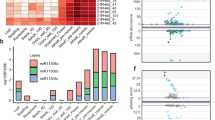
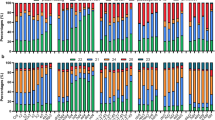
Abstract
Most eukaryotes produce small RNA (sRNA) mediators of gene silencing that bind to Argonaute proteins and guide them, by base pairing, to an RNA target. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) that normally target messenger RNAs for degradation or translational arrest are the best-understood class of sRNAs. However, in Arabidopsis thaliana flowers, miRNAs account for only 5% of the sRNA mass and less than 0.1% of the sequence complexity. The remaining sRNAs form a complex population of more than 100,000 different small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) transcribed from thousands of loci1,2,3,4,5. The biogenesis of most of the siRNAs in Arabidopsis are dependent on RNA polymerase IV (PolIV), a homologue of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase II2,3,6. A subset of these PolIV-dependent (p4)-siRNAs are involved in stress responses, and others are associated with epigenetic modifications to DNA or chromatin; however, the biological role is not known for most of them. Here we show that the predominant phase of p4-siRNA accumulation is initiated in the maternal gametophyte and continues during seed development. Expression of p4-siRNAs in developing endosperm is specifically from maternal chromosomes. Our results provide the first evidence for a link between genomic imprinting and RNA silencing in plants.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Aravin, A. A. et al. The small RNA profile during Drosophila melanogaster development. Dev. Cell 5, 337–350 (2003)
Kasschau, K. D. et al. Genome-wide profiling and analysis of Arabidopsis siRNAs. PLoS Biol. 5, 0479–0493 (2007)
Mosher, R. A., Schwach, F., Studholme, D. J. & Baulcombe, D. C. PolIVb influences RNA-directed DNA methylation independently of its role in siRNA biogenesis. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 105, 3145–3150 (2008)
Reinhart, B. J., Weinstein, E. G., Rhoades, M., Bartel, B. & Bartel, D. P. MicroRNAs in plants. Genes Dev. 16, 1616–1626 (2002)
Ruby, J. G. et al. Large-scale sequencing reveals 21U-RNAs and additional Micro-RNAs and endogenous siRNAs in C. elegans. Cell 127, 1193–1207 (2006)
Zhang, X., Henderson, I. R., Lu, C., Green, P. J. & Jacobsen, S. E. Role of RNA polymerase IV in plant small RNA metabolism. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 104, 4536–4541 (2007)
Herr, A. J., Jensen, M. B., Dalmay, T. & Baulcombe, D. RNA polymerase IV directs silencing of endogenous DNA. Science 308, 118–120 (2005)
Kanno, T. et al. Atypical RNA polymerase subunits required for RNA-directed DNA methylation. Nature Genet. 37, 761–765 (2005)
Onodera, Y. et al. Plant nuclear RNA polymerase IV mediates siRNA and DNA methylation-dependent heterochromatin formation. Cell 120, 613–622 (2005)
Pontier, D. et al. Reinforcement of silencing at transposons and highly repeated sequences requires the concerted action of two distinct RNA polymerases IV in Arabidopsis. Genes Dev. 19, 2030–2040 (2005)
Kakutani, T., Jeddeloh, J. A., Flowers, S. K., Munakata, K. & Richards, E. J. Developmental abnormalities and epimutations associated with DNA hypomethylation mutations. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 93, 12406–12411 (1996)
Singer, T., Yordan, C. & Martienssen, R. A. Robertson’s Mutator transposons in A. thaliana are regulated by the chromatin-remodeling gene Decrease in DNA Methylation (DDM1). Genes Dev. 15, 591–602 (2001)
Lu, C. et al. Elucidation of the small RNA component of the transcriptome. Science 309, 1567–1569 (2005)
Swiezewski, S. et al. Small RNA-mediated chromatin silencing directed to the 3′ region of the Arabidopsis gene encoding the developmental regulator, FLC. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 104, 3633–3638 (2007)
Vielle-Calzada, J. P., Baskar, R. & Grossniklaus, U. Delayed activation of the paternal genome during seed development. Nature 404, 91–94 (2000)
Jullien, P. E., Katz, A., Oliva, M., Ohad, N. & Berger, F. Polycomb group complexes self-regulate imprinting of the Polycomb group gene MEDEA in Arabidopsis. Curr. Biol. 16, 486–492 (2006)
Kinoshita, T. et al. One-way control of FWA imprinting in Arabidopsis endosperm by DNA methylation. Science 303, 521–523 (2004)
Jullien, P. E., Kinoshita, T., Ohad, N. & Berger, F. Maintenance of DNA methylation during the Arabidopsis life cycle is essential for parental imprinting. Plant Cell 18, 1360–1372 (2006)
Kinoshita, T., Yadegari, R., Harada, J. J., Goldberg, R. B. & Fischer, R. L. Imprinting of the MEDEA Polycomb gene in the Arabidopsis endosperm. Plant Cell 11, 1945–1952 (1999)
Kohler, C. et al. The Polycomb-group protein MEDEA regulates seed development by controlling expression of the MADS-box gene PHERES1. Genes Dev. 17, 1540–1553 (2003)
Slotkin, R. K. et al. Epigenetic reprogramming and small RNA silencing of transposable elements in pollen. Cell 136, 461–472 (2009)
Acknowledgements
We thank I. Furner for met1-1 seed and A. Davis for photography. This work was supported by the Gatsby Charitable Foundation, the European Union Sixth Framework Programme Integrated Project SIROCCO (grant LSHG-CT-2006-037900), a postdoctoral fellowship from the National Science Foundation (to R.A.M.), and Commonwealth and NSERC Scholarships (to C.W.M.). D.C.B. is funded as a Royal Society Research Professor.
Author Contributions Experiments were designed by R.A.M. and D.C.B. and executed by R.A.M. with assistance from C.W.M. Bioinformatic and statistical analyses were performed by K.A.K., R.M.D. and D.J.S. The manuscript was prepared by R.A.M. and D.C.B.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Deep sequencing libraries are deposited in NCBI GEO (GSE15348).
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
This file contains Supplementary Notes, Supplementary Tables S1-S3, Supplementary Figures S1-S4 with Legends and Supplementary References. (PDF 960 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mosher, R., Melnyk, C., Kelly, K. et al. Uniparental expression of PolIV-dependent siRNAs in developing endosperm of Arabidopsis. Nature 460, 283–286 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08084
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08084
This article is cited by
-
Small RNAs mediate transgenerational inheritance of genome-wide trans-acting epialleles in maize
Genome Biology (2022)
-
Interactive roles of chromatin regulation and circadian clock function in plants
Genome Biology (2019)
-
RNA-mediated transgenerational inheritance in ciliates and plants
Chromosoma (2018)
-
Molecular regulation of seed development and strategies for engineering seed size in crop plants
Plant Growth Regulation (2018)
-
Analysis of small RNAs revealed differential expressions during pollen and embryo sac development in autotetraploid rice
BMC Genomics (2017)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.