Abstract
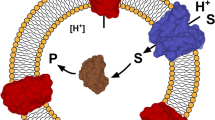
Organophosphorus hydrolase (OPH) was displayed and anchored onto the surface of Escherichia coli using an Lpp-OmpA fusion system. Production of the fusion proteins in membrane fractions was verified by immunoblotting with OmpA antisera. Inclusion of the organophosphorus hydrolase signal sequence was necessary for achieving enzymatic activity on the surface. More than 80% of the OPH activity was located on the cell surface as determined by protease accessibility experiments. Whole cells expressing OPH on the cell surface degraded parathion and paraoxon very effectively without any diffusional limitation, resulting in sevenfold higher rates of parathion degradation compared with whole cells with similar levels of intracellular OPH. Immobilization of these live biocatalysts onto solid supports could provide an attractive means for pesticide detoxification in place of immobilized enzymes, affording a reduced diffusional barrier.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Munnecke, D.M. 1980. Enzymatic detoxification of waste organophosphate pesticides. J. Agric. Food Chem. 28: 105–111.
Serdar, C.M. and Gibson, D.T. 1985. Enzymatic hydrolysis of organophosphates: Cloning and expression of a parathion hydrolase gene from Pseudomonas diminuta. Bio/Technology 3: 567–571.
Mulbry, W.W., Karns, J.S., Kearney, P.C., Nelson, J.O., McDaniel, C.S., and Wild, J.R. 1986. Identification of a plasmid-borne parathion hydrolase gene from Flavobacterium sp. by Southern hybridization with opdfrom Pseudomonas diminuta. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 51: 926–930.
Karns, J.S., Muldoon, M.T., Mulbury, W.W., Derbyshire, M.K., and Kearney, P.C. 1987. Use of microorganisms and microbial systems in the degradation of pesticides, pp. 156–170 in Biotechnology in agricultural chemistry. ACS symposium series. 334. LeBaron, H.M., Mumma, R.O., Honeycutt, R.C., and Duesing, J.H. (eds.) American Chemical Society, Washington, DC.
Attaway, H, Nelson, J.O., Baya, A.M., Voll, M.J., White, W.E., Grimes, D.J., and Colwell, R.R. 1987. Bacterial detoxification of diisopropyl fluorophosphate. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 53: 1685–1689.
Dumas, D.R., Durst, H.D., Landis, W.G., Raushel, F.M., and Wild, J.R. 1990. Inactivation of organophosphorus nerve agents by the phosphotriesterase from Pseudomonas diminuta. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 227: 155–159.
Dumas, D.P., Wild, J.R., and Raushel, F.M. 1989. Diisopropylfluorophosphate hydrolysis by a phosphotriesterase from Pseudomonas diminuta. Biotech. Appl. Biochem. 11: 235–243.
Munnecke, D.M. 1979. Hydrolysis of organophosphate insecticides by an immo-bilized-enzyme system. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 21: 2247–2261.
Caldwell, S.R. and Raushel, F.M. 1991. Detoxification of organophosphate pesticides using an immobilized phosphotriesterase from Pseudomonas diminuta. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 37: 103–109.
Leduc, M., Frehel, C., and van Heijenoort, J. 1985. Correlation between degradation and ultrastructure of peptidoglycan during autolysis of Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 161: 627–635.
Marvin, H.J.P., ter Beest, M.B.A., and Witholt, B. 1989. Release of outer membrane fragments from wild-type Escherichia coliand from several E. coli lipopolysaccharide mutants by EDTA and heat shock treatment. J. Bacteriol. 179: 5262–5267.
Francisco, J.A., Earhart, C.F., and Georgiou, G. 1992. Transport and anchoring of β-lactamase to the external surface of Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89: 2713–2717.
McDaniel, C.S., Harper, L.L., and Wild, J.R. 1988. Cloning and sequencing of a plasmid-borne gene (opd)encoding a phosphotriesterase. J. Bacteriol. 170: 306–2311.
Serdar, C.M.D.C., Murdock, D.C., and Rhode, M.F., 1989. Parathion hydrolase gene form Pseudomonas diminuta MG: Subcloning, complete nucleotide sequence, and expression of the mature portion of the enzyme in Escherichia coli. Bio/Technol. 7: 1151–1155.
Dumas, D.R., Caldwell, S.R., Wild, J.R., and Raushel, F.M. 1989. Purification and properties of the phosphotriesterase from Pseudomonas diminuta. J. Biol. Chem. 33: 19659–19665.
Phillips, J.P., Xin, J.H., Kirby, K., Milne, C.P., Krell, P., and Wild, J.R. 1990. Transfer and expression of an organophosphate insecticide-degrading gene from Pseudomonas in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87: 8155–8159.
Steiert, J.G., Pogell, B.M., Speedie, M.K., and Laredo, J. 1989. A gene coding for a membrane-bound hydrolase is expressed as a secreted soluble enzyme in Streptomyces lividans. Bio/Technology 7: 65–68.
Dave, K.I., Miller, C.E., and Wild, J.R. 1993. Characterization of organophosphorus hydrolases and the genetic manipulation of the phosphotriesterase from Pseudomonas diminuta. Chem.-Biol. Interactions 87: 55–68.
Francisco, J.A., Stathopoulos, C., Warren, R.A.J., Kilburn, D.G., and Georgiou, G. 1993. Specific adhesion and hydrolysis of cellulose by intact Escherichia coli expressing surface anchored cellulase or cellulose binding domains. Bio/Technology 11: 491–495.
Bowden, G.A., Paredes, A.M., and Georgiou, G. 1991. Structure and morphology of protein inclusion bodies in Escherichia coli. Bio/Technology 9: 725—730.
Bukau, B. 1993. Regulation of the Escherichia coli heat-shock response. Mol. Microbiol. 9: 671–680.
Mulbry, W.W. and Karns, J.S. 1989. Parathion hydrolase specified by the Flavobacterium opd gene: Relationship between the gene and protein. J. Bacteriol. 171: 6740–6746.
Stathopoulos, C., Georgiou, G., and Earhart, C.F. 1996. Characterization of Escherichia coliexpressing an Lpp'OmpA(46-159)-PhoA fusion protein localized in the outer membrane. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 45: 112–119.
Cordes, C., Meima, R., Twiest, B., Kazemier, B., Venema, G., van Dijl, J.M., and Bron, S. 1996. The expression of a plasmid-specified exported protein causes. structural plasmid instability in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 178: 5235–5242.
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E.F., Maniatis, T. 1989. Molecular cloning—a laboratory manual, 2nd edition. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY.
Currier, T.C. and Nester, E.W. 1976. Isolation of covalently closed circular DNA of high molecular weight from bacteria. Anal. Biochem. 76: 431–441.
Strauch, M.A., Spiegelman, G.B., Perego, M., Johnson, W.C., Burbulys, D., and Hoch, J.A. 1989. The transition state transcription regulator abrB of Bacillus subtilis is a DNA binding protein. EMBO J. 8: 1615–1621.
Laemmli, U.K. 1970. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227: 680–685.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Richins, R., Kaneva, I., Mulchandani, A. et al. Biodegradation of organophosphorus pesticides by surface-expressed organophosphorus hydrolase. Nat Biotechnol 15, 984–987 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1097-984
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1097-984
This article is cited by
-
Biomimetic single Al-OH site with high acetylcholinesterase-like activity and self-defense ability for neuroprotection
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Fusion proteins of organophosphorus hydrolase and pHluorin for a whole-cell biosensor for organophosphorus pesticide measurement
Analytical Sciences (2023)
-
Efficient Decontamination of Cationic Dyes from Synthetic Textile Wastewater Using Poly(acrylic acid) Composite Containing Amino Functionalized Biochar: A Mechanism Kinetic and Isotherm Study
Journal of Polymers and the Environment (2023)
-
Bioremediation of chlorpyrifos residues using some indigenous species of bacteria and fungi in wastewater
Environmental Monitoring and Assessment (2023)
-
An Enzymatic Reaction Modulated Fluorescence-on Omethoate Biosensor Based on Fe3O4@GO and Copper Nanoparticles
Journal of Analysis and Testing (2022)