Abstract
Pseudomonas aeruginosa uses a hierarchical quorum sensing (QS) network consisting of las, pqs and rhl regulatory elements to coordinate the expression of bacterial virulence genes. However, clinical isolates frequently contain loss-of-function mutations in the central las system. This motivated us to search for a mechanism that may functionally substitute las. Here we report identification of a new QS signal, IQS. Disruption of IQS biosynthesis paralyzes the pqs and rhl QS systems and attenuates bacterial virulence. Production of IQS is tightly controlled by las under normal culture conditions but is also activated by phosphate limitation, a common stressor that bacteria encounter during infections. Thus, these results have established an integrated QS system that connects the central las system and phosphate-stress response mechanism to the downstream pqs and rhl regulatory systems. Our discovery highlights the complexity of QS signaling systems and extends the gamut of QS and stress-response mechanisms.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
12 April 2012
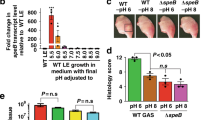
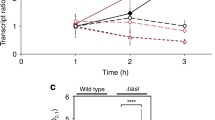
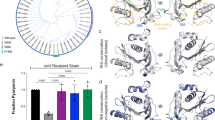
In the version of this article initially published online, the IQS structure used in Figure 2c and in the graphical abstract was incorrect. The error has been corrected for the PDF and HTML versions of this article.
References
Fuqua, C. & Greenberg, E.P. Listening in on bacteria: acyl-homoserine lactone signaling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 3, 685–695 (2002).
Federle, M.J. & Bassler, B.L. Interspecies communication in bacteria. J. Clin. Invest. 112, 1291–1299 (2003).
Winstanley, C. & Fothergill, L. The role of quorum sensing in chronic cystic fibrosis Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 290, 1–9 (2009).
Venturi, V. Regulation of quorum sensing in Pseudomonas. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 30, 274–291 (2006).
Williams, P. & Camara, M. Quorum sensing and environmental adaptation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a tale of regulatory networks and multifunctional signal molecules. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 12, 182–191 (2009).
Pesci, E.C. et al. Quinolone signaling in the cell-to-cell communication system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 11229–11234 (1999).
de Kievit, T.R., Kakai, Y., Register, J.K., Pesci, E.C. & Iglewski, B.H. Role of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa las and rhl quorum sensing systems in rhlI regulation. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 212, 101–106 (2002).
Gilbert, K.B., Kim, T.H., Gupta, R., Greenberg, E.P. & Schuster, M. Global position analysis of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-sensing transcription factor LasR. Mol. Microbiol. 73, 1072–1085 (2009).
Jensen, V. et al. RhlR expression in Pseudomonas aeruginosa is modulated by the Pseudomonas quinolone signal via PhoB-dependent and -independent pathways. J. Bacteriol. 188, 8601–8606 (2006).
Dekimpe, V. & Déziel, E. Revisiting the quorum sensing hierarchy in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: the transcriptional regulator RhlR regulates LasR-specific factors. Microbiology 155, 712–723 (2009).
Smith, E.E. et al. Genetic adaptation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa to the airways of cystic fibrosis patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 8487–8492 (2006).
Tingpej, P. et al. Phenotypic characterization of clonal and nonclonal Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains isolated from lungs of adults with cystic fibrosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 45, 1697–1704 (2007).
Rumbaugh, K.P. et al. Quorum sensing and the social evolution of bacterial virulence. Curr. Biol. 19, 341–345 (2009).
Wilder, C.N., Allada, G. & Schuster, M. Instantaneous within-patient diversity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-sensing populations from cystic fibrosis lung infections. Infect. Immun. 77, 5631–5639 (2009).
Hoffman, L.R. et al. Pseudomonas aeruginosa lasR mutants are associated with cystic fibrosis lung disease progression. J. Cyst. Fibros. 8, 66–70 (2009).
Karatuna, O. & Yagci, A. Analysis of quorum sensing–dependent virulence factor production and its relationship with antimicrobial susceptibility in Pseudomonas aeruginosa respiratory isolates. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 16, 1770–1775 (2010).
Gallagher, L.A. et al. Functions required for extracellular quinolone signaling by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 184, 6472–6480 (2002).
Diggle, S.P. et al. The Pseudomonas aeruginosa quinolone signal molecule overcomes the cell density-dependency of the quorum sensing hierarchy, regulates rhl-dependent genes at the onset of stationary phase and can be produced in the absence of LasR. Mol. Microbiol. 50, 29–43 (2003).
Lee, X. et al. Identification of the biosynthetic gene cluster for the Pseudomonas aeruginosa antimetabolite L-2-amino-4-methoxy-trans-3-butenoic acid. J. Bacteriol. 192, 4251–4255 (2010).
Wanner, B.L. Gene regulation by phosphate in enteric bacteria. J. Cell. Biochem. 51, 47–54 (1993).
Shor, R. et al. Severe hypophosphatemia in sepsis as a mortality predictor. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 36, 67–72 (2006).
Long, J., Zaborina, O., Holbrook, C., Zaborin, A. & Alverdy, J. Depletion of intestinal phosphate after operative injury activates the virulence of P. aeruginosa causing lethal gut-derived sepsis. Surgery 144, 189–197 (2008).
Zaborin, A. et al. Red death in Caenorhabditis elegans caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 106, 6327–6332 (2009).
Jeddi, R. et al. Risk factors of septic shock in patients with hematologic malignancies and Pseudomonas infections. Hematology 16, 160–165 (2011).
Dong, Y.H., Zhang, X.F., Xu, J.L., Tan, A.T. & Zhang, L.H. VqsM, a novel Ara-C–type global regulator of quorum sensing signaling and virulence in P. aeruginosa. Mol. Microbiol. 58, 552–564 (2005).
Slater, H., Alvarez-Morales, A., Barber, C.E., Daniels, M.J. & Dow, J.M. A two-component system involving an HD-GYP domain protein links cell-cell signaling to pathogenicity gene expression in Xanthomonas campestris. Mol. Microbiol. 38, 986–1003 (2000).
Dong, Y.H., Zhang, X.F., Xu, J.L., An, S.W. & Zhang, L.H. A novel two-component system BqsS-BqsR modulates quorum sensing–dependent biofilm decay in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Commun. Integr. Biol. 1, 88–96 (2008).
Ohman, D.E., Cryz, S.J. & Iglewski, B.H. Isolation and characterization of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO mutant that produces altered elastase. J. Bacteriol. 142, 836–842 (1980).
Diggle, S.P. et al. The Pseudomonas aeruginosa quinolone signal molecule overcomes the cell density-dependency of the quorum sensing hierarchy, regulates rhl-dependent genes at the onset of stationary phase and can be produced in the absence of LasR. Mol. Microbiol. 50, 29–43 (2003).
McClean, K.H. et al. Quorum sensing and Chromobacterium violaceum: exploitation of violacein production for the detection of N-acylhomoserine lactones. Microbiology 143, 3703–3711 (1997).
Zhang, H.B., Wang, L.H. & Zhang, L.H. Detection and analysis of quorum-quenching enzymes against acyl homoserine lactone quorum-sensing signals. Curr. Protoc. Microbiol. 5, 1C.3.1 (2007).
Nicas, T.I. & Iglewski, B.H. Isolation and characterization of transposon-induced mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa deficient in production of exoenzyme S. Infect. Immun. 45, 470–474 (1984).
Miller, J.H. A Short Course in Bacterial Genetics: a Laboratory Manual and Handbook for Escherichia coli and Related Bacteria (CSHL Press, New York, 1992).
Stiernagle, T. Maintenance of C. elegans in C. elegans: a Practical Approach (ed. Fay, D.) 1–11 (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1999).
Tan, M.W., Mahajan-Miklos, S. & Ausubel, F.M. Killing of Caenorhabditis elegans by Pseudomonas aeruginosa used to model mammalian bacterial pathogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 715–720 (1999).
Houthoofd, K., Braeckman, B.P. & Vanfleteren, J.R. The hunt for the record life span in Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 59, 408–410 (2004).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Biomedical Research Council, Agency of Science, Technology and Research (A*Star), Singapore.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.L. performed all experiments except those described below. J. Wu performed IQS purification and structural analysis. Y.D. and P.W. assisted in reporter strain construction and data analysis. Jianhe Wang and Jing Wang assisted in virulence assays. C.W. conducted bioinformatics analysis. C.C. performed RT-PCR analysis. Y.D. generated mutant strains and conducted phenotype analysis. J.L., J. Wu and L.-H.Z. designed experiments, analyzed data and wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Results (PDF 1516 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, J., Wu, J., Deng, Y. et al. A cell-cell communication signal integrates quorum sensing and stress response. Nat Chem Biol 9, 339–343 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.1225
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.1225