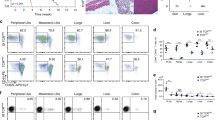
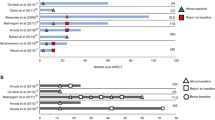
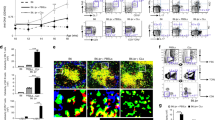
Abstract
We have recently isolated a panel of T–cell clones from chronic progressive multiple sclerosis (MS) patients that are capable of functioning as antigen–presenting cells and of expressing the costimulatory molecules B7–1 and B7–2. In this report we show that these T–cell clones are resistant to inhibitory regulation, including the induction of anergy and sensitivity to tumor growth factor–β (TGF–β)–induced growth inhibition. The resistance to anergy induction was associated with expression of B7 costimulatory molecules. These data suggest that lack of responsiveness to peripheral inhibitory signals may account for the entry of autoimmune diseases into a chronic progressive phase.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sinha, A.A., Lopez, M.T. & McDevitt, H.O. Autoimmune diseases: The failure of self tolerance. Science 248, 1380–1387 (1990).
Martin, R., McFarland, H.F. & McFarlin, D.E. Immunological aspects of de-myelinating diseases. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 10, 153–187 (1992).
Marcos, M.A.R. et al. Mutual cell interactions and the selection of immune repertoires: Implication in autoimmunity. Immunol Today 9, 204–213 (1988).
Schwartz, R.H. Acquisition of immunological self-tolerance. Cell 57, 1073–1081 (1989).
Blackman, M., Kappler, J. & Marrack, P. The role of the T cell receptor in positive and negative selection of developing T cells. Science 248, 1335–1341 (1990).
Blackman, M.A., Finkel, T.H., Kappler, J.W., Cambier, J. & Marrack, P. Altered antigen receptor signaling in anergic T cells from self-tolerant T-Cell receptor b-chain transgenic mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88, 6682–6686 (1991).
Burns, J., Rosenzweig, A., Zweiman, B. & Lisak, R.P. Isolation of myelin basic protein-reactive T cell lines from normal human blood. Cell Immunol. 81, 435–440 (1983).
Correale, J., McMillan, M., McCarthy, K., Le, T. & Weiner, L.P. Isolation and characterization of autoreactive proteolipid protein-peptide specific T-cell clones from multiple sclerosis patients. Neurology 45, 1370–1378 (1995).
Kappler, J.W., Staerz, V.D., Steinmetz, M. & von Boehmer, M. Self-tolerance eliminates T cells specific for Mis-modified products of the major histocompatibility complex. Nature 332, 35–40 (1988).
Karpus, W.J. & Swanborg, R.H. CD4+ suppressor cells inhibit the function of effec tor cells of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis through a mechanism involving transforming growth factor-beta. J. Immunol. 146, 1163–1168 (1991).
Mosmann, T.R. Cytokine secretion patterns and cross-regulation of T cell sub sets. Immunol. Res. 10, 183–188 (1991).
Cohen, I.R. & Young, D.B., Immunity, microbial immunity and the im munological homunculus. Immunol Today 12, 105–110 (1991).
Qin, S.X., Cobbold, S., Benjamin, R. & Waldmann, H. Induction of classical transplantation tolerance in the adult. J. Exp. Med. 169, 779–794 (1989).
Mueller, D.L., Jenkins, M.K. & Schwartz, R.H. Clonal expansion versus functional clonal inactivation: A costimulatory signalling pathway determines the outcome of T Cell antigen receptor occupancy. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 7 445–480 (1989).
Liu, Y. & Janeway, C.A. Jr., Interferon gamma plays a critical role in induced cell death of effector T cells: A possible third mechanism of self-tolerance. J. Exp. Med. 172, 1735–1739 (1990).
Gimmi, C.D. et al. B Cell surface antigen B7 provides a costimulatory signal that induces T cell to proliferate and secrete interleukin-2. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 88, 6575–6579 (1991).
Chen, C. & Nabvi, N. In vitro induction of T Cell anergy by blocking B7 and early T cell costimulatory molecule ETC-1/B7-2. Immunity 1, 147–154 (1994).
Linsley, P.S. et al. Immunosuppression in vivo by a soluble form of the CTLA-4 T cell activation molecule. Science 257, 792–795 (1992).
Lenschow, D.J. et al. Differential effects of anti-B7-1 and anti-B7-2 monoclonal antibody treatment on the development of diabetes in the nonobese diabetic mouse. J. Exp. Med. 181, 1145–1155 (1995).
Correale, J. et al. Antigen presentation by autoreactive proteolipid protein peptide-specific T cell clones from chronic progressive multiple sclerosis patients: Roles of co-stimulatory B7 molecules and IL-12. J. Neuroimmunol. (in the press).
Jenkins, M.K., Chen, C., Jung, G., Mueller, D.L. & Schwartz, R.H. Inhibition of antigen specific proliferation of type 1 murine T cell clones after stimulation with antigen and chemically modified antigen presenting cells. J Immunol. 144, 16–22 (1990).
Williams, M.E., Shea, C.M., Lichtman, A.H. & Abbas, A.K. Antigen receptor me diated anergy in resting T lymphocytes and T cell clones. Correlation with lymphokine secretion patterns. J. Immunol. 149, 1921–1926 (1991).
O'Hehir, R.E. & Lamb, J.R. Induction of specific clonal anergy in human T lym phocytes by Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxins. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 87, 8884–8888 (1990).
Jenkins, M. & Schwartz, R.H. Antigen presentation by chemically modified splenocytes induces antigen-specific T cell unresponsiveness in vitro and in vivo. J. Exp. Med. 165, 302–319 (1987).
Vandenbark, A.A., Celnik, B., Vainiene, M., Miller, S.D. & Offner, H. Myelin antigen-coupled splenocytes suppress experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in Lewis rat through a partial reversible anergy mechanism. J. Immunol. 155, 5861–5867 (1995).
Tan, P. et al. Induction of alloantigen-specific hyporesponsiveness in human T lymphocytes by blocking interaction of CD28 with its natural ligand B7/BB1. J. Exp. Med. 177 165–173 (1993).
Sayegh, M.H. et al. CD28-B7 blockade after alloantigen challenge in vivo in hibits Thl cytokines but spares Th2. J. Exp. Med. 181, 1869–1874 (1995).
Massague, J. The transforming growth factor-beta family. Annu. Rev. Cell Biol 6 597–641 (1990).
Miller, S.D. et al. Evolution of the T-cell repertoire during the course of experimental immune-mediated demyelinating diseases. Immunol Rev. 144, 225–244 (1995).
Olsson, T. et al. Increased numbers of T cells recognizing multiple myelin basic protein epitopes in multiple sclerosis. Eur. J. Immunol. 22, 1083–1087 (1992).
Bossu, P. et al. Mature CD4+ T lymphocytes from MRL/lpr mice are resistant to receptor-mediated tolerance and apoptosis. J. Immunol. 151, 7233–7239 (1993).
Dayan, C.M., Randall Chu, N., Londei, M., Rapoport, B. & Feldmann, M. T Cells involved in human autoimmune disease are resistant to tolerance induction. J. Immunol. 151, 1606–1613 (1993).
Miller, S.D. et al. Blockade of CD28/B7-1 interaction prevents epitope spreading and clinical relapses of murine EAE. Immunity 3, 739–745 (1995).
Kuiper, H.M., Lens, S.M.A., Hintzen, R.Q. & Van Lier, R.A.W. Lymphocyte co-stimulation: Multiple pathways, multiple functions? Res. Immunol. 146, 180–183 (1995).
Van Kemenade, F.J., Kuijpers, K.C., de Waal Malefijt, R., Van Lier, R. A. W. & Miedema, F. Skewing to the LFA-3 adhesion pathway by influenza infection of antigen-presenting cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 23, 635–639 (1993).
Kroemer, G. & Martinez-A, C. Mechanisms of self tolerance. Immunol. Today 13, 401–404 (1992).
Racke, M.K. et al. Prevention and treatment of chronic relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis by transforming growth factor beta-1. J. Immunol. 146, 3012–3017 (1991).
Kadin, M.E. et al. Loss of receptors for transforming growth factor beta in human T cell malignancies. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci USA 91, 6002–6006 (1994).
Hollsberg, P., Augobel, L.J. & Hafler, D.A. Human T cell lymphotropic virus type I-induced T cell activation: Resistance to TGF-beta-1 induced suppression. J. Immunol. 153, 566–573 (1994).
Kurtzke, J.F. Rating neurological impairment in multiple sclerosis: An expanded disability status scale (EDSS). Neurology 33, 1444–1452 (1983).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Correale, J., Gilmore, W., Lopez, J. et al. Defective post–thymic tolerance mechanisms during the chronic progressive stage of multiple sclerosis. Nat Med 2, 1354–1360 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1296-1354
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1296-1354