Abstract
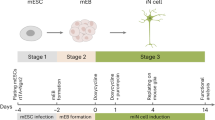
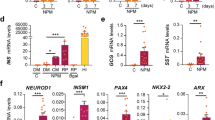
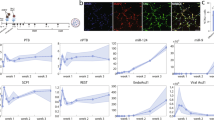
Forced expression of proneural transcription factors has been shown to direct neuronal conversion of fibroblasts. Because neurons are postmitotic, conversion efficiencies are an important parameter for this process. We present a minimalist approach combining two-factor neuronal programming with small molecule–based inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3β and SMAD signaling, which converts postnatal human fibroblasts into functional neuron-like cells with yields up to >200% and neuronal purities up to >80%.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Vierbuchen, T. et al. Nature 463, 1035–1041 (2010).
Takahashi, K. & Yamanaka, S. Cell 126, 663–676 (2006).
Pang, Z.P. et al. Nature 476, 220 (2011).
Vierbuchen, T. & Wernig, M. Nat. Biotechnol. 29, 892–907 (2011).
Broccoli, V., Caiazzo, M. & Dell'anno, M.T. J. Mol. Cell. Biol. 3, 322–323 (2011).
Chambers, S.M. et al. Nat. Biotechnol. 27, 275–280 (2009).
Li, R. et al. Cell Stem Cell 7, 51–63 (2010).
Lucas, F.R., Goold, R.G., Gordon-Weeks, P.R. & Salinas, P.C. J. Cell Sci. 111, 1351–1361 (1998).
Zaehres, H. et al. Exp. Hematol. 38, 809–818 (2010).
Lin, T. et al. Nat. Methods 6, 805–808 (2009).
Maherali, N. & Hochedlinger, K. Curr. Biol. 19, 1718–1723 (2009).
Polo, J.M. & Hochedlinger, K. Cell Stem Cell 7, 5–6 (2010).
Samavarchi-Tehrani, P. et al. Cell Stem Cell 7, 64–77 (2010).
Polleux, F., Whitford, K.L., Dijkhuizen, P.A., Vitalis, T. & Ghosh, A. Development 129, 3147–3160 (2002).
Koch, P., Siemen, H., Biegler, A., Itskovitz-Eldor, J. & Brüstle, O. Nucleic Acids Res. 34, e120 (2006).
Müller, F.J. et al. Nature 455, 401–405 (2008).
Müller, F.J. et al. Nat. Methods 8, 315–317 (2011).
Barnes, M., Freudenberg, J., Thompson, S., Aronow, B. & Pavlidis, P. Nucleic Acids Res. 33, 5914–5923 (2005).
Chen, J., Bardes, E.E., Aronow, B.J. & Jegga, A.G. Nucleic Acids Res. 37, W305–W311 (2009).
Caraux, G. & Pinloche, S. Bioinformatics 21, 1280–1281 (2005).
Acknowledgements
We thank D. Kühne for technical support, J. Itskovitz-Eldor (Technion, Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa, Israel) and W.S. Kunz (University of Bonn, Germany) for providing HPF, and M. Emond for fruitful discussions. This work was supported by grants from the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (01GN1009B and 01GN1008C to O.B. and 01GN1008A to P.W. and G.K.), the German Research Foundation (SFB-TR3 D2 to O.B.), the European Union (FP7-HEALTH-2007-B-22943-NeuroStemcell and HEALTH-F5-2010-266753-SCR&Tox to O.B.), the Stem Cell Network North Rhine Westphalia (L-072.0058 to J.L.), the Else Kröner-Fresenius-Stiftung Fellowship (F.-J.M.) and the Hertie Foundation (O.B.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.L. conceived and designed the study, performed experiments, assembled, analyzed and interpreted data and helped write the manuscript; J.M., J.D., D.P., J.K. and F.G. performed experiments and analyzed and interpreted data; F.-J.M. and S.H. analyzed and interpreted data; P.W. and G.K. provided materials; P.K. and O.B. conceived and designed study, assembled, analyzed and interpreted data and helped write the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
O.B. declares a competing financial interest as a co-founder of and stockholder in LIFE & BRAIN GmbH.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–9, Supplementary Note (PDF 9322 kb)
Supplementary Table 1
Gene expression profile of the converted HPFs (XLSX 19 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ladewig, J., Mertens, J., Kesavan, J. et al. Small molecules enable highly efficient neuronal conversion of human fibroblasts. Nat Methods 9, 575–578 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1972
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1972
This article is cited by
-
Human cell transformation by combined lineage conversion and oncogene expression
Oncogene (2021)
-
Improved modeling of human AD with an automated culturing platform for iPSC neurons, astrocytes and microglia
Nature Communications (2021)
-
Recent Advances in Understandings Towards Pathogenesis and Treatment for Intrauterine Adhesion and Disruptive Insights from Single-Cell Analysis
Reproductive Sciences (2021)
-
Direct Reprogramming of Somatic Cells to Neurons: Pros and Cons of Chemical Approach
Neurochemical Research (2021)
-
Generation of Hepatic Progenitor Cells from the Primary Hepatocytes of Nonhuman Primates Using Small Molecules
Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine (2021)