Abstract
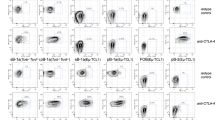
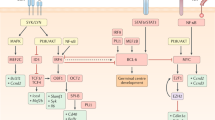
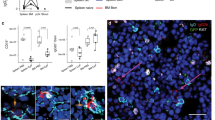
Antibody class defines function in B cell immunity, but how class is propagated into B cell memory remains poorly understood. Here we demonstrate that memory B cell subsets unexpectedly diverged across antibody class through differences in the effects of major transcriptional regulators. Conditional genetic deletion of the gene encoding the transcription factor T-bet selectively blocked the formation and antigen-specific response of memory B cells expressing immunoglobulin G2a (IgG2a) in vivo. Cell-intrinsic expression of T-bet regulated expression of the transcription factor STAT1, steady-state cell survival and transcription of IgG2a-containing B cell antigen receptors (BCRs). In contrast, the transcription factor RORα and not T-bet was expressed in IgA+ memory B cells, with evidence that knockdown of RORα mRNA expression and chemical inhibition of transcriptional activity also resulted in lower survival and BCR expression of IgA+ memory B cells. Thus, divergent transcriptional regulators dynamically maintain subset integrity to promote specialized immune function in class-specific memory B cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kurosaki, T., Aiba, Y., Kometani, K., Moriyama, S. & Takahashi, Y. Unique properties of memory B cells of different isotypes. Immunol. Rev. 237, 104–116 (2010).
McHeyzer-Williams, M.G., Okitsu, S.L., Wang, N.S. & McHeyzer-Williams, L.J. Molecular programming of B cell memory. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 12, 24–34 (2012).
Dogan, I. et al. Multiple layers of B cell memory with different effector functions. Nat. Immunol. 10, 1292–1299 (2009).
Fazilleau, N. et al. The function of follicular helper T cells is regulated by the strength of T cell antigen receptor binding. Nat. Immunol. 10, 375–384 (2009).
Engels, N. et al. Recruitment of the cytoplasmic adaptor Grb2 to surface IgG and IgE provides antigen receptor-intrinsic costimulation to class-switched B cells. Nat. Immunol. 10, 1018–1025 (2009).
Martin, S.W. & Goodnow, C.C. Burst-enhancing role of the IgG membrane tail as a molecular determinant of memory. Nat. Immunol. 3, 182–188 (2002).
Snapper, C.M. & Paul, W.E. Interferon-gamma and B cell stimulatory factor-1 reciprocally regulate Ig isotype production. Science 236, 944–947 (1987).
Stavnezer, J., Guikema, J.E. & Schrader, C.E. Mechanism and regulation of class switch recombination. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 26, 261–292 (2008).
Cazac, B.B. & Roes, J. TGF-beta receptor controls B cell responsiveness and induction of IgA in vivo. Immunity 13, 443–451 (2000).
Miller, S.A. & Weinmann, A.S. Common themes emerge in the transcriptional control of T helper and developmental cell fate decisions regulated by the T-box, GATA and ROR families. Immunology 126, 306–315 (2009).
Jetten, A.M. Retinoid-related orphan receptors (RORs): critical roles in development, immunity, circadian rhythm, and cellular metabolism. Nucl. Recept. Signal. 7, e003 (2009).
Lazarevic, V. & Glimcher, L.H. T-bet in disease. Nat. Immunol. 12, 597–606 (2011).
Zhu, J., Yamane, H., Cote-Sierra, J., Guo, L. & Paul, W.E. GATA-3 promotes Th2 responses through three different mechanisms: induction of Th2 cytokine production, selective growth of Th2 cells and inhibition of Th1 cell-specific factors. Cell Res. 16, 3–10 (2006).
Mohr, E. et al. IFN-γ produced by CD8 T cells induces T-bet-dependent and -independent class switching in B cells in responses to alum-precipitated protein vaccine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 107, 17292–17297 (2010).
Peng, S.L., Szabo, S.J. & Glimcher, L.H. T-bet regulates IgG class switching and pathogenic autoantibody production. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 5545–5550 (2002).
Yang, X.O. et al. T helper 17 lineage differentiation is programmed by orphan nuclear receptors RORα and RORγ. Immunity 28, 29–39 (2008).
Szabo, S.J. et al. Distinct effects of T-bet in TH1 lineage commitment and IFN-γ production in CD4 and CD8 T cells. Science 295, 338–342 (2002).
Intlekofer, A.M. et al. Anomalous type 17 response to viral infection by CD8+ T cells lacking T-bet and eomesodermin. Science 321, 408–411 (2008).
McHeyzer-Williams, L.J., Cool, M. & McHeyzer-Williams, M.G. Antigen-specific B cell memory: expression and replenishment of a novel B220- memory b cell compartment. J. Exp. Med. 191, 1149–1166 (2000).
Pelletier, N. et al. Plasma cells negatively regulate the follicular helper T cell program. Nat. Immunol. 11, 1110–1118 (2010).
Dent, A.L., Shaffer, A.L., Yu, X., Allman, D. & Staudt, L.M. Control of inflammation, cytokine expression, and germinal center formation by BCL-6. Science 276, 589–592 (1997).
Martins, G. & Calame, K. Regulation and functions of Blimp-1 in T and B lymphocytes. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 26, 133–169 (2008).
Beima, K.M. et al. T-bet binding to newly identified target gene promoters is cell type-independent but results in variable context-dependent functional effects. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 11992–12000 (2006).
Oestreich, K.J., Mohn, S.E. & Weinmann, A.S. Molecular mechanisms that control the expression and activity of Bcl-6 in TH1 cells to regulate flexibility with a TFH-like gene profile. Nat. Immunol. 13, 405–411 (2012).
Cimmino, L. et al. Blimp-1 attenuates Th1 differentiation by repression of ifng, tbx21, and bcl6 gene expression. J. Immunol. 181, 2338–2347 (2008).
Crozat, K. et al. Analysis of the MCMV resistome by ENU mutagenesis. Mamm. Genome 17, 398–406 (2006).
Cerutti, A. & Rescigno, M. The biology of intestinal immunoglobulin A responses. Immunity 28, 740–750 (2008).
Fagarasan, S., Kawamoto, S., Kanagawa, O. & Suzuki, K. Adaptive immune regulation in the gut: T cell-dependent and T cell-independent IgA synthesis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 28, 243–273 (2010).
Jaffar, Z., Ferrini, M.E., Herritt, L.A. & Roberts, K. Cutting edge: lung mucosal Th17-mediated responses induce polymeric Ig receptor expression by the airway epithelium and elevate secretory IgA levels. J. Immunol. 182, 4507–4511 (2009).
Lebman, D.A., Nomura, D.Y., Coffman, R.L. & Lee, F.D. Molecular characterization of germ-line immunoglobulin A transcripts produced during transforming growth factor type β-induced isotype switching. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87, 3962–3966 (1990).
Hamilton, B.A. et al. Disruption of the nuclear hormone receptor RORα in staggerer mice. Nature 379, 736–739 (1996).
Solt, L.A. et al. Suppression of TH17 differentiation and autoimmunity by a synthetic ROR ligand. Nature 472, 491–494 (2011).
Cogné, M. et al. A class switch control region at the 3′ end of the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus. Cell 77, 737–747 (1994).
Crotty, S. Follicular helper CD4 T cells (TFH). Annu. Rev. Immunol. 29, 621–663 (2011).
Reinhardt, R.L., Liang, H.E. & Locksley, R.M. Cytokine-secreting follicular T cells shape the antibody repertoire. Nat. Immunol. 10, 385–393 (2009).
Allen, C.D., Okada, T., Tang, H.L. & Cyster, J.G. Imaging of germinal center selection events during affinity maturation. Science 315, 528–531 (2007).
Victora, G.D. et al. Germinal center dynamics revealed by multiphoton microscopy with a photoactivatable fluorescent reporter. Cell 143, 592–605 (2010).
Maruyama, M., Lam, K.P. & Rajewsky, K. Memory B-cell persistence is independent of persisting immunizing antigen. Nature 407, 636–642 (2000).
Lam, K.P., Kuhn, R. & Rajewsky, K. In vivo ablation of surface immunoglobulin on mature B cells by inducible gene targeting results in rapid cell death. Cell 90, 1073–1083 (1997).
Fazilleau, N. et al. Lymphoid reservoirs of antigen-specific memory T helper cells. Nat. Immunol. 8, 753–761 (2007).
Chang, J.T. et al. Asymmetric T lymphocyte division in the initiation of adaptive immune responses. Science 315, 1687–1691 (2007).
Barnett, B.E. et al. Asymmetric B cell division in the germinal center reaction. Science 335, 342–344 (2012).
Nurieva, R.I. et al. Bcl6 mediates the development of T follicular helper cells. Science 325, 1001–1005 (2009).
Mondal, A., Sawant, D. & Dent, A.L. Transcriptional repressor BCL6 controls Th17 responses by controlling gene expression in both T cells and macrophages. J. Immunol. 184, 4123–4132 (2010).
Yang, X.O. et al. Molecular antagonism and plasticity of regulatory and inflammatory T cell programs. Immunity 29, 44–56 (2008).
Dzhagalov, I., Giguere, V. & He, Y.W. Lymphocyte development and function in the absence of retinoic acid-related orphan receptor α. J. Immunol. 173, 2952–2959 (2004).
Aiba, Y. et al. Preferential localization of IgG memory B cells adjacent to contracted germinal centers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 107, 12192–12197 (2010).
Pape, K.A., Taylor, J.J., Maul, R.W., Gearhart, P.J. & Jenkins, M.K. Different B cell populations mediate early and late memory during an endogenous immune response. Science 331, 1203–1207 (2011).
Gold, D.A. et al. RORalpha coordinates reciprocal signaling in cerebellar development through sonic hedgehog and calcium-dependent pathways. Neuron 40, 1119–1131 (2003).
Kane, C.D. & Means, A.R. Activation of orphan receptor-mediated transcription by Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IV. EMBO J. 19, 691–701 (2000).
Acknowledgements
We thank B. Beutler (The Scripps Research Institute) for mice with the Domino mutation of Stat1; and N. Cereb, S.Y. Yang and L. Boring for assistance with construction of the loxP-flanked Tbx21 allele. Supported by the US National Institutes of Health (TL1 RR025772-03 to N.S.W.; AI042370 and AI076458 to S.L.R; DK080201 and MH092769 to T.P.B.; and AI047231, AI040215 and AI071182 to M.G.M.-W.), the Swiss National Science Foundation (S.L.O.), Novartis Jubliaeumsstiftung (S.L.O.) and the Roche Research Foundation (S.L.O.). This is manuscript 21154 from The Scripps Research Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
N.S.W., L.J.M.-W. and M.G.M.-W. conceived of and designed the project; N.S.W. did all experiments and analyzed the data for all experiments; L.J.M.-W. identified T-bet in memory B cells and contributed to the preparation of the manuscript; S.L.O. contributed to experimental design; S.L.R. provided Tbx21F/F mice; T.P.B. provided SR1001; and N.S.W. and M.G.M.-W. wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–6 and Table 1 (PDF 1485 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, N., McHeyzer-Williams, L., Okitsu, S. et al. Divergent transcriptional programming of class-specific B cell memory by T-bet and RORα. Nat Immunol 13, 604–611 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.2294
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.2294
This article is cited by
-
Co-adjuvanting DDA/TDB liposomes with a TLR7 agonist allows for IgG2a/c class-switching in the absence of Th1 cells
npj Vaccines (2023)
-
Interferon-γ signal drives differentiation of T-bethi atypical memory B cells into plasma cells following Plasmodium vivax infection
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Deletion of the nuclear receptor RORα in macrophages does not modify the development of obesity, insulin resistance and NASH
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Integrative transcriptome and chromatin landscape analysis reveals distinct epigenetic regulations in human memory B cells
Nature Communications (2020)
-
ZBTB32 restrains antibody responses to murine cytomegalovirus infections, but not other repetitive challenges
Scientific Reports (2019)