Abstract
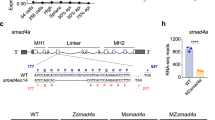
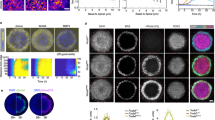
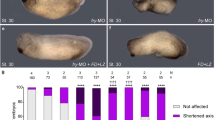
Fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) are pleiotrophic growth factors that control cell proliferation, migration, differentiation and embryonic patterning1. During early zebrafish embryonic development, FGFs regulate dorsoventral patterning by controlling ventral bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) expression2,3. FGFs function by binding and activating high-affinity tyrosine kinase receptors4. FGF activity is negatively regulated by members of the Sprouty family, which antagonize Ras signalling induced by receptor tyrosine kinases3,5,6,7,8. On the basis of similarities in their expression patterns during embryonic development, we have identified five genes that define a synexpression group — fgf8, fgf3, sprouty2, sprouty4, as well as a novel gene, sef (similar expression to fgf genes). Sef encodes a conserved putative transmembrane protein that shares sequence similarities with the intracellular domain of the interleukin 17 receptor9. Here we show that in zebrafish, Sef functions as a feedback-induced antagonist of Ras/Raf/MEK/MAPK-mediated FGF signalling.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goldfarb, M. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 7, 311–325 (1996).
Fürthauer, M., Thisse, C. & Thisse, B. Development 124, 4253–4264 (1997).
Fürthauer, M. Reifers, F. Brand, M. Thisse, B. & Thisse, C. Development 128, 2175–2186 (2001).
Klint, P. & Claesson-Welsh, L. Front. Biosci. 4, D165–D177 (1999).
Hacohen, N., Kramer, S., Sutherland, D., Hiromi, Y. & Krasnow, M. A. Cell 92, 253–263 (1998).
Casci, T., Vinos, J. & Freeman, M. Cell 96, 655–665 (1999).
Tefft, J. D. et al. Curr. Biol. 9, 219–222 (1999).
Minowada, G. et al. Development 126, 4465–4475 (1999).
Yao, Z. et al. Immunity 6, 811–821 (1995).
Reifers, F. et al. Development 125, 2381–2395 (1998).
Mohammadi, M. et al. Science 276, 955–960 (1997).
Umbhauer, M., Penzo-Mendez, A., Clavilier, L., Boucaut, J., Riou, J. J. Cell Sci. 113, 2865–2875 (2000).
Whitman, M. & Melton, D. A. Nature 357, 252–254 (1992).
Nasevicius, A. & Ekker, S. C. Nature Genet. 26, 216–220 (2000).
Mullins, M. C. et al. Development 123, 81–93 (1996).
Kim, J. et al. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 250, 516–530 (1998).
Fabian, J. R., Morrison, D. K. & Daar, I. O. J. Cell Biol. 122, 645–652. (1993).
Umbhauer, M., Marshall, C. J., Mason, C. S., Old, R. W. & Smith, J. C. Nature 376, 58–62 (1995).
Wilson, S. I., Graziano, E., Harland, R., Jessell, T. M. & Edlund, T. Curr. Biol. 10, 421–429 (2000).
Schulte-Merker, S. & Smith, J. C. Curr. Biol. 5, 62–67 (1995).
Daar, I. et al. Science 253,74–76 (1991).
Gabay, L., Seger, R. & Shilo, B. Z. Science 277,1103–1106 (1997).
Roehl, H. & Nusslein-Volhard, C. Curr. Biol. 7, 503–507 (2001).
Raible, F. & Brand, M. Mech. Dev. 107,105–117 (2001).
Kolch, W. Biochem. J. 351, 289–305 (2000).
Conlon, R. A. & Herrmann, B. G. Methods Enzymol. 225, 373–383 (1993).
Hofmann, K., Bucher, P., Falquet, L. & Bairoch, A. Nucleic Acids Res. 27, 215–219 (1999).
Thisse, C., Thisse, B., Halpern, M. E. & Postlethwait, J. H. Dev. Biol. 164, 420–429 (1994).
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to I. Daar, G. R. Martin, J-F. Riou, J. Smith, M. Umbhauer and M. Whitman for providing constructs used in this study. We thank I. Dawid for fruitful discussion and sharing data prior to publication. We thank V. Heyer, M. Koch, C. Lan for technical assistance and O. Nkundwa for caring for the zebrafish. M.F. was funded by the Ministère de l'Enseignement Supérieur de la Recherche, the Ligue Nationale Contre le Cancer and the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique. B.T., C.T. and S-L.A. were supported by funds from the Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale, the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique, the Hôpital Universitaire de Strasbourg, the Association pour la Recherche sur le Cancer the Ligue Nationale Contre le Cancer and the National Institute of Health (RO1 RR15402). W.L. was funded by a fellowship from INSERM.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fürthauer, M., Lin, W., Ang, SL. et al. Sef is a feedback-induced antagonist of Ras/MAPK-mediated FGF signalling. Nat Cell Biol 4, 170–174 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb750
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb750
This article is cited by
-
Identification and functional characterization of fish IL-17 receptors suggest important roles in the response to nodavirus infection
Marine Life Science & Technology (2024)
-
Loss of interleukin-17 receptor D promotes chronic inflammation-associated tumorigenesis
Oncogene (2021)
-
Combined whole-mount fluorescence in situ hybridization and antibody staining in zebrafish embryos and larvae
Nature Protocols (2020)
-
A parental requirement for dual-specificity phosphatase 6 in zebrafish
BMC Developmental Biology (2018)
-
Orphan receptor IL-17RD regulates Toll-like receptor signalling via SEFIR/TIR interactions
Nature Communications (2015)