Abstract
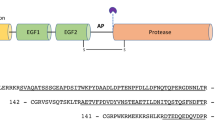
Purified tissue plasminogen activator synthesized by a human melanoma cell line has been partially characterized. On SDS gel electrophoresis, the purified samples exhibited a doublet at molecular weights 63,000 and 65,000. Staphylococcal V8 proteolytic digestion of the separated species yielded similar size fragments, indicating gross identity of the polypeptide chains. It was subsequently found that these species had differential binding to lysine-Sepharose, with the lower apparent molecular weight species binding with a higher affinity. Amino acid sequence determination of reverse phase HPLC tryptic fragments has resulted in the characterization of approximately 80 percent of the protein. The identification of a cDNA clone has allowed alignment of these tryptic peptides. The molecule was found to be composed of an amino terminal domain, two kringle structures, and a serine protease. The molecule is composed of 527 amino acids, and has potential glycosylation sites at asparagine positions 117, 184, 218, and 448. The peptide containing Asn 448 was sequenced and determined to be glycosylated, whereas a peptide containing Asn-218 was found not to be glycosylated. Comparison of the kringle and serine protease domains with other serine proteases is discussed.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gaffney, P.J. 1981. The fibrinolytic system, p. 198–224. In: Haemostasis and Thrombosis, Bloom, A. L., and Thomas, D. P., (eds.), Churchill Livingstone, Inc., New York.
Robbins, K.C., Summaria, L., Hsieh, B. and Shah, R.J. 1967. The peptide chains of human plasmin. Mechanism of activation of human plasminogen to plasmin. J. Biol. Chem. 242: 2333–2342.
Duckert, F. 1978. Urokinase, p. 209–237. In: Fibrinolytics and Antifibrinolytics, Markwardt, F., (ed.), Springer-Verlag, New York.
Wun, T.-C., Schleuing, W.-D. and Reich, E. 1982. Isolation and characterization of urokinase from human plasma. J. Biol. Chem. 257: 3276–3283.
Ratnoff, O.D. 1977. The surface-mediated initiation of blood coagulation and related phenomena, p. 25–55. In: Haemostasis: Biochemistry, Physiology, and Pathology, Ogston, D., Bennett, B., (eds.), John Wiley and Sons, London.
Kok, P. and Astrup, T. 1969. Isolation and purification of a tissue plasminogen activator and its comparison with urokinase. Biochemistry 8: 79–86.
Cole, E.R. and Bachmann, F.W. 1977. Purification and properties of plasminogen activator from pig heart. J. Biol. Chem. 252: 3729–3737.
Rijken, D.C., Wijngaards, G., Zaal-deJong, M. and Welbergen, J. 1979. Purification and partial characterization of plasminogen activator from human uterine tissue. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 580: 140–153.
Aoki, N. and von Kaulla, K.N. 1971. The extraction of tissue plasminogen activator from human cadavers and a description of some of its properties. Am. J. Clin. Path. 55: 171–179.
Rijken, D.C., Wijngaards, G. and Welbergen, J. 1979. Biochemical and immunological characterization of plasminogen activator from human tissue. Prog. Chem. Fibrinolysis Thrombolysis 4: 349–354.
Rijken, D.C. and Collen, D. 1981. Purification and characterization of the plasminogen activator secreted by human melanoma cells in culture. J. Biol. Chem. 256: 7035–7041.
Korninger, C. and Collen, D. 1981. Studies on the specific fibrinolytic effect of human extrinsic (tissue-type) plasminogen activator in human blood and in various animal species in vitro. Thrombos. Haemostas. (Stuttgart) 46: 561–565.
Hoylaerts, M., Rijken, D.C., Lijnen, H.R. and Collen, D. 1982. Kinetics of the activation of plasminogen by human tissue plasminogen activator. Role of fibrin. J. Biol. Chem. 257: 2912–2919.
Rijken, D.C., Hoylaerts, M. and Collen, D. 1982. Fibrinolytic properties of one-chain and two-chain human extrinsic (tissue-type) plasminogen activator. J. Biol. Chem. 257: 2920–2925.
Korninger, C., Stassen, J.M. and Collen, D. 1981. Turnover of human extrinsic (tissue-type) plasminogen activator in rabbits. Thromb. Haemostas. (Stuttgart) 46: 658–661.
Weimar, W., Stibbe, J., Van Seyer, A.J., Billiau, A., De Somer, B. and Collen, D. 1981. Specific lysis of an iliofemoral thrombus by administration of extrinsic (tissue-type) plasminogen activator. Lancet 2: 1018–1020.
Korninger, C., Matsuo, O., Suy, R., Stassen, J.M. and Collen, D. 1982. Thrombolysis with human extrinsic (tissue-type) plasminogen activator in dogs with femoral vein thrombosis. J. Clin. Invest. 69: 573–580.
Blix, S. 1962. The effectiveness of activators in clot lysis, with special reference to fibrinolytic therapy. A new method for determination of preformed clot lysis. Acta. Med. Scand. (Suppl 386) 1–24.
Wallen, P. 1977. Activation of plasminogen with urokinase and tissue activator, p. 91–102. In: Thrombosis and Urokinase, Paoletti, R. and Sherry, (eds.), Academic Press, London.
Camiolo, S.M., Thorsen, S., Astrup, T. 1971. Fibrinogen olysis and fibrinolysis with tissue plasminogen activator, urokinase, streptokinase-activated human globulin, and plasmin. Proc. Soc. Exper. Biol. Med. 138: 277–280.
Urokinase-Pulmonary Embolism Trial Study Group. 1974. Urokinase-streptokinase embolism trial. Phase II. J. Am. Med. Assn. 229: 1606–1613.
Gurewich, V., Hyde, E. and Lipinski, B. 1975. The resistance of fibrinogen and soluble fibrin monomer in blood to degradation by a potent plasminogen activator derived from cadaver limbs. Blood 46: 555–565.
Paoletti, R. and Sherry, S. (eds.) 1977. Thrombosis and Urokinase, Academic Press, New York, New York.
Pennica, D., Holmes, W.E., Kahr, W.J., Harkins, R.N., Vehar, G.A., Ward, C.A., Yelverton, E., Seeburg, P.H., Heyneker, H.L., Goeddel, D.V. and Collen, D. 1983. Cloning and expression of human tissue-type plasminogen activator cDNA in E. coli. Nature 301: 214–221.
Astrup, T. and Mullertz, S. 1952. The fibrin plate method for estimating fibrinolytic activity. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 40: 346–351.
Laemmli, U.K. 1970. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227: 680–685.
Morrissey, J.H. 1981. Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal. Biochem. 117: 307–310.
Crestfield, A.M., Moore, S. and Stein, W.J. 1963. The preparation and enzymatic hydrolysis of reduced and s-carboxymethylated proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 238: 622–627.
Kohr, W.J., Keck, R. and Harkins, R.N. 1982. Characterization of intact and trypsin-digested biosynthetic human growth hormone by high-pressure liquid chromatography. Anal. Biochem. 122: 348–359.
Cleveland, D.W., Fisher, S.G., Kirschner, M.W. and Laemmli, U.K. 1977. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J. Biol. Chem. 252: 1102–1106.
Weber, K. and Osborn, M. 1969. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecylsulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J. Biol. Chem. 244: 4406–4412.
Radcliffe, R. and Heinze, T. 1978. Isolation of plasminogen activator from human plasma by chromatography on lysine-sepharose. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 189: 185–194.
Pepper, D.S. and Allen, R. 1978. Isolation of characterization of human cadaver vascular endothelial activator. In Progress in Chem. Fibrinolysis Thrombolysis 3: 91–98.
Jackson, R.L. and Hirs, C.H.W. 1970. The primary structure of porcine pancreatic ribonuclease. I. The distribution and sites of carbohydrate attachment. J. Biol. Chem. 245: 624–636.
Marshall, R.D. 1974. Nature and metabolism of the carbohydrate/ peptide linkages of glycoproteins. Biochem. Soc. Symp. 40: 17–26.
Ronin, C., Bouchilloux, S., Granier, C. and Van Rietschoten, J. 1978. Enzymatic N-glycosylation of synthetic Asn-X-thr containing peptides. FEBS Letters 96: 179–182.
Scheffer, A.J. and Beintema, J.J. 1974. Horse pancreatic ribonuclease. Eur. J. Biochem. 46: 221–233.
Jackson, R.C. and Blobel, G. 1980. Post-translational processing of full-length presecretory proteins with canine pancreatic signal peptidase. Anals. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 343: 391–404.
Strauss, A.W., Bennett, C.D., Donohue, A.M., Rodkey, J.A. and Alberts, A.W. 1977. Rat liver pre-proalbumin: complete amino acid sequence of the pre-piece. Analysis of the direct translation product of albumin messenger RNA. J. Biol. Chem. 252: 6846–6855.
MacGillivray, R.T.A., Chung, D.W. and Davie, E.W. 1979. Biosynthesis of bovine plasma proteins in a cell-free system. Amino terminal sequence of preproalbumin. Eur. J. Biochem. 98: 477–485.
Lawn, R.M., Adelman, J., Bock, S.C., Franke, A.E., Houck, C.M., Najarian, R.C., Seeburg, P.H. and Wion, K.L. 1981. The sequence of human serum albumin cDNA and its expression in E. coli. Nucleic Acids Research 9: 6103–6114.
Wallen, P., Pohl, G., Bergsdorf, N., Ranby, M., Ny, T. and Jornvall, H. 1983. Purification and characterization of a melanoma cell plasminogen activator. Eur. J. Biochem. 132: 681–686.
Dayhoff, M.O. 1978. Atlas of Protein Sequence and Structure 5, Suppl. 3: 79–81.
Steffens, G.J., Gunzler, W.A., Oetting, F., Frankus, E. and Flohe, L. 1982. The complete amino acid sequence of low molecular mass urokinase from human urine. Hoppe-Seyler's Z. Physiol. Chem. 363: 1043–1058.
Furie, B., Bing, D.H., Feldmann, R.J., Robison, D.J., Burnier, J.P. and Furie, B.C. 1982. Computer-generated models of blood coagulation factor Xa, factor IXa, and thrombin based upon structural homology with other serine proteases. J. Biol. Chem. 257: 3875–3882.
Gregory, H. and Preston, B.M. 1977. The primary structure of human uro-gastrone. Int. J. Peptide and Protein Res. 9: 107–118.
Magnusson, S., Petersen, T.E., Sottrup-Jensen, L. and Claeys, H. 1975. Complete primary structure of prothrombin: Isolation, structure and reactivity of ten carboxylaled glutamic acid residues and regulation of prothrombin activation by thrombin, p. 123–149. In: Proteases and Biological Control, Reich, E., Rifkin, D.B., and Shaw, E., (eds.), Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, New York.
Magnusson, S., Sottrup-Jensen, L., Peterson, T.E., Dudek-Wojcie-chowska, G. and Claeys, H. 1976. Homologous “kringle” structures common to plasminogen and prothrombin. Substrate specificity of enzymes activating prothrombin and plasminogen, p. 203–238. In: Proteolysis and Physiological Regulation. Ribbons, D. W. and Brew, K., (eds.), Academic Press, New York.
Claeys, H., Sottrup-Jensen, L., Zajdel, M., Petersen, T.E. and Magnusson, S. 1976. Multiple gene duplication in the activation of plasminogen. Five regions of structural homology with the two internally homologous structures in prothrombin. FEBS Lett. 61: 20–24.
Sottrup-Jensen, L., Claeys, H., Zajdel, M., Peterson, T.E. and Magnusson, S. 1978. The primary structure of human plasminogen: Isolation of two lysine-binding fragments and one “mini”-plasminogen (MW, 38,000) by elastase-catalyzed specific limited proteolysis. Progress in chemical fibrinolysis and thrombolysis. Davidson, J.F., Samama, M. and Denoyers, P., (eds). 3: 191–209.
Gunzler, W.A., Steffens, G.J., Oetting, F., Kim, S.-M.A., Frankus, E. and Flohe, L. 1982. The primary structure of high molecular mass urokinase from human urine. The complete amino acid sequence of the A chain. Hoppe-Seyler's Z. Physiol. Chem. 363: 1155–1165.
Dayhoff, M.O. 1978. Atlas of Protein Sequence and Structure 5, Suppl. 3: 89.
Lerch, P.G., Rickli, E.E., Lergier, W. and Gillessen, D. 1980. Localization of individual lysine-binding regions in human plasminogen and investigations on their complex-forming properties. Eur. J. Biochem. 107: 7–13.
Heifetz, A., Keenan, R.W. and Elbein, A.D. 1979. Mechanism of action of tunicamycin on the UDP-Glc-NAc: dolychyl-phosphate Glc-NAc-1-phosphate transferase. Biochemistry 18: 2186–2192.
Ranby, M., Bergsdorf, N., Pohl, G. and Wallen, P. 1982. Isolation of two variants of naiive one-chain tissue plasminogen activator. FFBS Letters 146: 289–292.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vehar, G., Kohr, W., Bennett, W. et al. Characterization Studies on Human Melanoma Cell Tissue Plasminogen Activator. Nat Biotechnol 2, 1051–1057 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1284-1051
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1284-1051
This article is cited by
-
Secretion of Active Human Tissue Plasminogen Activator from the Filamentous Fungus Aspergillus Nidulans
Nature Biotechnology (1987)
-
Cloning and Expression of the Gene for Pro-urokinase in Escherichia coli
Bio/Technology (1985)