Abstract
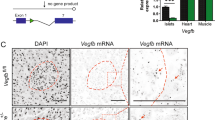
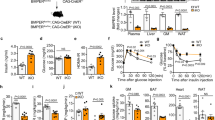
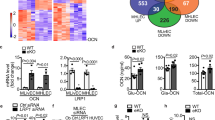
The prevalence of type 2 diabetes is rapidly increasing, with severe socioeconomic impacts1,2. Excess lipid deposition in peripheral tissues impairs insulin sensitivity and glucose uptake, and has been proposed to contribute to the pathology of type 2 diabetes3,4,5. However, few treatment options exist that directly target ectopic lipid accumulation6. Recently it was found that vascular endothelial growth factor B (VEGF-B) controls endothelial uptake and transport of fatty acids in heart and skeletal muscle7. Here we show that decreased VEGF-B signalling in rodent models of type 2 diabetes restores insulin sensitivity and improves glucose tolerance. Genetic deletion of Vegfb in diabetic db/db mice prevented ectopic lipid deposition, increased muscle glucose uptake and maintained normoglycaemia. Pharmacological inhibition of VEGF-B signalling by antibody administration to db/db mice enhanced glucose tolerance, preserved pancreatic islet architecture, improved β-cell function and ameliorated dyslipidaemia, key elements of type 2 diabetes and the metabolic syndrome. The potential use of VEGF-B neutralization in type 2 diabetes was further elucidated in rats fed a high-fat diet, in which it normalized insulin sensitivity and increased glucose uptake in skeletal muscle and heart. Our results demonstrate that the vascular endothelium can function as an efficient barrier to excess muscle lipid uptake even under conditions of severe obesity and type 2 diabetes, and that this barrier can be maintained by inhibition of VEGF-B signalling. We propose VEGF-B antagonism as a novel pharmacological approach for type 2 diabetes, targeting the lipid-transport properties of the endothelium to improve muscle insulin sensitivity and glucose disposal.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
World Health Organization . World Health Organization Diabetes Fact sheet no. 312. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs312/en/ (2011)
Diabetes Prevention Program (DPP) Research Group The Diabetes Prevention Program (DPP): description of lifestyle intervention. Diabetes Care 25, 2165–2171 (2002)
Perseghin, G. et al. Intramyocellular triglyceride content is a determinant of in vivo insulin resistance in humans: a 1H-13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy assessment in offspring of type 2 diabetic parents. Diabetes 48, 1600–1606 (1999)
Samuel, V. T., Petersen, K. F. & Shulman, G. I. Lipid-induced insulin resistance: unravelling the mechanism. Lancet 375, 2267–2277 (2010)
Unger, R. H. Lipotoxic diseases. Annu. Rev. Med. 53, 319–336 (2002)
Stumvoll, M., Goldstein, B. J. & van Haeften, T. W. Type 2 diabetes: principles of pathogenesis and therapy. Lancet 365, 1333–1346 (2005)
Hagberg, C. E. et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor B controls endothelial fatty acid uptake. Nature 464, 917–921 (2010)
Zimmet, P., Alberti, K. G. & Shaw, J. Global and societal implications of the diabetes epidemic. Nature 414, 782–787 (2001)
Schmitz-Peiffer, C. et al. Alterations in the expression and cellular localization of protein kinase C isozymes epsilon and theta are associated with insulin resistance in skeletal muscle of the high-fat-fed rat. Diabetes 46, 169–178 (1997)
Schmitz-Peiffer, C. Targeting ceramide synthesis to reverse insulin resistance. Diabetes 59, 2351–2353 (2010)
Boström, P. et al. SNARE proteins mediate fusion between cytosolic lipid droplets and are implicated in insulin sensitivity. Nature Cell Biol. 9, 1286–1293 (2007)
Bostrom, P. et al. The SNARE protein SNAP23 and the SNARE-interacting protein Munc18c in human skeletal muscle are implicated in insulin resistance/type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 59, 1870–1878 (2010)
Muoio, D. M. Metabolism and vascular fatty acid transport. N. Engl. J. Med. 363, 291–293 (2010)
Lahteenvuo, J. E. et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor-B induces myocardium-specific angiogenesis and arteriogenesis via vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1- and neuropilin receptor-1-dependent mechanisms. Circulation 119, 845–856 (2009)
Olofsson, B. et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor B, a novel growth factor for endothelial cells. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 93, 2576–2581 (1996)
Albrecht, I. et al. Suppressive effects of vascular endothelial growth factor-B on tumor growth in a mouse model of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumorigenesis. PLoS ONE 5, e14109 (2010)
Olofsson, B. et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor B (VEGF-B) binds to VEGF receptor-1 and regulates plasminogen activator activity in endothelial cells. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 95, 11709–11714 (1998)
Makinen, T. et al. Differential binding of vascular endothelial growth factor B splice and proteolytic isoforms to neuropilin-1. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 21217–21222 (1999)
Aase, K. et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor-B-deficient mice display an atrial conduction defect. Circulation 104, 358–364 (2001)
Karpanen, T. et al. Overexpression of vascular endothelial growth factor-B in mouse heart alters cardiac lipid metabolism and induces myocardial hypertrophy. Circ. Res. 103, 1018–1026 (2008)
Genuth, S. M., Przybylski, R. J. & Rosenberg, D. M. Insulin resistance in genetically obese, hyperglycemic mice. Endocrinology 88, 1230–1238 (1971)
Sparks, L. M. et al. A high-fat diet coordinately downregulates genes required for mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation in skeletal muscle. Diabetes 54, 1926–1933 (2005)
Mootha, V. K. et al. PGC-1α-responsive genes involved in oxidative phosphorylation are coordinately downregulated in human diabetes. Nature Genet. 34, 267–273 (2003)
Randle, P. J. Regulatory interactions between lipids and carbohydrates: the glucose fatty acid cycle after 35 years. Diabetes Metab. Rev. 14, 263–283 (1998)
Eckel, R. H., Grundy, S. M. & Zimmet, P. Z. The metabolic syndrome. Lancet 365, 1415–1428 (2005)
Scotney, P. D. et al. Human vascular endothelial growth factor B: characterization of recombinant isoforms and generation of neutralizing monoclonal antibodies. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 29, 1024–1029 (2002)
Fujimoto, W. Y. The importance of insulin resistance in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am. J. Med. 108 (suppl. 6a). 9–14 (2000)
Chaggar, P. S., Shaw, S. M. & Williams, S. G. Review article: thiazolidinediones and heart failure. Diab. Vasc. Dis. Res. 6, 146–152 (2009)
Kim, F. et al. Vascular inflammation, insulin resistance, and reduced nitric oxide production precede the onset of peripheral insulin resistance. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 28, 1982–1988 (2008)
Kubota, T. et al. Impaired insulin signaling in endothelial cells reduces insulin-induced glucose uptake by skeletal muscle. Cell Metab. 13, 294–307 (2011)
Andrikopoulos, S., Blair, A. R., Deluca, N., Fam, B. C. & Proietto, J. Evaluating the glucose tolerance test in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 295, E1323–E1332 (2008)
Mangiafico, S. P. et al. A primary defect in glucose production alone cannot induce glucose intolerance without defects in insulin secretion. J. Endocrinol. 210, 335–347 (2011)
Wong, N. et al. Deficiency in interferon-γ results in reduced body weight and better glucose tolerance in mice. Endocrinology 152, 3690–3699 (2011)
Nyqvist, D., Kohler, M., Wahlstedt, H. & Berggren, P. O. Donor islet endothelial cells participate in formation of functional vessels within pancreatic islet grafts. Diabetes 54, 2287–2293 (2005)
Kawasaki, F., Matsuda, M., Kanda, Y., Inoue, H. & Kaku, K. Structural and functional analysis of pancreatic islets preserved by pioglitazone in db/db mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 288, E510–E518 (2005)
Lamont, B. J. et al. Peripheral insulin resistance develops in transgenic rats overexpressing phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase in the kidney. Diabetologia 46, 1338–1347 (2003)
Visinoni, S. et al. Increased glucose production in mice overexpressing human fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase in the liver. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 295, E1132–E1141 (2008)
Kraegen, E. W. et al. Development of muscle insulin resistance after liver insulin resistance in high-fat-fed rats. Diabetes 40, 1397–1403 (1991)
Nolan, C. J. & Proietto, J. The feto-placental glucose steal phenomenon is a major cause of maternal metabolic adaptation during late pregnancy in the rat. Diabetologia 37, 976–984 (1994)
Acknowledgements
We thank S. Wittgren and A. Gustafsson for technical assistance, and G. Christofori for the RIP VEGF-B mice. C.E.H. was supported by the Frans Wilhelm och Waldemar von Frenckells Fond and Wilhelm och Else Stockmanns Stiftelse. D.N. was supported by the Swedish Society for Medical Research. This study was supported by the Ludwig Institute for Cancer Research, the Novo Nordisk Foundation, the Swedish Cancer Foundation, the Swedish Research Council, Torsten och Ragnar Söderbergs Stiftelser, Dr Peter Wallenbergs Foundation for Economics and Technology, the Swedish Heart and Lung Foundation, the Diabetes Foundation and Karolinska Institutet.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C.E.H. designed and performed in vivo mouse experiments, collected the material, performed transcriptional analysis and wrote the paper; A.M. performed in vivo mouse experiments, transcriptional analyses, ORO analyses, plasma analyses, triglyceride content measurements, all histological analyses of the pancreas and helped write the paper; A.F. performed ORO analyses, assisted with in vivo mouse studies and helped write the paper; L.M. assisted with in vivo studies; B.C.F. performed the rat study; P.S. helped design and interpret the rat study, helped write the paper and developed and supplied the 2H10, rat/mouse chimaeric 2H10 and 6H6 antibodies; D.N. performed the islet isolation and triglyceride content measurements; E.S., L.L. and S.S.-E. performed and analysed the PET scan data; J.P. and S.A. designed, supervised and analysed the rat study; H.O. and Å.S. provided expertise in diabetes, advised on islet analysis, interpreted results and commented on the manuscript; A.N. helped design and interpret the rat study, and helped write the paper; U.E. designed and supervised the study, analysed and interpreted the data and helped write the paper. All authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
U.E. is a consultant to CSL Limited and is an inventor on a patent describing the role of VEGF-B in type 2 diabetes; P.S. and A.N. are employees of CSL Limited, own shares in CSL Limited and are inventors on a patent describing the antibody 2H10.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Figures
This file contains Supplementary Figures 1-12. (PDF 1402 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hagberg, C., Mehlem, A., Falkevall, A. et al. Targeting VEGF-B as a novel treatment for insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nature 490, 426–430 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11464
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11464
This article is cited by
-
Melatonin attenuates diabetic cardiomyopathy by increasing autophagy of cardiomyocytes via regulation of VEGF-B/GRP78/PERK signaling pathway
Cardiovascular Diabetology (2024)
-
Combining albumin deficiency and acute exercise reduces hepatic lipid droplet size in mice
Lipids in Health and Disease (2023)
-
Lycium barbarum Polysaccharides Promotes Mitochondrial Biogenesis and Energy Balance in a NAFLD Cell Model
Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine (2022)
-
Cellular crosstalk of glomerular endothelial cells and podocytes in diabetic kidney disease
Journal of Cell Communication and Signaling (2022)
-
Serum vascular endothelial growth factor b and metabolic syndrome incidence in the population based cohort Di@bet.es study
International Journal of Obesity (2022)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.