Abstract
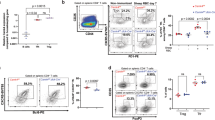
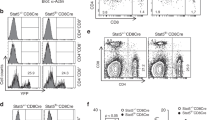
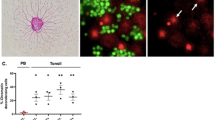
After autoimmune inflammation, interactions between CD95 and its ligand (CD95L) mediate thyrocyte destruction in Hashimoto's thyroiditis (HT). Conversely, thyroid autoimmune processes that lead to Graves' disease (GD) result in autoantibody-mediated thyrotropin receptor stimulation without thyrocyte depletion. We found that GD thyrocytes expressed CD95 and CD95L in a similar manner to HT thyrocytes, but did not undergo CD95-induced apoptosis either in vivo or in vitro. This pattern was due to the differential production of TH1 and TH2 cytokines. Interferon γ promoted caspase up-regulation and CD95-induced apoptosis in HT thyrocytes, whereas interleukin 4 and interleukin 10 protected GD thyrocytes by potent up-regulation of cFLIP and Bcl-xL, which prevented CD95-induced apoptosis in sensitized thyrocytes. Thus, modulation of apoptosis-related proteins by TH1 and TH2 cytokines controls thyrocyte survival in thyroid autoimmunity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas, A. K., Murphy, K. M. & Sher, A. Functional diversity of helper T lymphocytes. Nature 383, 787–793 ( 1996).
Romagnani, S. The Th1/Th2 paradigm. Immunol. Today 18, 263–266 (1997).
Weetman, A. P. & McGregor, A. M. Autoimmune thyroid disease: further developments in our understanding. Endocr. Rev. 15, 788–830 (1994).
Dayan, C. M. & Daniels, G. H. Chronic autoimmune thyroiditis . N. Engl. J. Med. 335, 99– 107 (1996).
Iwatani, Y., Hidaka, Y., Matsuzuka, F., Kuma, K. & Amino, N. Intrathyroidal lymphocyte subsets, including unusual CD4+ CD8+ cells and CD3loTCRαβlo/−CD4−CD8− cells, in autoimmune thyroid disease. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 93, 430–436 ( 1993).
Roura-Mir, C. et al. Single-cell analysis of intrathyroidal lymphocytes shows differential cytokine expression in Hashimoto's and Graves' disease. Eur. J. Immunol. 27, 3290–3302 ( 1997).
De Maria, R. & Testi, R. Fas-FasL interactions: a common pathogenetic mechanism in organ-specific autoimmunity. Immunol. Today 19, 121–125 (1998).
Caturegli, P. et al. IgG subclass distribution of thyroglobulin antibodies in patients with thyroid disease. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 98, 464–469 (1994).
Nagata, S. Apoptosis by death factor. Cell 88, 355– 365 (1997).
Green, D. R. Apoptotic pathways: the roads to ruin. Cell 94, 695–698 (1998).
Tschopp, J., Irmler, M. & Thome, M. Inhibition of fas death signals by FLIPs. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 10, 552–528 (1998).
Rasper, D. M. et al. Cell death attenuation by `Usurpin', a mammalian DED-caspase homologue that precludes caspase-8 recruitment and activation by the CD-95 (Fas, APO-1) receptor complex. Cell Death Differ. 5 , 271–288 (1998).
Krammer, P. H. CD95(APO-1/Fas)-mediated apoptosis: live and let die. Adv. Immunol. 71, 163–210 ( 1999).
Waldner, H., Sobel, R. A., Howard, E. & Kuchroo, V. K. Fas- and FasL-deficient mice are resistant to induction of autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Immunol. 159, 3100–3103 (1997).
Sabelko, K. A., Kelly, K. A., Nahm, M. H., Cross, A. H. & Russell, J. H. Fas and Fas ligand enhance the pathogenesis of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis, but are not essential for immune privilege in the central nervous system. J. Immunol. 159, 3096–3099 ( 1997).
Giordano, C. et al. Potential involvement of Fas and its ligand in the pathogenesis of Hashimoto's thyroiditis. Science 275, 960–963 (1997).
Mitsiades, N. et al. Fas/Fas ligand up-regulation and Bcl-2 down-regulation may be significant in the pathogenesis of Hashimoto's thyroiditis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 83, 2199– 2203 (1998).
Stassi, G. et al. Fas/Fas ligand-driven T cell apoptosis as a consequence of ineffective thyroid immunoprivilege in Hashimoto's thyroiditis. J. Immunol. 162, 263–267 (1999).
Leithauser, F. et al. Constitutive and induced expression of APO-1, a new member of the nerve growth factor/tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, in normal and neoplastic cells. Lab. Invest. 69, 415–429 (1993).
Kawakami, A. et al. Thyroid-stimulating hormone inhibits Fas antigen-mediated apoptosis of human thyrocytes in vitro. Endocrinology 137, 3163–3169 (1996).
Hammond, L. J. et al. Analysis of apoptosis in relation to tissue destruction associated with Hashimoto's autoimmune thyroiditis. J. Pathol. 182, 138–144 (1997).
Bretz, J. D., Arscott, P. L., Myc, A. & Baker, J. R. Jr Inflammatory cytokine regulation of Fas-mediated apoptosis in thyroid follicular cells. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 25433– 25438 (1999).
De Maria, R. et al. Negative regulation of erythropoiesis by caspase-mediated cleavage of GATA-1. Nature 401, 489– 493 (1999).
Sarvetnick, N. et al. Loss of pancreatic islet tolerance induced by β-cell expression of interferon-γ. Nature 346, 844–847 (1990).
Gallichan, W. S., Balasa, B., Davies, J. D. & Sarvetnick, N. Pancreatic IL-4 expression results in islet-reactive Th2 cells that inhibit diabetogenic lymphocytes in the nonobese diabetic mouse. J. Immunol. 163, 1696–1703 ( 1999).
van der Veen, R. C. & Stohlman, S. A. Encephalitogenic Th1 cells are inhibited by Th2 cells with related peptide specificity: relative roles of interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-10. J. Neuroimmunol. 48, 213–220 (1993).
Racke, M. K. et al. Cytokine-induced immune deviation as a therapy for inflammatory autoimmune disease. J. Exp. Med. 180, 1961 –1966 (1994).
Buer, J. et al. Interleukin 10 secretion and impaired effector function of major histocompatibility complex class II-restricted T cells anergized in vivo . J. Exp. Med. 187, 177– 183 (1998).
Stohlman, S. A., Pei, L., Cua, D. J., Li, Z. & Hinton, D. R. Activation of regulatory cells suppresses experimental allergic encephalomyelitis via secretion of IL-10. J. Immunol. 163, 6338–6344 ( 1999).
Pujol-Borrell, R. et al. HLA class II induction in human islet cells by interferon-γ plus tumour necrosis factor or lymphotoxin. Nature 326, 304–306 (1987).
Dibbert, B. et al. Role for Bcl-xL in delayed eosinophil apoptosis mediated by granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and interleukin-5 . Blood 92, 778–783 (1998).
Levy, Y. & Brouet, J. C. Interleukin-10 prevents spontaneous death of germinal center B cells by induction of the bcl-2 protein. J. Clin. Invest. 93, 424–428 (1994).
Green, D. R. & Reed, J. C. Mitochondria and apoptosis. Science 281, 1309–1312 ( 1998).
Ashkenazi, A. & Dixit, V. M. Death receptors: signaling and modulation. Science 281, 1305– 1308 (1998).
Srinivasula, S. M. et al. FLAME-1, a novel FADD-like anti-apoptotic molecule that regulates Fas/TNFR1-induced apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 18542–18545 (1997).
Scaffidi, C., Schmitz, I., Krammer, P. H. & Peter, M. E. The role of c-FLIP in modulation of CD95-induced apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 1541–1548 (1999).
Grignani, F. et al. High-efficiency gene transfer and selection of human hematopoietic progenitor cells with a hybrid EBV/retroviral vector expressing the green fluorescence protein. Cancer Res. 58, 14 –19 (1998).
Acknowledgements
Supported by grants from AIRC (to R. D. M.) and Telethon-Italy, grant number E.735 (to G. S.). D. D. L. is a recipient of a Telethon fellowship. A. Z. is a recipient of a FIRC fellowship. We thank M. Catalano for excellent technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stassi, G., Di Liberto, D., Todaro, M. et al. Control of target cell survival in thyroid autoimmunity by T helper cytokines via regulation of apoptotic proteins. Nat Immunol 1, 483–488 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/82725
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/82725
This article is cited by
-
Interleukin 10 expression is related to aggressiveness and poor prognosis of patients with thyroid cancer
Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy (2017)
-
The ratio of Mcl-1 and Noxa determines ABT737 resistance in squamous cell carcinoma of the skin
Cell Death & Disease (2014)
-
Possible link between Hashimoto's thyroiditis and oral lichen planus: a novel association found
Clinical Oral Investigations (2013)
-
Distinct roles of cytolytic effector molecules for antigen‐restricted killing by CTL in vivo
Immunology & Cell Biology (2010)
-
Apoptosis resistance in epithelial tumors is mediated by tumor-cell-derived interleukin-4
Cell Death & Differentiation (2008)