Abstract
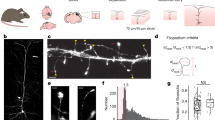
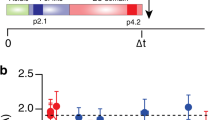
Dendrites of CA1 pyramidal neurons in mature rat hippocampal slices were exposed to different levels of synaptic activation. In some slices, synaptic transmission was blocked with glutamate receptor antagonists, sodium and calcium channel blockers and/or a nominally calcium-free medium with high magnesium. In other slices, synapses were activated with low-frequency control stimulation or repeated tetanic stimulation. In slices with blocked synaptic transmission, dendrites were spinier than in either of the activated states. Thus, mature neurons can increase their numbers of spines, possibly compensating for lost synaptic activity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gray, E. G. Axo-somatic and axo-dendritic synapses of the cerebral cortex: An electron microscopic study. J. Anat. 93, 420– 433 (1959).
Harris, K. M. & Kater, S. B. Dendritic spines: Cellular specializations imparting both stability and flexibility to synaptic function. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 17, 341–371 (1994).
Harris, K. M., Jensen, F. E. & Tsao, B. Three-dimensional structure of dendritic spines and synapses in rat hippocampus (CA1) at postnatal day 15 and adult ages: Implications for the maturation of synaptic physiology and long-term potentiation. J. Neurosci. 12, 2685–2705 (1992).
Fiala, J. C., Feinberg, M., Popov, V. & Harris, K. M. Synaptogenesis via dendritic filopodia in developing hippocampal area CA1. J. Neurosci. 18, 8900–8911 (1998).
Papa, M., Bundman, M. C., Greenberger, V. & Segal, M. Morphological analysis of dendritic spine development in primary cultures of hippocampal neurons. J. Neurosci. 15, 1–11 (1995).
Papa, M. & Segal, M. Morphological plasticity in dendritic spines of cultured hippocampal neurons. Neuroscience 71, 1005–1011 (1996).
Kossel, A. H., Williams, C. V., Schweizer, M. & Kater, S. B. Afferent innervation influences the development of dendritic branches and spines via both activity-dependent and non-activity-dependent mechanisms. J. Neurosci. 17, 6314– 6324 (1997).
Halpain, S., Hipolito, A. & Saffer, L. Regulation of F-actin stability in dendritic spines by glutamate receptors and calcineurin. J. Neurosci. 18, 9835–9844 (1998).
Annis, C. M., O'Dowd, D. K. & Robertson, R. T. Activity-dependent regulation of dendritic spine density on cortical pyramidal neurons in organotypic slice cultures. J. Neurobiol. 25, 1483–1493 (1994).
McAllister, A. K., Katz, L. C. & Lo, D. C. Neurotrophin regulation of cortical dendritic growth requires activity. Neuron 17, 1057– 1064 (1996).
Collin, C., Miyaguchi, K. & Segal, M. Dendritic spine density and LTP induction in cultured hippocampal slices. J. Neurophysiol. 77, 1614–1623 (1997).
Maletic-Savatic, M., Malinow, R. & Svoboda, K. Rapid dendritic morphogenesis in CA1 hippocampal dendrites induced by synaptic activity. Science 283, 1923–1927 (1999).
Engert, F. & Bonhoeffer, T. Dendritic spine changes associated with hippocampal long-term synaptic plasticity. Nature 399, 66–70 (1999).
Dalva, M. B., Ghosh, A. & Shatz, C. J. Independent control of dendritic and axonal form in the developing lateral geniculate nucleus. J. Neurosci. 14, 3588–3602 (1994).
Rocha, M. & Sur, M. Rapid acquisition of dendritic spines by visual thalamic neurons after blockade of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 8026– 8030 (1995).
Bravin, M., Morando, L., Vercelli, A., Rossi, F. & Strata, P. Control of spine formation by electrical activity in the adult rat cerebellum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 1704–1709 ( 1999).
Turrigiano, G. G., Leslie, K. R., Desai, N. S., Rutherford, L. C. & Nelson, S. B. Activity-dependent scaling of quantal amplitude in neocortical neurons. Nature 391 , 892–896 (1998).
Woolley, C. S., Gould, E., Frankfurt, M. & McEwen, B. S. Naturally occurring fluctuation in dendritic spine density on adult hippocampal pyramidal neurons. J. Neurosci. 10, 4035– 4039 (1990).
Gould, E., Woolley, C. S., Frankfurt, M. & McEwen, B. S. Gonadal steroids regulate dendritic spine density in hippocampal pyramidal cells in adulthood. J. Neurosci. 10, 1286 –1291 (1990).
Greenough, W. T. & Bailey, C. H. The anatomy of a memory: Convergence of results across a diversity of tests. Trends Neurosci. 11, 142–147 (1988).
Bailey, C. H. & Kandel, E. R. Structural changes accompanying memory storage. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 55, 397–426 (1993).
Moser, M. B., Trommald, M. & Andersen, P. An increase in dendritic spine density on hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells following spatial learning in adult rats suggests the formation of new synapses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91, 12673–12675 (1994).
Boyer, C., Schikorski, T. & Stevens, C. F. Comparison of hippocampal dendritic spines in culture and in brain. J. Neurosci. 18, 5294– 5300 (1998).
McKinney, R. A., Capogna, M., Durr, R., Gahwiler, B. H. & Thompson, S. M. Miniature synaptic events maintain dendritic spines via AMPA receptor activation. Nat. Neurosci. 2, 44–49 (1999).
Harris, K. M. Structure, development, and plasticity of dendritic spines. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 9, 343–348 (1999).
Kirov, S. A., Sorra, K. E. & Harris, K. M. Slices have more synapses than perfusion-fixed hippocampus from both young and mature rats. J. Neurosci. 19, 2876–2886 (1999).
Dailey, M. E. & Smith, S. J. The dynamics of dendritic structure in developing hippocampal slices. J. Neurosci. 16, 2983–2994 (1996).
Jensen, F. E. & Harris, K. M. Preservation of neuronal ultrastructure in hippocampal slices using rapid microwave-enhanced fixation. J. Neurosci. Methods 29, 217–230 (1989).
Sorra, K. E. & Harris, K. M. Stability in synapse number and size at 2 hr after long-term potentiation in hippocampal area CA1. J. Neurosci. 18, 658–671 (1998).
Trommald, M., Jensen, V. & Andersen, P. Analysis of dendritic spines in rat CA1 pyramidal cells intracellularly filled with a fluorescent dye. J. Comp. Neurol. 353, 260–274 ( 1995).
Rusakov, D. A. & Stewart, M. G. Quantification of dendritic spine populations using image analysis and a tilting disector. J. Neurosci. Methods 60, 11– 21 (1995).
Horner, C. H. Plasticity of the dendritic spine. Prog. Neurobiol. 41, 281–321 (1993).
Chang, F. L. & Greenough, W. T. Lateralized effects of monocular training on dendritic branching in adult split-brain rats. Brain Res. 232, 283–292 ( 1982).
Andersen, P. & Soleng, A. F. Long-term potentiation and spatial training are both associated with the generation of new excitatory synapses. Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev. 26, 353– 359 (1998).
Choi, D. W. Glutamate neurotoxicity and diseases of the nervous system. Neuron 1, 623–634 ( 1988).
Frankenhaeuser, B. & Hodgkin, A. L. The action of calcium on the electrical properties of squid axons. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 137, 218–244 ( 1957).
Taylor, C. P. & Dudek, F. E. Synchronous neural afterdischarges in rat hippocampal slices without active chemical synapses. Science 218, 810–812 ( 1982).
Haas, H. L. & Jefferys, J. G. Low-calcium field burst discharges of CA1 pyramidal neurones in rat hippocampal slices. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 354, 185–201 ( 1984).
Fifkova, E. Actin in the nervous-system. Brain Res. 9, 187–215 (1985).
Janmey, P. A. Phosphoinositides and calcium as regulators of cellular actin assembly and disassembly. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 56, 169 –191 (1994).
Fischer, M., Kaech, S., Knutti, D. & Matus, A. Rapid actin-based plasticity in dendritic spines. Neuron 20, 847–854 (1998).
Nusser, Z. et al. Cell type and pathway dependence of synaptic AMPA receptor number and variability in the hippocampus. Neuron 21 , 545–559 (1998).
Gomperts, S. N., Rao, A., Craig, A. M., Malenka, R. C. & Nicoll, R. A. Postsynaptically silent synapses in single neuron cultures. Neuron 21, 1443– 1451 (1998).
Petralia, R. S. et al. Selective acquisition of AMPA receptors over postnatal development suggests a molecular basis for silent synapses. Nat. Neurosci. 2, 31–36 ( 1999).
Shi, S. H. et al. Rapid spine delivery and redistribution of AMPA receptors after synaptic NMDA receptor activation. Science 284 , 1811–1816 (1999).
Paul, L. A. & Scheibel, A. B. Structural substrates of epilepsy. Adv. Neurol. 44, 775–786 (1986).
Jiang, M., Lee, C. L., Smith, K. L. & Swann, J. W. Spine loss and other persistent alterations of hippocampal pyramidal cell dendrites in a model of early-onset epilepsy. J. Neurosci. 18, 8356–8368 (1998).
Muller, M., Gahwiler, B. H., Rietschin, L. & Thompson, S. M. Reversible loss of dendritic spines and altered excitability after chronic epilepsy in hippocampal slice cultures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90, 257–261 ( 1993).
Drakew, A., Muller, M., Gahwiler, B. H., Thompson, S. M. & Frotscher, M. Spine loss in experimental epilepsy: quantitative light and electron microscopic analysis of intracellularly stained CA3 pyramidal cells in hippocampal slice cultures. Neuroscience . 70, 31–45 ( 1996).
Segal, M. Morphological alterations in dendritic spines of rat hippocampal neurons exposed to N-methyl-D-aspartate. Neurosci. Lett 193, 73–76 (1995).
Acknowledgements
We thank J. Fiala for improving IGL Trace for use with confocal microscopy and for his input on this work. We also thank M. Feinberg and A. Goddard for technical support. This work was supported by NIH grants NS21184, NS33574, MH/DA57351, which is funded jointly by NIMH, NIDA, NASA (K.M.H) and the Mental Retardation Research Center grant P30-HD18655 to Joseph Volpe.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kirov, S., Harris, K. Dendrites are more spiny on mature hippocampal neurons when synapses are inactivated. Nat Neurosci 2, 878–883 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/13178
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/13178
This article is cited by
-
Mice with cleavage-resistant N-cadherin exhibit synapse anomaly in the hippocampus and outperformance in spatial learning tasks
Molecular Brain (2021)
-
Associative properties of structural plasticity based on firing rate homeostasis in recurrent neuronal networks
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Imbalance between firing homeostasis and synaptic plasticity drives early-phase Alzheimer’s disease
Nature Neuroscience (2018)
-
Rewiring of neuronal networks during synaptic silencing
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Lesion-induced and activity-dependent structural plasticity of Purkinje cell dendritic spines in cerebellar vermis and hemisphere
Brain Structure and Function (2016)