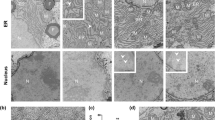
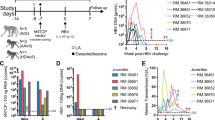
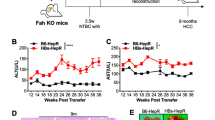
Abstract
A model for hepatitis B virus-associated chronic liver disease has been made using cloned hepatitis B virus DNA as a transgene in a severe combined immunodeficient host. These mice consistently support virus gene expression and replication. After adoptive transfer of unprimed, syngeneic splenocytes, these mice cleared virus from liver and serum, and developed chronic liver disease. This model will permit identification of the host and virus contributions to chronic liver disease in the absence of tolerance.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blumberg, B.S. The current state of the prevention of HBV infection, the carrier state and hepatocellular carcinoma. Res. Virol. 148, 91–94 (1997).
Hoofnagle, J.H., & Lau, D. New therapies for chronic hepatitis B. J. Viral Hepat. 4, 41–50 (1997).
Saracco, G., & Rizzetto, M. A practical guide to the use of interferons in the management of hepatitis virus infections. Drugs 53, 74–85 ( 1997).
Honkoop, P., Niesters, H.G., de Man, R.A., Osterhaus, A.D., & Schalm, S.W. Lamivudine resistance in immunocompetent chronic hepatitis B. Incidence and patterns. J. Hepatol. 26, 1393–1395 (1997).
Pugh, J.C., & Bassendine, M.F. Molecular biology of hepadnavirus replication. British Med. Bull. 46, 329– 353 (1990).
Robinson, W.S., Marion, P., Feitelson, M.A., & Siddidjui, A. in Viral Hepatitis, 1981 International Symposium. (eds. Szmuness, W., Alter, H.J., & Maynard, J.E.) 57–68 (Franklin Institute Press, Philadelphia, 1982).
Summers, J. Three recently described animal virus models for hepatitis B virus. Hepatology 1, 179–183 ( 1981).
Mason, W.S. et al. Characterization of the antiviral effects of 2' carbodeoxyguanosine in ducks chronically infected with duck hepatitis B virus. Hepatology 19, 398–411 ( 1994).
Korba, B.A. et al. Liver-targeted antiviral nucleosides: enhanced antiviral activity of phosphatidyl-dideoxyguanosine versus dideoxyguanosine in woodchuck hepatitis virus infection in vivo. Hepatology 23, 958–963 (1996).
Babinet, C., Farza, H., Morello, D., Hadchouel, M., & Pourcel, C. Specific expression of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) in transgenic mice. Science 230, 1160– 1163 (1985).
Chisari, F.V. et al. A transgenic mouse model of the chronic hepatitis B surface antigen carrier state. Science 230, 1157 –60 (1985).
Farza, H. et al. Replication and gene expression of hepatitis B virus in a transgenic mouse that contains the complete viral genome. J. Virol. 62, 4144–4152 (1988).
Araki, K. et al. Expression and replication of hepatitis B virus genome in transgenic mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86, 207 –211 (1989).
Moriyama, T. et al. Immunobiology and pathogenesis of hepatocellular injury in hepatitis B virus transgenic mice. Science 248, 361–364 (1990).
Ando, K. et al. Mechanisms of class I restricted immunopathology. A transgenic mouse model of fulminant hepatitis. J. Exp. Med. 178 , 1541–1554 (1993).
Feitelson, M.A., DeTolla, L,J. & Zhou, X.D. A chronic carrierlike state is established in nude mice injected with cloned hepatitis B virus DNA. J. Virol. 62, 1408–1415 (1988).
Nakamoto, Y., Guidotti, L.G., Kuhlen, C.V., Fowler, P., & Chisari, F.V. Immune pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Exp. Med. 188, 341– 350 (1998).
Will, H. et al. Cloned HBV DNA causes hepatitis in chimpanzees. Nature 299, 740–742 ( 1982).
Blum, H.E., Haase A.T., Harris J,D., Walker, D. & Vyas, G.N. Asymmetric replication of hepatitis B virus DNA in human liver: demonstration of cytoplasmic minus-strand DNA by blot analyses and in situ hybridization. Virology 139, 87–96 (1984).
Ruiz-Opazo, N., Chakraborty, P.R. & Shafritz, D.A. Characterization of viral genomes in the liver and serum of chimpanzee long-term hepatitis B virus carriers: a possible role for supercoiled HBV DNA in persistent HBV infection. J. Cell. Biochem. 19, 281–292 ( 1982).
Tiollais, P., Pourcel, C. & Dejean A. The hepatitis B virus. Nature 317, 489–495 (1985).
Lerner, R.A. et al. Chemically synthesized peptides predicted from the nucleotide sequence of the hepatitis B virus genome elicit antibodies reactive with the native envelope protein of Dane particles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 78, 3403–3407 ( 1981).
Ray, M.B. Hepatitis B Virus Antigens in Tissues (University Park Press, Baltimore, Maryland, 1979).
Wang, W., London, W.T., Lega, L. & Feitelson, M.A. Hepatitis B x antigen in liver from carrier patients with chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis. Hepatology 14, 29–37 (1991).
Wang, W., London, W.T. & Feitelson, M.A. Hepatitis B x antigen in hepatitis B virus carrier patients with liver cancer. Cancer Res. 51, 4971–4977 (1991).
Omata, M. Significance of extrahepatic replication of hepatitis B virus. Hepatology 12, 364–366 ( 1990).
Guidotti, L.G., Matzke, B., Schaller, H. & Chisari, F.V. High level hepatitis B virus replication in transgenic mice. J. Virol. 69 , 6158–6169 (1995).
Dienstag, J.L. in Viral Hepatitis and Liver Disease (eds. Vyas, G.N., Dienstag, J.L., & Hoofnagle, J.H.) 135–166 (Grune & Stratton, New York, 1984).
Feitelson, M.A. Hepatitis B virus gene products as immunological targets in chronic infection. Mol. Biol. Med. 6, 367– 393 (1989).
Shanmuganathan, S., Waters, J.A., Karayiannis, P., Thursz, M. & Thomas, H.C. Mapping of the cellular immune responses to woodchuck hepatitis core antigen epitopes in chronically infected woodchucks. J. Med. Virol. 52, 128– 135 (1997).
Lohrengel, B., Lu, M. & Roggendorf, M. Molecular cloning of the woodchuck cytokines: TNF-alpha, IFN-gamma, and IL-6. Immunogenetics 47, 332–335 (1998).
Milich, D.R. et al. Autoantibody production in hepatitis B e antigen transgenic mice elicited with a self T-cell peptide and inhibited with nonself peptides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88, 4348– 4352 (1991).
Wirth, S., Guidotti, L.G., Ando, K., Schlicht, H.J. & Chisari, F.V. Breaking tolerance leads to autoantibody production but not autoimmune liver disease in hepatitis B virus envelope transgenic mice. J. Immunol. 154, 2504– 2515 (1995).
Thomas, H.C. The hepatitis B virus and the host response. J. Hepatol. 11(Suppl 1), S83–S89 (1990 ).
Hoofnagle, J.H., & Alter, H.J. in Viral Hepatitis and Liver Disease (eds. Vyas, G.N., Dienstag, J.L., & Hoofnagle, J.H.) 97–114 (Grune & Stratton, New York, 1984).
Hoofnagle, J.H., & Schafer, D.F. Serologic markers of hepatitis B virus infection. Semin. Liver Dis. 6 , 1–10 (1986).
Hogan, B., Beddington, R., Costantini, F., & Lacy, E. in Manipulating the Mouse Embryo: A Laboratory Manual 2nd edn. (Cold Spring Harbor Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York, 1994).
Sambrook, J., Fritsch E.F., & Maniatis, T. in Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual 2nd edn. (Cold Spring Harbor Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York, 1989).
Feitelson, M.A. et al. Pathogenesis of post-transfusion viral hepatitis in children with β-thalassemia. Hepatology 19, 558–568 (1994).
Feitelson, M.A. & Clayton, M.M. The X antigen/antibody markers in hepadnavirus infections. II. Antibodies to the X gene product(s). Gastroenterology 99, 500– 507 (1990).
Schaeffer, D.O., Hosgood, G., Oakes, M.G., St. Amant, L.G. & Koon, C.E. An alternative technique for partial hepatectomy in mice. Lab. Animal Sci. 44, 189– 190 (1994).
Waynforth, H.B. in Experimental and Surgical Techniques in the Rat 2nd edn. (Academic, London, 1992).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank C. Calkins and L. Eisenlohr for discussions, and J. Song for assisting in screening mice for virus. This work was supported by NIH grants CA48656 and CA66971, and by a grant from the Alcoholic Beverage Medical Research Foundation to M.A.F. This work was also supported by a pilot project from AA07186 to E. Rubin. The Kimmel Cancer Center Transgenic and Knockout Mouse Facility is supported, in part, by NIH grant CA56036.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Larkin, J., Clayton, M., Sun, B. et al. Hepatitis B virus transgenic mouse model of chronic liver disease. Nat Med 5, 907–912 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/11347
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/11347
This article is cited by
-
Critical role of bile acid (BA) in the cellular entry and permissiveness of Hepatitis B virus in vitro
Molecular & Cellular Toxicology (2020)
-
The doses of plasmid backbone plays a major role in determining the HBV clearance in hydrodynamic injection mouse model
Virology Journal (2018)
-
The dose of HBV genome contained plasmid has a great impact on HBV persistence in hydrodynamic injection mouse model
Virology Journal (2017)
-
Natural killer cell activation contributes to hepatitis B viral control in a mouse model
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
An autophagosome-based therapeutic vaccine for HBV infection: a preclinical evaluation
Journal of Translational Medicine (2014)