Abstract
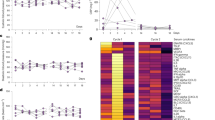
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin disorder that affects approximately 2–3% of the population worldwide and has severe effects on patients’ physical and psychological well-being1,2,3. The discovery that psoriasis is an immune-mediated disease has led to more targeted, effective therapies; recent advances have focused on the interleukin (IL)-12/23p40 subunit shared by IL-12 and IL-23. Evidence suggests that specific inhibition of IL-23 would result in improvement in psoriasis. Here we evaluate tildrakizumab, a monoclonal antibody that targets the IL-23p19 subunit, in a three-part, randomized, placebo-controlled, sequential, rising multiple-dose phase I study in patients with moderate-to-severe psoriasis to provide clinical proof that specific targeting of IL-23p19 results in symptomatic improvement of disease severity in human subjects. A 75% reduction in the psoriasis area and severity index (PASI) score (PASI75) was achieved by all subjects in parts 1 and 3 (pooled) in the 3 and 10 mg kg−1 groups by day 196. In part 2, 10 out of 15 subjects in the 3 mg kg−1 group and 13 out of 14 subjects in the 10 mg kg−1 group achieved a PASI75 by day 112. Tildrakizumab demonstrated important clinical improvement in moderate-to-severe psoriasis patients as demonstrated by improvements in PASI scores and histological samples.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
13 May 2015
A second affiliation was added for author T.K. and affiliations were renumbered accordingly.
References
Schön, M. P. & Boehncke, W. H. Psoriasis. N. Engl. J. Med. 352, 1899–1912 (2005)
Lowes, M. A., Bowcock, A. M. & Krueger, J. G. Pathogenesis and therapy of psoriasis. Nature 445, 866–873 (2007)
Krueger, G. et al. The impact of psoriasis on quality of life: results of a 1998 National Psoriasis Foundation patient-membership survey. Arch. Dermatol. 137, 280–284 (2001)
Leonardi, C. L. et al. Efficacy and safety of ustekinumab, a human interleukin-12/23 monoclonal antibody, in patients with psoriasis: 76-week results from a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (PHOENIX 1). Lancet 371, 1665–1674 (2008)
Papp, K. A. et al. Efficacy and safety of ustekinumab, a human interleukin-12/23 monoclonal antibody, in patients with psoriasis: 52-week results from a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (PHOENIX 2). Lancet 371, 1675–1684 (2008)
Toichi, E. et al. An anti-IL-12p40 antibody down-regulates type 1 cytokines, chemokines, and IL-12/IL-23 in psoriasis. J. Immunol. 177, 4917–4926 (2006)
Oppmann, B. et al. Novel p19 protein engages IL-12p40 to form a cytokine, IL-23, with biological activities similar as well as distinct from IL-12. Immunity 13, 715–725 (2000)
Lee, E. et al. Increased expression of interleukin 23 p19 and p40 in lesional skin of patients with psoriasis vulgaris. J. Exp. Med. 199, 125–130 (2004)
Chan, J. R. et al. IL-23 stimulates epidermal hyperplasia via TNF and IL-20R2-dependent mechanisms with implications for psoriasis pathogenesis. J. Exp. Med. 203, 2577–2587 (2006)
Lowes, M. A., Suárez-Fariñas, M. & Krueger, J. G. Immunology of psoriasis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 32, 227–255 (2014)
Villanova, F. et al. Characterization of innate lymphoid cells in human skin and blood demonstrates increase of NKp44+ ILC3 in psoriasis. J. Invest. Dermatol. 134, 984–991 (2014)
Keijsers, R. R. et al. Balance of Treg vs. T-helper cells in the transition from symptomless to lesional psoriatic skin. Br. J. Dermatol. 168, 1294–1302 (2013)
Krueger, J. G. et al. IL-17A is essential for cell activation and inflammatory gene circuits in subjects with psoriasis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 130, 145–154 (2012)
Hueber, W. et al. Effects of AIN457, a fully human antibody to interleukin-17A, on psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, and uveitis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2, 52ra72 (2010)
Ngiow, S. F., Teng, M. W. & Smyth, M. J. A balance of interleukin-12 and -23 in cancer. Trends Immunol. 34, 548–555 (2013)
Bustamante, J., Picard, C., Boisson-Dupuis, S., Abel, L. & Casanova, J. L. Genetic lessons learned from X-linked Mendelian susceptibility to mycobacterial diseases. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1246, 92–101 (2011)
Papp, K. A. et al. Long-term safety of ustekinumab in patients with moderate-to-severe psoriasis: final results from 5 years of follow-up. Br. J. Dermatol. 168, 844–854 (2013)
United States Food and Drug Administration. Guidance for Industry; Assay Development for Immunogenicity Testing of Therapeutic Proteins. Available at http://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/Guidances/UCM192750.pdf (2009)
Torzicky, M. et al. Platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 (PECAM-1/CD31) and CD99 are critical in lymphatic transmigration of human dendritic cells. J. Invest. Dermatol. 132, 1149–1157 (2012)
Trozak, D. J. Histologic grading system for psoriasis vulgaris. Int. J. Dermatol. 33, 380–381 (1994)
Wolk, K. et al. The Th17 cytokine IL-22 induces IL-20 production in keratinocytes: a novel immunological cascade with potential relevance in psoriasis. Eur. J. Immunol. 39, 3570–3581 (2009)
Sa, S. M. et al. The effects of IL-20 subfamily cytokines on reconstituted human epidermis suggest potential roles in cutaneous innate defense and pathogenic adaptive immunity in psoriasis. J. Immunol. 178, 2229–2240 (2007)
Guttman-Yassky, E. et al. Low expression of the IL-23/Th17 pathway in atopic dermatitis compared to psoriasis. J. Immunol. 181, 7420–7427 (2008)
Liang, S. C. et al. Interleukin (IL)-22 and IL-17 are coexpressed by Th17 cells and cooperatively enhance expression of antimicrobial peptides. J. Exp. Med. 203, 2271–2279 (2006)
Homey, B. et al. Up-regulation of macrophage inflammatory protein-3 α/CCL20 and CC chemokine receptor 6 in psoriasis. J. Immunol. 164, 6621–6632 (2000)
Lew, W., Lee, E. & Krueger, J. G. Psoriasis genomics: analysis of proinflammatory (type 1) gene expression in large plaque (Western) and small plaque (Asian) psoriasis vulgaris. Br. J. Dermatol. 150, 668–676 (2004)
Fredriksson, T. & Pettersson, U. Severe psoriasiseoral therapy with a new retinoid. Dermatologica 157, 238–244 (1978)
Langley, R. G. Effective and sustainable biologic treatment of psoriasis: what can we learn from new clinical data? J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 26 (suppl. 2). 21–29 (2012)
Stary, G., Bangert, C., Stingl, G. & Kopp, T. Dendritic cells in atopic dermatitis: expression of FcepsilonRI on two distinct inflammation-associated subsets. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 138, 278–290 (2005)
Ackerman, A. B., Boer, A., Bennin, B. & Gottlieb, G. J. Histologic Diagnosis of Inflammatory Skin Diseases: an Algorithmic Method Based on Pattern Analysis 3rd edn (Ardor Scribendi, 2005)
Bangert, C., Friedl, J., Stary, G., Stingl, G. & Kopp, T. Immunopathologic features of allergic contact dermatitis in humans: participation of plasmacytoid dendritic cells in the pathogenesis of the disease? J. Invest. Dermatol. 121, 1409–1418 (2003)
Bangert, C. et al. Clinical and cytological effects of pimecrolimus cream 1% after resolution of active atopic dermatitis lesions by topical corticosteroids: a randomized controlled trial. Dermatology 222, 36–48 (2011)
Skvara, H. et al. The PKC inhibitor AEB071 may be a therapeutic option for psoriasis. J. Clin. Invest. 118, 3151–3159 (2008)
Acknowledgements
The authors thank E. Marcantonio (Merck & Co., Inc.) for his supervision of research and review of this manuscript and J. Pawlowski (Merck & Co., Inc) for editorial and administrative assistance with this manuscript. This study was funded by Merck & Co., Inc.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors provided substantive suggestions and critically reviewed the manuscript. T.K., E.R., C.B., A.M., E.P.B. and S.K. wrote sections of the initial draft. T.K., E.R., C.B., E.P.B., H.K., T.K.M., A.S.Z., W.M.B., X.S.H., D.M. and S.K. collected/assembled data and/or performed or supervised analyses. T.K., A.H., D.X. and X.S.H. were involved in the design and planning of the study.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
T.K. and H.K. and E.R. received research support from Merck & Co., Inc. E.R. received travel support from Merck & Co., Inc., and speaker’s fees, travel support, or served on advisory boards for AbbVie, Novartis, Pfizer, Janssen and Amgen. C.B. received travel support from Merck. C.Z. has served as a scientific consultant for Abbvie, Pfizer, Janssen-Cilag, Merck & Co., Inc., Eli Lilly, Takeda and Novartis and clinical study investigator for AbbVie, Amgen, Eli Lilly, Merck & Co., Inc., Takeda and Novartis. T.M. is an employee of Orlando Clinical Research Center, which was contracted by Merck to conduct the trial. E.P.B., A.H., W.M.B., T.K.M., D.X., X.S.H., A.M., A.S.Z., D.M., F.V.A. and S.K. are current or former employees of Merck & Co., Inc, and may own Merck stock. C.B. and E.G. have no competing interests.
Extended data figures and tables
Extended Data Figure 1 Tildrakizumab binds to IL-23, but not IL-12.
a, b, Biacore sensorgrams showing the 37 °C binding kinetics of human IL-23 (a) and human IL-12 (b) to immobilized tildrakizumab as a threefold dilution series from 0.091 to 22.2 nM. The association phase was measured for 220 s followed by a dissociation phase measurement for 1,800 s. The affinity of tildrakizumab for IL-23 is ∼300 pM.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kopp, T., Riedl, E., Bangert, C. et al. Clinical improvement in psoriasis with specific targeting of interleukin-23. Nature 521, 222–226 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14175
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14175
This article is cited by
-
Mirikizumab Pharmacokinetics in Patients with Moderately to Severely Active Ulcerative Colitis: Results from Phase III LUCENT Studies
Clinical Pharmacokinetics (2023)
-
Variants of beta-glucan polysaccharides downregulate autoimmune inflammation
Communications Biology (2022)
-
Characterization of chromatin accessibility in psoriasis
Frontiers of Medicine (2022)
-
Update on Tildrakizumab for Psoriasis
Current Dermatology Reports (2019)
-
Patient and Physician Preferences for Therapy Characteristics for Psoriasis: A Discrete Choice Experiment in Japan
PharmacoEconomics - Open (2019)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.