Abstract
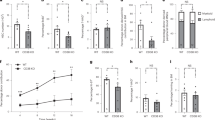
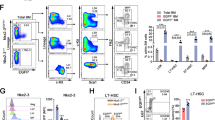
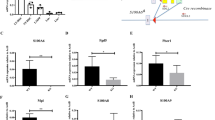
The capacity to fine-tune cellular bioenergetics with the demands of stem-cell maintenance and regeneration is central to normal development and ageing, and to organismal survival during periods of acute stress. How energy metabolism and stem-cell homeostatic processes are coordinated is not well understood. Lkb1 acts as an evolutionarily conserved regulator of cellular energy metabolism in eukaryotic cells and functions as the major upstream kinase to phosphorylate AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and 12 other AMPK-related kinases1,2,3. Whether Lkb1 regulates stem-cell maintenance remains unknown. Here we show that Lkb1 has an essential role in haematopoietic stem cell (HSC) homeostasis. We demonstrate that ablation of Lkb1 in adult mice results in severe pancytopenia and subsequent lethality. Loss of Lkb1 leads to impaired survival and escape from quiescence of HSCs, resulting in exhaustion of the HSC pool and a marked reduction of HSC repopulating potential in vivo. Lkb1 deletion has an impact on cell proliferation in HSCs, but not on more committed compartments, pointing to context-specific functions for Lkb1 in haematopoiesis. The adverse impact of Lkb1 deletion on haematopoiesis was predominantly cell-autonomous and mTOR complex 1 (mTORC1)-independent, and involves multiple mechanisms converging on mitochondrial apoptosis and possibly downregulation of PGC-1 coactivators and their transcriptional network, which have critical roles in mitochondrial biogenesis and function. Thus, Lkb1 serves as an essential regulator of HSCs and haematopoiesis, and more generally, points to the critical importance of coupling energy metabolism and stem-cell homeostasis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alessi, D. R., Sakamoto, K. & Bayascas, J. R. LKB1-dependent signaling pathways. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 75, 137–163 (2006)
Hardie, D. G. AMP-activated/SNF1 protein kinases: conserved guardians of cellular energy. Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 8, 774–785 (2007)
Shackelford, D. B. & Shaw, R. J. The LKB1-AMPK pathway: metabolism and growth control in tumour suppression. Nature Rev. Cancer 9, 563–575 (2009)
Adams, G. B. & Scadden, D. T. The hematopoietic stem cell in its place. Nature Immunol. 7, 333–337 (2006)
Moore, K. A. & Lemischka, I. R. Stem cells and their niches. Science 311, 1880–1885 (2006)
Orkin, S. H. & Zon, L. I. Hematopoiesis: an evolving paradigm for stem cell biology. Cell 132, 631–644 (2008)
Vooijs, M., Jonkers, J. & Berns, A. A highly efficient ligand-regulated Cre recombinase mouse line shows that LoxP recombination is position dependent. EMBO Rep. 2, 292–297 (2001)
Shaw, R. J. et al. The tumor suppressor LKB1 kinase directly activates AMP-activated kinase and regulates apoptosis in response to energy stress. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 101, 3329–3335 (2004)
Corradetti, M. N., Inoki, K., Bardeesy, N., DePinho, R. A. & Guan, K. L. Regulation of the TSC pathway by LKB1: evidence of a molecular link between tuberous sclerosis complex and Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. Genes Dev. 18, 1533–1538 (2004)
Chen, C. et al. TSC-mTOR maintains quiescence and function of hematopoietic stem cells by repressing mitochondrial biogenesis and reactive oxygen species. J. Exp. Med. 205, 2397–2408 (2008)
Gan, B. & DePinho, R. A. mTORC1 signaling governs hematopoietic stem cell quiescence. Cell Cycle 8, 1003–1006 (2009)
Gan, B. et al. mTORC1-dependent and -independent regulation of stem cell renewal, differentiation, and mobilization. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 105, 19384–19389 (2008)
Ito, K., Bernardi, R. & Pandolfi, P. P. A novel signaling network as a critical rheostat for the biology and maintenance of the normal stem cell and the cancer-initiating cell. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 19, 51–59 (2009)
Yilmaz, O. H. et al. Pten dependence distinguishes haematopoietic stem cells from leukaemia-initiating cells. Nature 441, 475–482 (2006)
Gurumurthy, S. et al. The Lkb1 metabolic sensor maintains haematopoietic stem cell survival. Nature 10.1038/nature09572 (this issue)
Nakada, D., Saunders, T. L. & Morrison, S. J. Lkb1 regulates cell cycle and energy metabolism in haematopoietic stem cells. Nature 10.1038/nature09571 (this issue)
Puigserver, P. & Spiegelman, B. M. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator 1α (PGC-1α): transcriptional coactivator and metabolic regulator. Endocr. Rev. 24, 78–90 (2003)
Shaw, R. J. et al. The kinase LKB1 mediates glucose homeostasis in liver and therapeutic effects of metformin. Science 310, 1642–1646 (2005)
Kelly, D. P. & Scarpulla, R. C. Transcriptional regulatory circuits controlling mitochondrial biogenesis and function. Genes Dev. 18, 357–368 (2004)
Bardeesy, N. et al. Loss of the Lkb1 tumour suppressor provokes intestinal polyposis but resistance to transformation. Nature 419, 162–167 (2002)
Tothova, Z. et al. FoxOs are critical mediators of hematopoietic stem cell resistance to physiologic oxidative stress. Cell 128, 325–339 (2007)
Hock, H. et al. Gfi-1 restricts proliferation and preserves functional integrity of haematopoietic stem cells. Nature 431, 1002–1007 (2004)
Li, C. & Wong, W. H. DNA-Chip Analyzer (dChip). in The Analysis of Gene Expression Data: Methods and Software (eds Parmigiani, G., Garrett. E. S., Irizarry, R. & Zeger, S. L.) (Springer, 2003)
Paik, J. H. et al. FoxOs are lineage-restricted redundant tumor suppressors and regulate endothelial cell homeostasis. Cell 128, 309–323 (2007)
Ji, H., Vokes, S. A. & Wong, W. H. A comparative analysis of genome-wide chromatin immunoprecipitation data for mammalian transcription factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 34, e146 (2006)
Ahn, B. H. et al. A role for the mitochondrial deacetylase Sirt3 in regulating energy homeostasis. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 105, 14447–14452 (2008)
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to A. Berns for providing the Rosa26-creERt2 mouse strain. We are also grateful to S. Zhou for assistance in the animal facility and C. Lim for assistance with genotyping. We thank S. Lazo-Kallanian, J. Daley and P. Schow for assistance with flow cytometry. We also thank N. Bardeesy and S. Morrison for communicating unpublished information; A. Stegh for comments on apoptosis; and D. Nakada for western blotting protocol from sorted HSCs. This research was supported by U01CA141508 (R.A.D. and L.C.), R21CA135057 (R.A.D. and B.G.) and DOD TSCRP Career Transition Award (TS093049) (B.G.). B.G. and J.H. are the Research Fellows of the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society. Y.A.W. is supported by Multiple Myeloma Research Foundation. R.A.D. was supported by an American Cancer Society Research Professorship and the Robert A. and Renee E. Belfer Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
B.G. and R.A.D. designed the experiments, interpreted the data and wrote the manuscript. B.G., S.J., J.H., L.Z. and E.F.-S. performed experiments. Y.L. and L.C. conducted the microarray and promoter analyses. E.S. and S.C. contributed reagents. L.C. and Y.A.W. contributed to the writing of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
This file contains Supplementary Figures 1-11 with legends and Supplementary Table 1. (PDF 673 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gan, B., Hu, J., Jiang, S. et al. Lkb1 regulates quiescence and metabolic homeostasis of haematopoietic stem cells. Nature 468, 701–704 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09595
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09595
This article is cited by
-
Induction of mitochondrial recycling reverts age-associated decline of the hematopoietic and immune systems
Nature Aging (2023)
-
SLC7A11 expression level dictates differential responses to oxidative stress in cancer cells
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Actin cytoskeleton vulnerability to disulfide stress mediates disulfidptosis
Nature Cell Biology (2023)
-
Effects of smoking on the tissue regeneration-associated functions of human endometrial stem cells via a novel target gene SERPINB2
Stem Cell Research & Therapy (2022)
-
Myeloid liver kinase B1 contributes to lung inflammation induced by lipoteichoic acid but not by viable Streptococcus pneumoniae
Respiratory Research (2022)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.