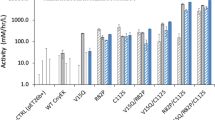
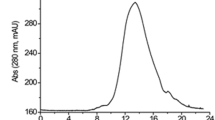
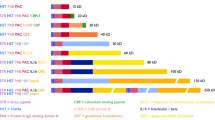
Abstract
Using different types of efficient Escherichia coli expression systems, we have been able to obtain levels of human tissue-type plasminogen activator (tPA) reaching at least five percent of total bacterial proteins. The natural precursor of tPA (pre-tPA) expressed in E. coli accumulates, most probably in the cytoplasm, partly due to the low efficiency of the tPA leader sequence as a signal for secretion into the E. coli periplasm. We also expressed mature tPA in an insoluble, aggregated form and treatments were developed that permitted significant renaturation of this protein from the lysis pellet. Further characterization and purification of the rena-tured tPA polypeptide strongly suggest that a fully active enzyme, very similar to the eukaryotic product can be obtained, despite the total lack of glycosylation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vehar, G.A., Spellman, M.W., Keyt, B.A., Ferguson, C.K., Keck, R.G., Chloupek, R.C., Harris, R., Bennett, W.F., Builder, S.E. and Hancock, W.S. 1986. Characterization studies of human tissue-type plasminogen activator produced by recombinant DNA technology. Cold Spring Harbor Symp. Quant. Biol., 5:551–562.
Wallén, P., Ranby, M., Begsdorf, N. and Kok, P. 1981. Purification and characterization of tissue plasminogen activator: on the occurence of two different forms and their enzymatic properties. Prog. Chem. Fibrinolysis Thrombolysis 5:16–23.
Astrup, T. 1978. Fibrinolysis: an overview. Prog. Fibnnolys. 3:1–57.
Pennica, D., Holmes, W.E., Kohr, W.J., Harkins, R.N., Vehar, G.A., Ward, C.A., Bennet, W.F., Yelverton, E., Seeburg, P.H., Heyneker, H.L., Godal, D.V. and Collen, D. 1983. Cloning and expression of human tissue-type plasminogen activator in E. coli . Nature 301:214–221.
Ny, T., Elgh, F. and Lund, B. 1984. The structure of the human tissue-type plasminogen activator gene: correlation of intron and exon structures to functional and structural domains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 81:5355–5359.
Pohl, G., Källström, M., Bergsdorf, N., Wallén, P. and Jörnvall, H. 1984. Tissue plasminogen activator: peptide analyses confirm an indirectly derived amino acid sequence, identify the active site serine residue, establish glycosylation sites and localize variant differences. Biochemistry 23:3701–3707.
Kaufman, R.F., Wasley, L.C., Spiliotes, A.J., Gossels, S.D., Latt, S.A., Larsen, G.R. and Kay, R.M. 1985. Coamplification and coexpression of human tissue-type plasminogen activator and murine dihydrofolate reductase sequences in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 5:1750–1759.
Dodd, L., Jalalpour, S., Southwick, W., Newsome, P., Browne, M.J., and Robinson, J.H. 1986. Large scale, rapid purification of recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator. FEBS Lett. 209:13–17.
Van Zonneveld, A.J., Veerman, H. and Pannekoek, H. 1986. Autonomous functions of structural domains on human tissue-type plasminogen activator. Proc Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 83:4670–4674.
Holmes, W.E., Pennica, D., Blaber, M., Rey, M.W., Günzler, W.A., Steffens, G.J. and Heyneker, H.L. 1985. Cloning and expression of the gene for pro-urokmase in Escherichia coli . Bio/Technology 3:923–929.
Winkler, M.E. and Blaber, M. 1986. Purification and characterization of recombinant single-chain urokinase produced in Escherichia coli . Biochemistry 25:4041–4045.
Harris, T.J.R., Patel, T., Marston, F.A.O., Little, S. and Emtage, J.S., Opdenakker, G., Volckaert, G., Rombauts, W., Billiau, A. and De Somer, P. 1986. Cloning of cDNA coding for human tissue-type plasminogen activator and its expression in Escherichia coli . Mol. Biol. Med. 3:279–292.
Jörnvall, H., Pohl, G., Begsdorf, N. and Wallén, P. 1983. Differential proteolysis and evidence for a residue exchange in tissue plasminogen activator suggest possible association between two types of protein microheterogeneity. FEBS Lett. 156:47–50.
Wulff, D.L. and Rosenberg, M. 1983. Establishment of repressor synthesis, p. 53–74. In: Lambda II. Cold Spring Harbor Monograph Series.
Reyes, O. 1982. Characterization of the recombination function of coliphage Φ 80 as analogous to the recF recombinative pathway of Escherichia coli . Virology 123:357–371.
Phillips, T.A., VanBogelen, R.A., Neidhardt, F.C. 1984. lon gene product of Escherichia coli is a heat-shock protein. J. Bacteriol. 159:283–287.
Dunn, J.J. and Studier, F.W. 1980. The transcription termination site at the end of the early region of bacteriophage T7 DNA. Nucleic Acid Res. 8:2119–2132.
Matteucci, M. and Lipetsky, H. 1986. Alkaline phosphatase fusions: a tag to identify mutations that result in increased expression of secreted human growth hormone from E. coli . Bio/Technology 4:51–55.
Lavina, M., Pugsley, A.P. and Moreno, F. 1986. Identification, mapping, cloning and characterization of a gene (Sbma) required for microcin B17 action on Escherichia coli K12. J. Gen. Microbiol. 132:1685–1693.
Verheijen, J.H., Mullaart, E., Chang, G.T.G., Kluft, C. and Wijngaards, G. 1982. A simple sensitive spectrophotometric assay for extrinsic (tissue-type) plasminogen activator applicable to measurements in plasma. Thromb. Haemostasis 48:266–269.
Ranby, M. and Wallén, P. 1985. Enzymatic properties of tissue-type plasminogen activator. In: Contemporary Issues in Haemostasis and Thrombosis: Thrombolysis. Collen D., Lijnen, H. R., and Verstraete, M. (Eds.). Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, UK.
Ben-Bassat, A. and Bauer, K. 1987. Amino-terminal processing of proteins. Nature 326:315.
Latta, M., Knapp, M., Sarmientos, P., Bréfort, G., Becquart, J., Guerrier, L., Jung, G. and Mayaux, J.F. 1987. Synthesis and purification of mature human serum albumin from E. coli . Bio/Technology 5:1309–1314.
Rijken, D.C., Emeis, J.J. and Gerwig, G.J. 1985. On the composition and function of the carbohydrate moiety of plasminogen activator from human melanoma cells. Thromb. Haemostasis 54:788–791.
Gray, G.L., Baldridge, J.S., McKeown, K.S., Hayneker, H.L., and Nan Chang, C. 1985. Periplasmic production of correctly processed human growth hormone in E. coli: Natural and bacterial signal sequences are interchangeable. Gene 39:247–254.
Wickner, T.W. and Lodish, H.F. 1985. Multiple mechanisms of protein insertion into and across membranes. Science 230:400–407.
Gill, G.S., Zaworski, P.G., Marotti, K.R. and Rehberg, E.F. 1988. Secretion of human tissue-type plasminogen activator (tPA) by strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: initial characterization of the secreted material. Yeast 4 (Special issue): 148.
Upshall, A., Kumar, A.A., Bailey, M.C., Parker, M.D., Favreau, M.A., Lewison, K.P., Joseph, M.L., Maraganore, J.M. and MacKnight, G.L. 1987. Secretion of active human tissue plasminogen activator from the filamentous fungus Aspergillus nidulans . Bio/Technology 5:1301–1304.
Genetica. 1986. Microbiological preparation of human tissue plasminogen activator and conversion of the enzyme into its active form. EP 0 236 209 (European Patent Application).
Messing, J. 1983. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods in Enzymol. 101:20–79.
Hoffman, C.S. and Wright, A. 1985. Fusions of secreted proteins to alkaline phosphatase: an approach for studying protein secretion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82:5107–5111.
Yanish-Perron, C., Vieira, J. and Messing, J. 1985. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequence of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene 33:103–119.
Gunsalus, R.P. and Yanofsky, C. 1980. Nucleotide sequence and expression of Escherihia coli trpR, the structural gene for the trp aporepressor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 77:7117–7121.
Neidhardt, F.C., Bloch, P.L. and Smith, D.F. 1974. Culture medium for enterobacteria. J. Bacteriol. 119:736–747.
Brickman, E. and Beckwith, J. 1975. Analysis of the regulation of Escherichia coli alkaline phosphatase synthesis using deletions and Φ80 transducing phages. J. Mol. Biol. 96:307–316.
Koshland, D. and Botstein, D. 1980. Secretion of the beta-lactamase requires the carboxy end of the protein. Cell 20:749–760.
Miller, J.H. 1972. Experiments in Molecular Genetics. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, NY.
Astrup, J. and Mullertz, S. 1952. The fibrin plate method for estimating fibrinolytic activity . Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 40:346–351.
Fletcher, A.P. 1954. The measurements of components of the plasminogen-plasmin system in biological fluids. Biochem. J. 56:677–682.
Philo, R.D. and Gaffney, P.J. 1981. Plasmin potency estimates: influence of the substrate used in the assay. Thromb. Haemostasis 45:107–109.
Bradford, M.M. 1972. A rapid and sensitive assay for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72:248–254.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sarmientos, P., Duchesne, M., Denèfle, P. et al. Synthesis and Purification of Active Human Tissue Plasminogen Activator From Escherichia coli. Nat Biotechnol 7, 495–501 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0589-495
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0589-495