Abstract
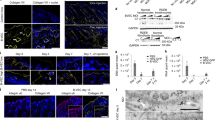
Dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (DEB) is a family of inherited mechano-bullous disorders that are caused by mutations in the type VII collagen gene and for which ex vivo gene therapy has been considered. To develop a simpler approach for treating DEB, we evaluated the feasibility of protein-based therapy by intradermally injecting human recombinant type VII collagen into mouse skin and a DEB human skin equivalent transplanted onto mice. The injected collagen localized to the basement membrane zone of both types of tissues, was organized into human anchoring fibril structures and reversed the features of DEB disease in the DEB skin equivalent.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Briggaman, R.A. & Wheeler, C.E. Jr. J. Invest. Dermatol. 65, 71–84 (1975).
Sakai, L.Y., Keene, D.R., Morris, N.P. & Burgeson, R.E. J. Cell Biol. 103, 1577–1586 (1986).
Burgeson, R.E. J. Invest. Dermatol. 101, 252–255 (1993).
Uitto, J. & Christiano, A.M. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 287, 16–22 (1994).
Uitto, J. & Christiano, A.M. J. Clin. Invest. 90, 687–692 (1992).
Lin, A.N. & Carter, D.M. (eds) Epidermolysis Bullosa: Basic and Clinical Aspects(Springer-Verlag, New York, 1992).
Chen, M. et al. Nat. Genet. 32, 670–675 (2002).
Ortiz-Urda, S. et al. Nat. Med. 8, 1166–1170 (2002).
Woodley, D.T. et al. J. Invest. Dermatol. 121, 1021–1028 (2003).
Oritz-Urda, S. et al. J. Clin. Invest. 111, 251–255 (2003).
Chen, M., Costa, F.K., Lindvay, C.R., Han, Y.P. & Woodley, D.T. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 2118–2124 (2002).
Chen, M. et al. J. Invest. Dermatol. 108, 68–72 (1997).
Keene, D.R., Sakai, L.Y., Lunstrum, G.P., Morris, N.P. & Burgeson, R.E. J. Cell Biol. 104, 611–621 (1987).
Medalie D.A. et al. J. Invest. Dermatol. 107, 121–127 (1996).
Kim, Y.H., Woodley, D.T., Wynn, K.C., Giomi, W. & Bauer, E.A. J. Invest. Dermatol. 98, 191–197 (1992).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants RO1 AR47981 (M.C.) and RO1 AR33625 (D.T.W.) from the US National Institutes of Health. We thank S. Tufa for technical support of immunoelectron microscopy.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Fig. 1
Dose-dependent deposition of injected human type VII collagen at the mouse's BMZ. (PDF 203 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 2
Sustained incorporation of human type VII collagen at the BMZ of hairless immunocompetent mice after a single intradermal injection. (PDF 1266 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 3
Incorporation of subsequently injected type VII collagen into the mouse's BMZ regardless the presence of anti-type VII collagen antibodies. (PDF 1061 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Woodley, D., Keene, D., Atha, T. et al. Injection of recombinant human type VII collagen restores collagen function in dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Nat Med 10, 693–695 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1063
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1063
This article is cited by
-
Molecular co-assembled strategy tuning protein conformation for cartilage regeneration
Nature Communications (2024)
-
Investigational Treatments for Epidermolysis Bullosa
American Journal of Clinical Dermatology (2021)
-
Clinical Perspectives of Gene-Targeted Therapies for Epidermolysis Bullosa
Dermatology and Therapy (2021)
-
Molecular Therapeutics in Development for Epidermolysis Bullosa: Update 2020
Molecular Diagnosis & Therapy (2020)
-
A Gene Gun-mediated Nonviral RNA trans-splicing Strategy for Col7a1 Repair
Molecular Therapy - Nucleic Acids (2016)