at the active zone of synapses that forms a ternary complex with RIM1 and munc13–1. J. Cell Biol. 158, 577– 590 (2002).
Unlu, M., Morgan, M.E. & Minden, J.S. Difference gel electrophoresis: a single gel method for detecting changes in protein extracts. Electrophoresis 18, 2071– 2077 (1997).
Che, F.Y. & Fricker, L.D. Quantitation of neuropeptides in Cpe(fat)/Cpe(fat) mice using differential isotopic tags and mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 74, 3190– 3198 (2002).
Schirmer, E.C., Florens, L., Guan, T., Yates, J.R., III & Gerace, L. Nuclear membrane proteins with potential disease links found by subtractive proteomics. Science 301, 1380– 1382 (2003).
Mootha, V.K. et al. Integrated analysis of protein composition, tissue diversity, and gene regulation in mouse mitochondria. Cell 115, 629– 640 (2003).
Gavin, A.C. et al. Functional organization of the yeast proteome by systematic analysis of protein complexes. Nature 415, 141– 147 (2002).
Ho, Y. et al. Systematic identification of protein complexes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by mass spectrometry. Nature 415, 180– 183 (2002).
Ohi, M.D. et al. Proteomics analysis reveals stable multiprotein complexes in both fission and budding yeasts containing Myb-related Cdc5p/Cef1p, novel pre-mRNA splicing factors, and snRNAs. Mol. Cell. Biol. 22, 2011– 2024 (2002).
Shevchenko, A., Schaft, D., Roguev, A., Pijnappel, W.W. & Stewart, A.F. Deciphering protein complexes and protein interaction networks by tandem affinity purification and mass spectrometry: analytical perspective. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 1, 204– 212 (2002).
Gully, D., Moinier, D., Loiseau, L. & Bouveret, E. New partners of acyl carrier protein detected in Escherichia coli by tandem affinity purification. FEBS Lett. 548, 90– 96 (2003).
Forler, D. et al. An efficient protein complex purification method for functional proteomics in higher eukaryotes. Nat. Biotechnol. 21, 89– 92 (2003).
Knuesel, M. et al. Identification of novel protein-protein interactions using a versatile mammalian tandem affinity purification expression system. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2, 1225– 1233 (2003).
Husi, H., Ward, M.A., Choudhary, J.S., Blackstock, W.P. & Grant, S.G. Proteomic analysis of NMDA receptor-adhesion protein signaling complexes. Nat. Neurosci. 3, 661– 669 (2000).
Becamel, C. et al. Synaptic multiprotein complexes associated with 5-HT(2C) receptors: a proteomic approach. EMBO J. 21, 2332– 2342 (2002).
Kim, M., Jiang, L.H., Wilson, H.L., North, R.A. & Surprenant, A. Proteomic and functional evidence for a P2X7 receptor signalling complex. EMBO J. 20, 6347– 6358 (2001).
Li, S. et al. A map of the interactome network of the metazoan C. elegans . Science 303, 540– 543 (2004).
Giot, L. et al. A protein interaction map of Drosophila melanogaster . Science 302, 1727– 1736 (2003).
von Mering, C. et al. Comparative assessment of large-scale data sets of protein-protein interactions. Nature 417, 399– 403 (2002).
Castellucci, V.F., Kennedy, T.E., Kandel, E.R. & Goelet, P. A quantitative analysis of 2-D gels identifies proteins in which labeling is increased following long-term sensitization in Aplysia. Neuron 1, 321– 328 (1988).
Huganir, R.L. & Greengard, P. cAMP-dependent protein kinase phosphorylates the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 80, 1130– 1134 (1983).
Ficarro, S.B. et al. Phosphoproteome analysis by mass spectrometry and its application to Saccharomyces cerevisiae . Nat. Biotechnol. 20, 301– 305 (2002).
Yoshimura, Y. et al. Identification of protein substrates of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II in the postsynaptic density by protein sequencing and mass spectrometry. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 290, 948– 954 (2002).
Raghothama, C. & Pandey, A. Absolute systems biology—measuring dynamics of protein modifications. Trends Biotechnol. 21, 467– 470 (2003).
Blagoev, B. et al. A proteomics strategy to elucidate functional protein-protein interactions applied to EGF signaling. Nat. Biotechnol. 21, 315– 318 (2003).
Korolainen, M.A., Goldsteins, G., Alafuzoff, I., Koistinaho, J. & Pirttila, T. Proteomic analysis of protein oxidation in Alzheimer's disease brain. Electrophoresis 23, 3428– 3433 (2002).
Castegna, A. et al. Proteomic identification of nitrated proteins in Alzheimer's disease brain. J. Neurochem. 85, 1394– 1401 (2003).
Huang, C.M. et al. Proteomic analysis of proteins in PC12 cells before and after treatment with nerve growth factor: increased levels of a 43-kDa chromogranin B-derived fragment during neuronal differentiation. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 92, 81– 192 (2001).
Maurer, M.H., Feldmann, R.E. Jr, Futterer, C.D. & Kuschinsky, W. The proteome of neural stem cells from adult rat hippocampus. Proteome Sci. 1, 4 (2003).
Lafon-Cazal, M. et al. Proteomic analysis of astrocytic secretion in the mouse. Comparison with the cerebrospinal fluid proteome. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 24438– 24448 (2003).
Mouledous, L. et al. Navigated laser capture microdissection as an alternative to direct histological staining for proteomic analysis of brain samples. Proteomics 3, 610– 615 (2003).
Husi, H. & Grant, S.G. Proteomics of the nervous system. Trends Neurosci. 24, 259– 266 (2001).
Husi, H. & Grant, S.G. Construction of a protein-protein interaction database (PPID) for synaptic biology. in Neuroscience Databases: A Practical Guide 51– 62 (Kluwer, Boston, Dordrecht, London, 2002).
Grant, S.G. Systems biology in neuroscience: bridging genes to cognition. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 13, 577– 582 (2003).
Ideker, T. et al. Integrated genomic and proteomic analyses of a systematically perturbed metabolic network. Science 292, 929– 934 (2001).
Jeong, H., Mason, S.P., Barabasi, A.L. & Oltvai, Z.N. Lethality and centrality in protein networks. Nature 411, 41– 42 (2001).
Grant, S.G.N. An integrative neuroscience program linking mouse genes to cognition and disease. in Behavioral Genetics in the Postgenomic Era (ed. J.C. Defries, R. Plomin, I.W. Craig & P. McGuffin) 123– 138 (American Psychological Association, Washington, DC, USA, 2002).
Enard, W. et al. Intra- and interspecific variation in primate gene expression patterns. Science 296, 340– 343 (2002).
Chou, H.H. et al. Inactivation of CMP-N-acetylneuraminic acid hydroxylase occurred prior to brain expansion during human evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 11736– 11741 (2002).
Acknowledgements
We thank J.V. Turner for secretarial assistance and L. Yu for assistance with illustrations. J.C. and S.G.N.G. are supported by the Wellcome Trust and Genes to Cognition program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choudhary, J., Grant, S. Proteomics in postgenomic neuroscience: the end of the beginning. Nat Neurosci 7, 440–445 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1240
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1240
This article is cited by
-
Current trends in biomarker discovery and analysis tools for traumatic brain injury
Journal of Biological Engineering (2019)
-
The Application of Proteomics to Traumatic Brain and Spinal Cord Injuries
Current Neurology and Neuroscience Reports (2017)
-
Gender differences in white matter pathology and mitochondrial dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease with cerebrovascular disease
Molecular Brain (2016)
-
Plasma proteome coverage is increased by unique peptide recovery from sodium deoxycholate precipitate
Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry (2016)
-
Proteomic Studies on the Development of the Central Nervous System and Beyond
Neurochemical Research (2010)