Abstract
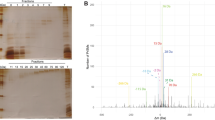
We have used electrospray mass spectrometry (ESMS) in combination with protein chemistry and genetics to delineate post-translational modifications in yeast of barley α-amylase 1 (AMY1), a 45 kD enzyme crucial for production of malt, an important starting material in the manufacture of beer and whisky. In addition to signal peptide processing these modifications are: (1) removal of C-terminal Arg-Ser by Kex1p, (2) glutathionylation of Cys95, (3) O-glycosylation, and (4) additional degradation of the C-terminus.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tekamp-Olson, P. and Valenzuela, P. 1990. Gene expression and engineering in yeast and other fungi. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 1: 28–35.
Hitzeman, R.A., Chen, C.Y., Dowbenko, D.J., Renz, M.E., Liu, C., Pai, R., Simpson, N.J., Kohr, W.J., Singh, A., Chisholm, V., Hamilton, R. and Chang, C.N. 1990. Use of heterologous and homologous signal sequences for secretion of heterologous proteins from yeast. Meth. Enzymol. 185: 421–440.
Olsen, O. and Thomsen, K.K. 1991. Improvement of bacterial β-glucanase thermostability by glycosylation. J. Gen. Microbiol. 137: 579–585.
Shuster, J.R. 1991. Gene expression in yeast: protein secretion. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2: 685–690.
Taniyama, Y., Seko, C. and Kikuchi, M. 1990. Secretion in yeast of mutant human lysozyme with and without glutathione bound to cysteine 95. J. Biol. Chem. 265: 16767–167710.
Søgaard, M., Olsen, F.L. and Svensson, B. 1991. C-terminal processing of barley α-amylase 1 in malt, aleurone protoplasts, and yeast. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88: 8140–8144.
George-Nascimento, C., Gyenes, A., Halloran, S.M., Merryweather, J., Valenzuela, P., Steimer, K.S., Masiarz, F.R. and Randolph, A. 1988. Characterization of recombinant human epidermal growth factor produced in yeast. Biochemistry 27: 797–802.
Vlasuk, G.P., Bencen, G.H., Scarborough, R.M., Tsai, P.-K., Whang, J.L., Maack, T., Camargo, M.J.F., Kirsher, S.W. and Abraham, J.A. 1986. Expression and secretion of biologically active human atrial natriuretic peptide in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 261: 4789–4796.
Riehl-Bellon, N., Carvallo, D., Acker, M., VanDorsselaer, A., Marquet, M., Loison, G., Lemoine, Y., Brown, S.W., Courtney, M. and Roitsch, C. 1989. Purification and biochemical characterization of recombinant hirudin produced by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochemistry 28: 2941–2949.
Roepstorff, P. and Richter, W.J. 1992. Status of, and development in, mass spectrometry of peptides and proteins. Int. J. Mass. Spectrom. Ion Proc. 118/119: 789–809.
Søgaard, M., Kadziola, A., Baser, R. and Svensson, B. 1993. Site-directed mutagenesis of His93, Asp 180, Glu205, His290 and Asp291 at the active site and Trp279 at the raw starch binding site in barley α-amylase. J. Biol. Chem. In press.
Søgaard, M. and Svensson, B. 1990. Expression of cDNAs encoding barley α-amylase 1 and 2 in yeast and characterization of the secreted proteins. Gene 94: 173–179.
Rogers, J.C. and Milliman, C. 1983. Isolation and sequence analysis of a barley α-amylase cDNA clone. J. Biol. Chem. 258: 8169–8174.
Matrix assisted laser desorption ionization mass spectrometric peptide mapping in combination with Edman degradation indicated an error in the published sequence of the clone E cDNA (ref. 13), Val (GTC) being found instead of Ala (GCC) at position 284 of the mature protein, as later confirmed by DNA sequencing (J.S.A., M.S., B.S. and PR., unpublished data).
Svensson, B., Mundy, J., Gibson, R.M. and Svendsen, I. 1985. Partial amino acid sequences of α-amylase isozymes from barley malt. Carlsberg Res. Commun. 50: 15–22.
Kukuruzinska, M.A., Bergh, M.L.E. and Jackson, B.J. 1987. Protein glycosylation in yeast. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 56: 915–944.
Tachibana, C. and Stevens, T.H. 1992. The yeast EUG1 gene encodes an endoplasmic reticulum protein that is functionally related to protein disulfide isomerase. Mol. Cell. Biol. 12: 4601–4611.
Dmochowska, A., Dignard, D., Henning, D., Thomas, D.Y. and Bussey, H. 1987. Yeast KEX1 gene encodes a putative protease with a carboxypeptidase B-like function involved in killer toxin and α-factor precursor processing. Cell 50: 573–584.
Rogers, J.C. 1985. Two barley a-amylase gene families are regulated differently in aleurone cells. J. Biol. Chem. 260: 3731–3738.
Hwang, C., Sinsker, A.J. and Lodish, H.F. 1992. Oxidized redox state of glutathione in the endoplasmic reticulum. Science 257: 517–523.
Braakman, I., Helenius, J. and Helenius, A. 1992. Role of ATP and disulfide bonds during protein folding in the endoplasmic reticulum. Nature 356: 260–262.
Braakman, I., Helenius, J. and Helenius, A. 1992. Manipulating disulfide bond formation in the endoplasmic reticulum. EMBO J. 11: 1717–1722.
Meister, A. and Anderson, M.E. 1983. Glutathione. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 52: 711–760.
Horton, R.M., Hunt, H.D., Ho, S.N., Pullen, J.K. and Pease, L.R. 1989. Engineering hybrid genes without the use of restriction enzymes: Gene splicing by overlap extension. Gene 77: 61–68.
Kuipers, O.P., Boot, H.J. and de Vos, W.M. 1991. Improved site-directed mutagenesis method using PCR. Nucl. Acid. Res. 19: 4558–4560.
Riddles, P.W., Blakeley, R.L. and Zerner, B. 1983. Reassessment of Ellmanns reagent. Meth. Enzymol. 91: 49–60.
Dubois, M., Gilles, K.A., Hamilton, J.K., Rebers, P.A. and Smith, F. 1956. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 28: 350–356.
Allan, M.H. and Vestal, M.L. 1992. Design and performance of a novel electrospray interface. J. Am. Soc. Mass. Spectrom. 13: 18–26.
Mandrup, S., Højrup, P., Kristiansen, K. and Knudsen, J. 1991. Gene synthesis, expression in Escerichia coli, purification and characterization of the recombinant bovine acyl-CoA-binding protein. Biochem J. 276: 817–823.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Søgaard, M., Andersen, J., Roepstorff, P. et al. Electrospray Mass Spectrometry Characterization of Post-Translational Modifications of Barley α-Amylase 1 Produced in Yeast. Nat Biotechnol 11, 1162–1165 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1093-1162
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1093-1162
This article is cited by
-
Plasticity in plastid redox networks: evolution of glutathione-dependent redox cascades and glutathionylation sites
BMC Plant Biology (2021)
-
Protein engineering in the ?-amylase family: catalytic mechanism, substrate specificity, and stability
Plant Molecular Biology (1994)