Abstract
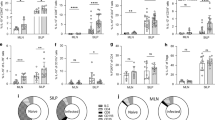
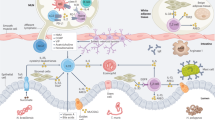
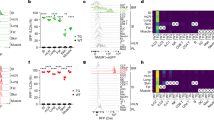
Innate immunity provides the first line of defence against invading pathogens and provides important cues for the development of adaptive immunity. Type-2 immunity—responsible for protective immune responses to helminth parasites1,2 and the underlying cause of the pathogenesis of allergic asthma3,4—consists of responses dominated by the cardinal type-2 cytokines interleukin (IL)4, IL5 and IL13 (ref. 5). T cells are an important source of these cytokines in adaptive immune responses, but the innate cell sources remain to be comprehensively determined. Here, through the use of novel Il13-eGFP reporter mice, we present the identification and functional characterization of a new innate type-2 immune effector leukocyte that we have named the nuocyte. Nuocytes expand in vivo in response to the type-2-inducing cytokines IL25 and IL33, and represent the predominant early source of IL13 during helminth infection with Nippostrongylus brasiliensis. In the combined absence of IL25 and IL33 signalling, nuocytes fail to expand, resulting in a severe defect in worm expulsion that is rescued by the adoptive transfer of in vitro cultured wild-type, but not IL13-deficient, nuocytes. Thus, nuocytes represent a critically important innate effector cell in type-2 immunity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maizels, R. M., Pearce, E. J., Artis, D., Yazdanbakhsh, M. & Wynn, T. A. Regulation of pathogenesis and immunity in helminth infections. J. Exp. Med. 206, 2059–2066 (2009)
Perrigoue, J. G., Marshall, F. A. & Artis, D. On the hunt for helminths: innate immune cells in the recognition and response to helminth parasites. Cell. Microbiol. 10, 1757–1764 (2008)
Holgate, S. T. & Polosa, R. Treatment strategies for allergy and asthma. Nature Rev. Immunol. 8, 218–230 (2008)
Larché, M., Robinson, D. S. & Kay, A. B. The role of T lymphocytes in the pathogenesis of asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 111, 450–463 (2003)
Fallon, P. G. et al. IL-4 induces characteristic Th2 responses even in the combined absence of IL-5, IL-9, and IL-13. Immunity 17, 7–17 (2002)
Grünig, G. et al. Requirement for IL-13 independently of IL-4 in experimental asthma. Science 282, 2261–2263 (1998)
Urban, J. F. J. et al. IL-13, IL-4Rα, and Stat6 are required for the expulsion of the gastrointestinal nematode parasite Nippostrongylus brasiliensis . Immunity 8, 255–264 (1998)
Min, B. et al. Basophils produce IL-4 and accumulate in tissues after infection with a Th2-inducing parasite. J. Exp. Med. 200, 507–517 (2004)
Ohnmacht, C. & Voehringer, D. Basophil effector function and homeostasis during helminth infection. Blood 113, 2816–2825 (2009)
Perrigoue, J. G. et al. MHC class II-dependent basophil-CD4+ T cell interactions promote TH2 cytokine-dependent immunity. Nature Immunol. 10, 697–705 (2009)
Voehringer, D. The role of basophils in helminth infection. Trends Parasitol. 25, 551–556 (2009)
Yoshimoto, T. et al. Basophils contribute to TH2-IgE responses in vivo via IL-4 production and presentation of peptide-MHC class II complexes to CD4+ T cells. Nature Immunol. 10, 706–712 (2009)
McKenzie, G. J., Bancroft, A., Grencis, R. K. & McKenzie, A. N. A distinct role for interleukin-13 in Th2-cell-mediated immune responses. Curr. Biol. 8, 339–342 (1998)
Walter, D. M. et al. Critical role for IL-13 in the development of allergen-induced airway hyperreactivity. J. Immunol. 167, 4668–4675 (2001)
Voehringer, D., Reese, T. A., Huang, X., Shinkai, K. & Locksley, R. M. Type 2 immunity is controlled by IL-4/IL-13 expression in hematopoietic non-eosinophil cells of the innate immune system. J. Exp. Med. 203, 1435–1446 (2006)
Arinobu, Y. et al. Developmental checkpoints of the basophil/mast cell lineages in adult murine hematopoiesis. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 102, 18105–18110 (2005)
Haig, D. M. et al. Effects of stem cell factor (kit-ligand) and interleukin-3 on the growth and serine proteinase expression of rat bone-marrow-derived or serosal mast cells. Blood 83, 72–83 (1994)
McKenzie, G. J., Fallon, P. G., Emson, C. L., Grencis, R. K. & McKenzie, A. N. Simultaneous disruption of interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-13 defines individual roles in T helper cell type 2-mediated responses. J. Exp. Med. 189, 1565–1572 (1999)
Fallon, P. G. et al. Identification of an interleukin (IL)-25-dependent cell population that provides IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 at the onset of helminth expulsion. J. Exp. Med. 203, 1105–1116 (2006)
Shinkai, Y. et al. RAG-2-deficient mice lack mature lymphocytes owing to inability to initiate V(D)J rearrangement. Cell 68, 855–867 (1992)
Cui, J. et al. Requirement for Vα14 NKT cells in IL-12-mediated rejection of tumors. Science 278, 1623–1626 (1997)
Tono, T. et al. c-kit gene was not transcribed in cultured mast cells of mast cell-deficient Wsh/Wsh mice that have a normal number of erythrocytes and a normal c-kit coding region. Blood 80, 1448–1453 (1992)
Liu, P., Jenkins, N. A. & Copeland, N. G. A highly efficient recombineering-based method for generating conditional knockout mutations. Genome Res. 13, 476–484 (2003)
Warming, S., Costantino, N., Court, D. L., Jenkins, N. A. & Copeland, N. G. Simple and highly efficient BAC recombineering using galK selection. Nucleic Acids Res. 33, e36 (2005)
Acknowledgements
We thank members of the McKenzie laboratory for their comments on the manuscript. We thank D. Cousins for assistance with preliminary microarray analysis. R.J.F. was supported by Asthma UK. P.G.F. is supported by Science Foundation Ireland.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
D.R.N., S.H.W. and A.B. performed experiments, interpreted data, provided intellectual input and wrote the paper; R.J.F. and T.K.A.L. performed the infection studies; M.D. performed cell isolation studies; C.B. and C.M.K. performed microarray studies and Luminex; P.G.F. provided reagents and intellectual input; R.P. and H.E.J. provided reagents and experimental assistance; A.N.J.M. conceived the study and wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
S.H.W. and A.N.J.M. were supported by a grant from Centocor.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
This file contains Supplementary Figures S1-S9 with legends and Supplementary Table 1. (PDF 754 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Neill, D., Wong, S., Bellosi, A. et al. Nuocytes represent a new innate effector leukocyte that mediates type-2 immunity. Nature 464, 1367–1370 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08900
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08900
This article is cited by
-
Potential anthelmintic effect of chitosan on Syphacia muris infecting Wistar rats: biochemical, immunological, and histopathological studies
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
LSD1 drives intestinal epithelial maturation and controls small intestinal immune cell composition independent of microbiota in a murine model
Nature Communications (2024)
-
A diversity of novel type-2 innate lymphoid cell subpopulations revealed during tumour expansion
Communications Biology (2024)
-
Group 2 innate lymphoid cells and their surrounding environment
Inflammation and Regeneration (2023)
-
m6A RNA modification regulates innate lymphoid cell responses in a lineage-specific manner
Nature Immunology (2023)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.