Abstract
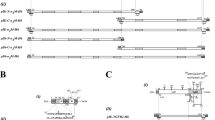
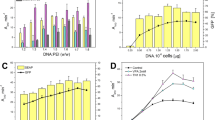
We have developed a new gene expression and secretion system for Streptomyces lividans and used it to produce soluble forms of a human T-cell receptor CD4 at levels greater than 300 mg/l. The system uses the transcription, translation and secretion signals of the serine protease inhibitor gene STI-II which is naturally produced by S. longisporus. Using these signals, soluble derivatives of CD4 were secreted directly into the culture supernatant as correctly processed soluble, biologically active proteins. High level expression of the CD4 proteins depended on the transcription initiation signal, the amino acid sequence surrounding the signal peptide cleavage site and temporally controlled protease activities. We discuss these results in the context of the potential of this system for producing other eukaryotic proteins in Streptomyces.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brawner, M., Poste, G., Rosenberg, M. and Westpheling, J. 1991. Streptomyces: a host for heterologous gene expression. Current Opinion in Biotechnology 2: 674–681.
Engels, J.W. and Koller, K.-P. 1992. Gene expression and secretion of eukaryotic foreign proteins in Streptomyces, p. 31–53. In: Transgenesis. Murray, J. A. H. (Ed.). John Wiley & Sons Ltd, NY.
Gay, D., Maddon, P., Sekely, R., Talle, M.A., Godfrey, M., Long, E., Goldstein, G., Chess, L., Axel, R., Kappler, J. and Marrack, J. 1987. Functional interaction between human T-cell protein CD4 and the major histocom-patibility complex HLADR antigen. Nature 328: 626–629.
Sleckman, B.P., Peterson, A., Jones, W.K., Foran, J.A., Greenstein, J.L., Seed, B. and Burakoff, S.J. 1987. Expression and function of CD4 in a murine T-cell hybridoma. Nature 328: 351–353.
Doyle, C. and Strominger, J.L. 1987. Interaction between CD4 and class II MHC molecules mediates cell adhesion. Nature 330: 256–259.
Arthos, J., Deen, K.C., Chaikin, M.A., Fornwald, J.A., Sathe, G., Sattentau, Q.J., Clapham, P.R., Weiss, R.A., McDougal, J.S., Pietropaolo, C., Axel, R., Truneh, A., Maddon, P.J. and Sweet, R.W. 1989. Identification of the residues in human CD4 critical for the binding of HIV. Cell 57: 69–181
Garlick, R.L., Kirschner, R.J., Eckenrade, F.M., Tarpley, W.G. and Tomich, C.-S.C. 1990. Escherchia coli expression, purification and biological activity of a truncated soluble CD4. AIDS Res. and Hum. Retroviruses 6: 65–79.
Smith, D.H., Byrn, R.A., Marsters, S.A., Gregory, T., Groopman, J.E. and Capon, D.J. 1987. Blocking of HIV-1 infectivity by a soluble, secreted form of the CD4 antigen. Science 238: 1704–1707.
Fisher, R.A., Bertonis, J.M., Meier, W., Johnson, V.A., Costopoulos, D.S., Liu, T., Tizard, R., Walker, B.D., Hirsch, M.S., Schooley, R.T. and Flavell, R.A. 1988. HIV infection is blocked in vitro by recombinant soluble CD4. Nature 331: 76–78.
Hussey, R.E., Richardson, N.E., Kowalski, M., Brown, N.R., Chang, H.-C., Siliciano, R.R., Dorman, T., Walker, B., Sodroski, J. and Reinherz, E.L. 1988. A soluble CD4 protein selectively inhibits HIV replication and syncytium formation. Nature 331: 78–81.
Deen, K.C., McDougal, J.S., Inacker, R., Folena-Wasserman, G., Arthos, J., Rosenberg, J., Maddon, P.J., Axel, R. and Sweet, R.W. 1988. A soluble form of CD4 (T4) protein inhibits AIDS virus infection. Nature 331: 82–84.
Strickler, J.E., Berka, T.R., Gorniak, J., Rosenberg, J., Keys, R., Rowland, J.J., Rosenberg, M. and Taylor, D.P. 1992. Two novel Slreptomyces protein protease inhibitors. J. Biol. Chem. 267: 3236–3241.
Brawner, M., Fornwald, J., Rosenberg, M., Poste, G. and Westpheling, J. 1990. Heterologous gene expression in Streptomyces, p. 85–93. In: Proceedings of the 6th International Symposium on Genetics of Industrial Microorganisms. Heslot, H., Davies, J., Florent, J., Bobichon, L., Durand, G. and Penasse, L. (Eds.). Société Francaise de Microbiologie, Strasbourg, France.
Li, P., Beckwith, J. and Inouye, H. 1988. Alteration of the amino terminus of the mature sequence of a periplasmic protein can severely affect protein export in Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85: 7685–7689.
Summers, R.G., Harris, C.R. and Knowles, J.R. 1989. A conservative amino acid substitution, argimne for lysme, abolishes export of a hybrid protein in Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 264: 20082–20088.
Liss, L.R., Johnson, B.L. and Oliver, D.B. 1985. Export defect adjacent to the processing site of staphylococcal nuclease is suppressed by a prlA mutation. J. Bacteriol. 164: 925–928.
Yamane, K. and Mizushima, S. 1988. Introduction of basic amino acid residues after the signal peptide inhibits protein translocation across the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 263: 19690–19696.
Eckhardt, T., Strickler, J., Gorniak, L., Burnett, W.V. and Fare, L.J. 1987. Characterization of the promoter, signal sequence and amino acid terminus of a secreted β-galactosidase from Streptomyces lividans. J. Bacteriol. 169: 4249–4256.
Classon, B.J., Tsagaratos, J., Kirszbaum, L., Maddox, J., Mackay, C.R., Brandon, M., McKenzie, I.F.C. and Walker, I.D. 1986. The L3T4 antigen in mouse and the sheep equivalent are immunoglobulin like. Immunogenetics 23: 129–132.
Peterson, A. and Seed, B. 1988. Genetic analysis of monoclonal antibody and HIV binding sites on the human lymphocyte antigen CD4. Cell 54: 65–72.
Sattentau, Q.J., Dalgleish, A.G., Weiss, R.A. and Beverly, P.C.L. 1986. Epitopes of the CD4 antigen and HIV infection. Science 234: 1120–1123.
Dalgleish, A.G., Beverly, P.C.L., Clapham, P.R., Crawford, D.H., Greaves, M.F. and Weiss, R.A. 1984. The CD4 (T4) antigen is an essential component of the receptor for the AIDS retrovirus. Nature 312: 763–766.
Klatzman, D., Champagne, E., Chamaret, S., Gruest, J., Guetard, P., Hercend, T., Gluckman, J.-C. and Montagnier, L. 1984. T-lymphocyte T4 molecule behaves as the receptor for human retrovirus LAV. Nature 312: 767–768.
Maddon, P.J., Dalgleish, A.G., McDougal, J.S., Clapham, P.R., Weiss, R.A. and Axel, R. 1986. The T4 gene encodes the AIDS virus receptor and is expressed in the immune system and the brain. Cell 47: 333–348.
McDougal, J.S., Kennedy, M.S., Sligh, J.M., Cort, S.P., Mawle, A. and Nicholson, J.K.A. 1986. Binding of HTLV-III/LAV to T4+ T cells by a complex of the 110K viral protein and the T4 molecule. Science 231: 382–385.
Watt, R.A., Shatzman, A.R. and Rosenberg, M. 1985. Expression and characterization of the human c-myc DNA binding protein. Mol. Cell. Biol. 5: 448–456.
Buell, G., Schulz, M.-F., Selzer, G., Chollet, A., Movva, N.R., Semon, D., Escanez, S. and Kawashima, E. 1985. Optimizing the expression in E. coli of a synthetic gene encoding somatomedin-C (IGF-I). Nuc. Acids. Res. 13: 1923–1938.
Sloma, A., Rufo, G.A., Theriault, K.A., Dwyer, M., Wilson, S.W. and Pero, J. 1991. Cloning and chracterization of the gene for an additional extracellular serine protease of Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 173: 6889–6895.
Staunton, D.E., Marlin, S.D., Stratowa, C., Dustin, M.L. and Springer, T.A. 1988. Primary structure of ICAM-1 demonstrates interaction between members of the immunoglobulin and integrin supergene families. Cell 52: 925–933.
Bevilacqua, M.P., Stengelin, S., Gimbrone, M.A. and Seed, B. 1989. Endotheial leukocyte adhesion molecule: an inducible receptor for neutrophils related to complement regulatory proteins and lectins. Science 243: 1160–1165.
Maniatis, T., Fritsch, E.F. and Sambrook, J. 1982. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY.
Yanisch-Perron, C., Vieira, J. and Messing, J. 1985. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene 33: 103–119.
Katz, E., Thompson, C.J. and Hopwood, D.A. 1983. Cloning and expression of the tyrosinase gene from Streptomyces antibioticus in Streptomyces lividans. J. Gen. Microbiol. 129: 2703–2714.
Kieser, T., Hopwood, D.A., Wright, H.M. and Thompson, C.J. 1982. pIJ101, a multi-copy broad host-range Streptomyces plasmid:functional analysis and development of DNA cloning vectors. Mol. Gen. Genet. 185: 223–238.
Kunkel, T.A. 1985. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82: 488–492.
Littman, D.R., Maddon, P.J. and Axel, R. 1988. Corrected CD4 sequence. Cell 55: 541.
Bibb, M.J., Ward, J.M., Kieser, T., Cohen, S.N. and Hopwood, D.A. 1981. Excision of chromosomal DNA sequences from Streptomyces coeticolor forms a novel family of plasmids detectable in Streptomyces lividans. Mol. Gen. Genet. 184: 230–240.
Thompson, C.J., Ward, J.M. and Hopwood, D.A. 1982. Cloning of antibiotic resistance and nutritional genes in streptomycetes. J. Bacteriol. 151: 668–677.
Laemmli, U.K. 1970. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227: 680–685.
Towbin, H., Staehelin, T. and Gordon, J. 1979. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets:procedure and some applications. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 76: 4350–4354.
Brawner, M.E., Auerbach, J.I., Fornwald, J.A., Rosenberg, M. and Taylor, D.P. 1985. Characterization of Streptomyces promoter sequences using the Escherichia coli galactokinase gene. Gene 40: 191–201.
Matsudaira, P. 1987. Sequences from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 262: 10035–10038.
Thompson, C.J., Ward, J.M. and Hopwood, D.A. 1980. DNA cloning in Streptomyces: resistance genes from antibiotic-producing species. Nature 286: 525–527.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fornwald, J., Donovan, M., Gerber, R. et al. Soluble Forms of the Human T Cell Receptor CD4 are Efficiently Expressed by Streptomyces lividans. Nat Biotechnol 11, 1031–1036 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0993-1031
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0993-1031
This article is cited by
-
Metabolic and evolutionary insights into the closely-related species Streptomyces coelicolor and Streptomyces lividans deduced from high-resolution comparative genomic hybridization
BMC Genomics (2010)
-
Comparative genomic hybridizations reveal absence of large Streptomyces coelicolor genomic islands in Streptomyces lividans
BMC Genomics (2007)
-
Actinomycetes as host cells for production of recombinant proteins
Microbial Cell Factories (2005)
-
Codon adjustment to maximise heterologous gene expression inStreptomyces lividans can lead to decreased mRNA stability and protein yield
Molecular and General Genetics MGG (1996)