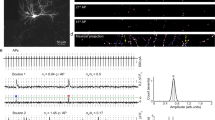
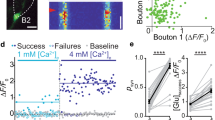
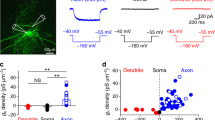
Abstract
Most fast-acting neurotransmitters are rapidly cleared from synaptic regions. This feature isolates synaptic sites, rendering the time course of synaptic responses independent of the number of active synapses. We found an exception at glycinergic synapses on granule cells of the rat dorsal cochlear nucleus. Here the duration of inhibitory postsynaptic currents (IPSCs) was dependent on the number of presynaptic axons that were stimulated and on the number of vesicles that were released from each axon. Increasing the stimulus number or frequency, or blocking glycine uptake, slowed synaptic decays, whereas a low-affinity competitive antagonist of glycine receptors (GlyRs) accelerated IPSC decay. These effects could be explained by unique features of GlyRs that are activated by pooling of glycine across synapses. Functionally, increasing the number of IPSPs markedly lengthened the period of spike inhibition following the cessation of presynaptic stimulation. Thus, temporal properties of inhibition can be controlled by activity levels in multiple presynaptic cells or by adjusting release probability at individual synapses.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Katz, B. & Miledi, R. The binding of acetylcholine to receptors and its removal from the synaptic cleft. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 231, 549–574 (1973).
Barrett, E.F. & Stevens, C.F. The kinetics of transmitter release at the frog neuromuscular junction. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 227, 691–708 (1972).
Barbour, B., Keller, B.U., Llano, I. & Marty, A. Prolonged presence of glutamate during excitatory synaptic transmission to cerebellar Purkinje cells. Neuron 12, 1331–1343 (1994).
Jones, M.V. & Westbrook, G.L. Desensitized states prolong GABAA channel responses to brief agonist pulses. Neuron 15, 181–191 (1995).
Legendre, P. A reluctant gating mode of glycine receptor channels determines the time course of inhibitory miniature synaptic events in zebrafish hindbrain neurons. J. Neurosci. 18, 2856–2870 (1998).
Takahashi, T., Momiyama, A., Hirai, K., Hishinuma, F. & Akagi, H. Functional correlation of fetal and adult forms of glycine receptors with developmental changes in inhibitory synaptic receptor channels. Neuron 9, 1155–1161 (1992).
Otis, T., Zhang, S. & Trussell, L.O. Direct measurement of AMPA receptor desensitization induced by glutamatergic synaptic transmission. J. Neurosci. 16, 7496–7504 (1996).
Kinney, G.A., Overstreet, L.S. & Slater, N.T. Prolonged physiological entrapment of glutamate in the synaptic cleft of cerebellar unipolar brush cells. J. Neurophysiol. 78, 1320–1333 (1997).
Otis, T.S., Wu, Y.C. & Trussell, L.O. Delayed clearance of transmitter and the role of glutamate transporters at synapses with multiple release sites. J. Neurosci. 16, 1634–1644 (1996).
Silver, R.A., Cull-Candy, S.G. & Takahashi, T. Non-NMDA glutamate receptor occupancy and open probability at a rat cerebellar synapse with single and multiple release sites. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 494, 231–250 (1996).
Kondo, S. & Marty, A. Synaptic currents at individual connections among stellate cells in rat cerebellar slices. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 509, 221–232 (1998).
Biro, A.A., Holderith, N.B. & Nusser, Z. Release probability–dependent scaling of the postsynaptic responses at single hippocampal GABAergic synapses. J. Neurosci. 26, 12487–12496 (2006).
Cathala, L., Holderith, N.B., Nusser, Z., DiGregorio, D.A. & Cull-Candy, S.G. Changes in synaptic structure underlie the developmental speeding of AMPA receptor–mediated EPSCs. Nat. Neurosci. 8, 1310–1318 (2005).
Isaacson, J.S., Solis, J.M. & Nicoll, R.A. Local and diffuse synaptic actions of GABA in the hippocampus. Neuron 10, 165–175 (1993).
Banks, M.I., Li, T.B. & Pearce, R.A. The synaptic basis of GABAA,slow. J. Neurosci. 18, 1305–1317 (1998).
Lu, T. & Trussell, L.O. Inhibitory transmission mediated by asynchronous transmitter release. Neuron 26, 683–694 (2000).
Legendre, P. The glycinergic inhibitory synapse. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 58, 760–793 (2001).
Burzomato, V., Beato, M., Groot-Kormelink, P.J., Colquhoun, D. & Sivilotti, L.G. Single-channel behavior of heteromeric alpha1beta glycine receptors: an attempt to detect a conformational change before the channel opens. J. Neurosci. 24, 10924–10940 (2004).
Lu, T., Rubio, M.E. & Trussell, L.O. Glycinergic transmission shaped by the co-release of GABA in a mammalian auditory synapse. Neuron 57, 524–535 (2008).
Beato, M. The time course of transmitter at glycinergic synapses onto motoneurons. J. Neurosci. 28, 7412–7425 (2008).
Brand, A., Behrend, O., Marquardt, T., McAlpine, D. & Grothe, B. Precise inhibition is essential for microsecond interaural time difference coding. Nature 417, 543–547 (2002).
Singer, J.H. & Berger, A.J. Contribution of single-channel properties to the time course and amplitude variance of quantal glycine currents recorded in rat motoneurons. J. Neurophysiol. 81, 1608–1616 (1999).
Harty, T.P. & Manis, P.B. Kinetic analysis of glycine receptor currents in ventral cochlear nucleus. J. Neurophysiol. 79, 1891–1901 (1998).
Mager, S. et al. Steady states, charge movements and rates for a cloned GABA transporter expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Neuron 10, 177–188 (1993).
Wadiche, J.I., Arriza, J.L., Amara, S.G. & Kavanaugh, M.P. Kinetics of a human glutamate transporter. Neuron 14, 1019–1027 (1995).
Oertel, D. & Young, E.D. What's a cerebellar circuit doing in the auditory system? Trends Neurosci. 27, 104–110 (2004).
Balakrishnan, V. & Trussell, L.O. Synaptic inputs to granule cells of the dorsal cochlear nucleus. J. Neurophysiol. 99, 208–219 (2008).
Awatramani, G.B., Turecek, R. & Trussell, L.O. Inhibitory control at a synaptic relay. J. Neurosci. 24, 2643–2647 (2004).
Magnusson, A.K., Kapfer, C., Grothe, B. & Koch, U. Maturation of glycinergic inhibition in the gerbil medial superior olive after hearing onset. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 568, 497–512 (2005).
Silver, R.A., Traynelis, S.F. & Cull-Candy, S.G. Rapid time course miniature and evoked excitatory currents at cerebellar synapses in situ. Nature 355, 163–166 (1992).
Pitt, S.J., Sivilotti, L.G. & Beato, M. High intracellular chloride slows the decay of glycinergic currents. J. Neurosci. 28, 11454–11467 (2008).
Christie, J.M. & Jahr, C.E. Multivesicular release at Schaffer collateral-CA1 hippocampal synapses. J. Neurosci. 26, 210–216 (2006).
Tong, G. & Jahr, C.E. Block of glutamate transporters potentiates postsynaptic excitation. Neuron 13, 1195–1203 (1994).
Atkinson, B.N. et al. ALX 5407: a potent, selective inhibitor of the hGlyT1 glycine transporter. Mol. Pharmacol. 60, 1414–1420 (2001).
Whitehead, K.J. et al. Positive N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor modulation by selective glycine transporter-1 inhibition in the rat dorsal spinal cord in vivo. Neuroscience 126, 381–390 (2004).
Beato, M., Burzomato, V. & Sivilotti, L.G. The kinetics of inhibition of rat recombinant heteromeric alpha1beta glycine receptors by the low-affinity antagonist SR-95531. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 580, 171–179 (2007).
Wang, P. & Slaughter, M.M. Effects of GABA receptor antagonists on retinal glycine receptors and on homomeric glycine receptor alpha subunits. J. Neurophysiol. 93, 3120–3126 (2005).
Fucile, S., de Saint Jan, D., David-Watine, B., Korn, H. & Bregestovski, P. Comparison of glycine and GABA actions on the zebrafish homomeric glycine receptor. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 517, 369–383 (1999).
Gentet, L.J. & Clements, J.D. Binding site stoichiometry and the effects of phosphorylation on human alpha1 homomeric glycine receptors. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 544, 97–106 (2002).
Mohammadi, B. et al. Kinetic analysis of recombinant mammalian alpha(1) and alpha(1)beta glycine receptor channels. Eur. Biophys. J. 32, 529–536 (2003).
Twyman, R.E. & Macdonald, R.L. Kinetic properties of the glycine receptor main- and sub-conductance states of mouse spinal cord neurones in culture. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 435, 303–331 (1991).
Barbour, B. & Hausser, M. Intersynaptic diffusion of neurotransmitter. Trends Neurosci. 20, 377–384 (1997).
Carter, A.G. & Regehr, W.G. Prolonged synaptic currents and glutamate spillover at the parallel fiber to stellate cell synapse. J. Neurosci. 20, 4423–4434 (2000).
Alibardi, L. Ultrastructural distribution of glycinergic and GABAergic neurons and axon terminals in the rat dorsal cochlear nucleus, with emphasis on granule cell areas. J. Anat. 203, 31–56 (2003).
Wadiche, J.I. & Jahr, C.E. Multivesicular release at climbing fiber–Purkinje cell synapses. Neuron 32, 301–313 (2001).
Dumoulin, A., Triller, A. & Dieudonne, S. IPSC kinetics at identified GABAergic and mixed GABAergic and glycinergic synapses onto cerebellar Golgi cells. J. Neurosci. 21, 6045–6057 (2001).
Kraushaar, U. & Backus, K.H. Characterization of GABA(A) and glycine receptors in neurons of the developing rat inferior colliculus. Pflugers Arch. 445, 279–288 (2002).
Veruki, M.L., Gill, S.B. & Hartveit, E. Spontaneous IPSCs and glycine receptors with slow kinetics in wide-field amacrine cells in the mature rat retina. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 581, 203–219 (2007).
Piechotta, K., Weth, F., Harvey, R.J. & Friauf, E. Localization of rat glycine receptor alpha1 and alpha2 subunit transcripts in the developing auditory brainstem. J. Comp. Neurol. 438, 336–352 (2001).
Awatramani, G.B., Turecek, R. & Trussell, L.O. Staggered development of GABAergic and glycinergic transmission in the MNTB. J. Neurophysiol. 93, 819–828 (2005).
Acknowledgements
We thank H. Huang, C.E. Jahr and M.E. Roberts for comments on the manuscript and H. Sundaram for the gift of ORG-25543. This work was supported by US National Institutes of Health grant NS028901.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
V.B. conducted the electrophysiological experiments, analysis and manuscript preparation. S.P.K. performed immunohistochemistry and analysis. P.D.R. conducted diffusion modeling. L.O.T. conducted kinetic modeling, data analysis and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–7, Supplementary Methods and Supplementary Results (PDF 4495 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Balakrishnan, V., Kuo, S., Roberts, P. et al. Slow glycinergic transmission mediated by transmitter pooling. Nat Neurosci 12, 286–294 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.2265
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.2265
This article is cited by
-
Cytokine inflammatory threat, but not LPS one, shortens GABAergic synaptic currents in the mouse spinal cord organotypic cultures
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2019)
-
Synapsin II desynchronizes neurotransmitter release at inhibitory synapses by interacting with presynaptic calcium channels
Nature Communications (2013)