Abstract
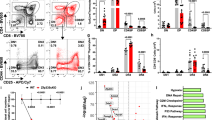
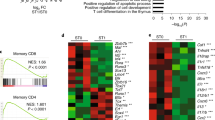
The gene Bcl11b, which encodes zinc finger proteins, and its paralog, Bcl11a, are associated with immune-system malignancies. We have generated Bcl11b-deficient mice that show a block at the CD4−CD8− double-negative stage of thymocyte development without any impairment in cells of B- or γδ T cell lineages. The Bcl11b−/− thymocytes showed unsuccessful recombination of Vβ to Dβ and lacked the pre–T cell receptor (TCR) complex on the cell surface, owing to the absence of Tcrb mRNA expression. In addition, we saw profound apoptosis in the thymus of neonatal Bcl11b−/− mice. These results suggest that Bcl11b is a key regulator of both differentiation and survival during thymocyte development.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fischer, A. & Malissen, B. Natural and engineered disorders of lymphocyte development. Science 280, 237–243 (1998).
von Boehmer, H. et al. Pleiotropic changes controlled by the pre-T-cell receptor. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 11, 135–142 (1999).
Mombaerts, P. et al. Mutations in T-cell antigen receptor genes α and β block thymocyte development at different stages. Nature 360, 225–231 (1992).
Fehling, H.J., Krotkova, A., Saint-Ruf, C. & von Boehmer, H. Crucial role of the pre-T-cell receptor α gene in development of αβ but not γδ T cells. Nature 375, 795–798 (1995).
Haks, M.C., Krimpenfort, P., Borst, J. & Kruisbeek, A.M. The CD3γ chain is essential for development of both the TCRαβ and TCRγδ lineages. EMBO J. 17, 1871–1882 (1998).
Mombaerts, P., Anderson, S.J., Perlmutter, R.M., Mak, T.W. & Tonegawa, S. An activated lck transgene promotes thymocyte development in RAG-1 mutant mice. Immunity 1, 261–267 (1994).
Molina, T.J. et al. Profound block in thymocyte development in mice lacking p56lck. Nature 357, 161–164 (1992).
Aifantis, I., Gounari, F., Scorrano, L., Borowski, C. & von Boehmer, H. Constitutive pre-TCR signaling promotes differentiation through Ca2+ mobilization and activation of NF-κB and NFAT. Nat. Immunol. 2, 403–409 (2001).
Zhang, L., Camerini, V., Bender, T.P. & Ravichandran, K.S. A nonredundant role for the adapter protein Shc in thymic T cell development. Nat. Immunol. 3, 749–755 (2002).
Bueno, O.F., Brandt, E.B., Rothenberg, M.E. & Molkentin, J.D. Defective T cell development and function in calcineurin Aβ-deficient mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 9398–9403 (2002).
van de Wetering, M., de Lau, W. & Clevers, H. WNT signaling and lymphocyte development. Cell 109, S13–S19 (2002).
Ioannidis, V., Beermann, F., Clevers, H. & Held, W. The β-catenin-TCF-1 pathway ensures CD4+CD8+ thymocyte survival. Nat. Immunol. 2, 691–697 (2001).
Gounari, F. et al. Somatic activation of β-catenin bypasses pre-TCR signaling and TCR selection in thymocyte development. Nat. Immunol. 2, 863–969 (2001).
Maraskovsky, E. et al. Bcl-2 can rescue T lymphocyte development in interleukin-7 receptor-deficient mice but not in mutant rag-1−/− mice. Cell 89, 1011–1019 (1997).
Newton, K., Harris, A.W. & Strasser, A. FADD/MORT1 regulates the pre-TCR checkpoint and can function as a tumour suppressor. EMBO J. 19, 931–941 (2000).
Jiang, D., Lenardo, M.J. & Zuniga-Pflücker, J.C. p53 prevents maturation to the CD4+CD8+ stage of thymocyte differentiation in the absence of T cell receptor rearrangement. J. Exp. Med. 183, 1923–1928 (1996).
Haks, M.C., Krimpenfort, P., van den Brakel, J.H.N. & Kruisbeek, A.M. Pre-TCR signaling and inactivation of p53 induces crucial cell survival pathways in pre-T cells. Immunity 11, 91–101 (1999).
Shinbo, T. et al. Allelic loss mapping and physical delineation of a region harboring a putative thymic lymphoma suppressor gene on mouse chromosome 12. Oncogene 18, 4131–4136 (1999).
Wakabayashi, Y. et al. Homozygous deletions and point mutations of the Rit1/Bcl11b gene in γ-ray induced mouse thymic lymphomas. Biophys. Biochem. Res. Commun. 301, 598–603.
Satterwhite, E. et al. The BCL11 gene family: involvement of BCL11A in lymphoid malignancies. Blood 98, 3413–3420 (2001).
Avram, D. et al. Isolation of a novel family of C2H2 zinc finger proteins implicated in transcriptional repression mediated by chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter transcription factor (COUP-TF) orphan nuclear receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 10315–10322 (2000).
Yagi, T. et al. Homologous recombination at c-fyn locus of mouse embryonic stem cells with use of diphtheria toxin A-fragment gene in negative selection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87, 9918–9922 (1990).
Hirokawa, K., Utsuyama, M., Moriizumi, E. & Handa, S. Analysis of the thymic microenvironment by monoclonal antibodies with special reference to thymic nurse cells. Thymus 8, 349–360 (1986).
Polyak, K.J. et al. p27Kip1, a cyclin-Cdk inhibitor, links transforming growth factor-β and contact inhibition to cell cycle arrest. Genes & Dev. 8, 9–22 (1994).
Wang, X. The expanding role of mitochondria in apoptosis. Genes & Dev. 15, 2922–2933 (2001).
Cheng, E.H. et al. BCL-2, BCL-x(L) sequester BH3 domain-only molecules preventing BAX-and BAK-mediated mitochondrial apoptosis. Mol. Cell 8, 705–711 (2001).
Ma, A. et al. Bclx regulates the survival of double-positive thymocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 4763–4767 (1995).
Bouillet, P. et al. Proapoptotic Bcl-2 relative Bim required for certain apoptotic responses, leukocyte homeostasis, and to preclude autoimmunity. Science 286, 1735–1738 (1999).
Bouillet, P. et al. BH3-only Bcl-2 family member Bim is required for apoptosis of autoreactive thymocytes. Nature 415, 922–926 (2002).
Sleckman, B.P., Gorman, J.R. & Alt, F.W. Accessibility control of antigen-receptor variable-region gene assembly: role of cis-acting elements. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 14, 459–481 (1996).
Lauzurica, P. & Krangel, M.S. Enhancer-dependent and -independent steps in the rearrangement of a human T cell receptor delta transgene. J. Exp. Med. 179, 43–55 (1994).
McMurry, M.T. & Krangel, M.S. A role for histone acetylation in the developmental regulation of VDJ recombination. Science 287, 495–498 (2000).
Avram, D., Fields, A., Senawong, T., Topark-Ngarm, A. & Leid, M. COUP-TF (chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter transcription factor)-interacting protein 1 (CTIP1) is a sequence-specific DNA binding protein. Biochem. J. 368, 555–563 (2002).
Nisha, N.H., Kang, C., Hsing, L.C., Zhang, J. & Winoto, A. T cell-specific FADD-deficient mice: FADD is required for early T cell development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 6307–6312 (2001).
Engel, I., Johns, C., Bain, G., Rivera, R.R. & Murre, C. Early thymocyte development is regulated by modulation of E2A protein activity. J. Exp. Med. 194, 733–745 (2001).
Evan, G. & Littlewood, T. A matter of life and cell death. Science 281, 1317–1322 (1998).
Evan, G.I. et al. Induction of apoptosis in fibroblasts by c-myc protein. Cell 69, 119–128 (1992).
Jacks, T. et al. Effects of an Rb mutation in the mouse. Nature 359, 295–300 (1992).
Almasan, A. et al. Deficiency of retinoblastoma protein leads to inappropriate S-phase entry, activation of E2F-responsive genes, and apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 5436–5440 (1995).
Knudsen, K.E. et al. RB-dependent S-phase response to DNA damage. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20, 7751–7763 (2000).
Nakamura, T. et al. Evi9 encodes a novel zinc finger protein that physically interacts with BCL6, a known human B-cell proto-oncogene product. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20, 3178–3186 (2000).
Liu, P. et al. Bcl11a is essential for normal lymphoid development. Nat. Immunol. advance online publication, 28 April 2003 (doi:10.1038/ni925).
Anderson, S.J., Abraham, K.M., Nakayama, T., Singer, A. & Perlmutter, R.M. Inhibition of T-cell receptor β-chain gene rearrangement by overexpression of the non-receptor protein tyrosine kinase p56lck. EMBO J. 11, 4877–4886 (1992).
Nutt, S.L., Heavey, B., Rolink, A.G., & Busslinger, M. Commitment to the B-lymphoid lineage depends on the transcription factor Pax5. Nature 401, 556–562 (1999).
Watanabe, H., Miyaji, C., Seki, S. & Abo, T. c-kit+ stem cells and thymocyte precursors in the livers of adult mice. J. Exp. Med. 184, 687–693 (1996).
Toba, K. et al. Cell kinetic study of normal human bone marrow hematopoiesis and acute leukemia using 7AAD/PY. Eur. J. Haematol. 64, 10–21 (2000).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for scientific research from the Ministry of Education, Science, Culture and Sports and by a Health Science Research Grant from the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare of Japan. We thank K. Toba for cell cycle analysis by flow cytometry, and A. Balmain, K. Hirokawa, T. Abo, M. Naito and A. Shimizu for helpful comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wakabayashi, Y., Watanabe, H., Inoue, J. et al. Bcl11b is required for differentiation and survival of αβ T lymphocytes. Nat Immunol 4, 533–539 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/ni927
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ni927
This article is cited by
-
Reprogramming immune cells activity by furin-like enzymes as emerging strategy for enhanced immunotherapy in cancer
British Journal of Cancer (2023)
-
Reactivation of corticogenesis-related transcriptional factors BCL11B and SATB2 after ischemic lesion of the adult mouse brain
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Immunoglobulin genes expressed in lymphoblastoid cell lines discern and predict lithium response in bipolar disorder patients
Molecular Psychiatry (2023)
-
Symbiotic bacteria-dependent expansion of MR1-reactive T cells causes autoimmunity in the absence of Bcl11b
Nature Communications (2022)
-
A double-negative thymocyte-specific enhancer augments Notch1 signaling to direct early T cell progenitor expansion, lineage restriction and β-selection
Nature Immunology (2022)