Abstract
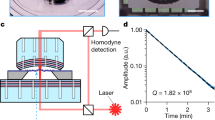
Macroscopic mechanical objects and electromagnetic degrees of freedom can couple to each other through radiation pressure. Optomechanical systems in which this coupling is sufficiently strong are predicted to show quantum effects and are a topic of considerable interest. Devices in this regime would offer new types of control over the quantum state of both light and matter1,2,3,4, and would provide a new arena in which to explore the boundary between quantum and classical physics5,6,7. Experiments so far have achieved sufficient optomechanical coupling to laser-cool mechanical devices8,9,10,11,12, but have not yet reached the quantum regime. The outstanding technical challenge in this field is integrating sensitive micromechanical elements (which must be small, light and flexible) into high-finesse cavities (which are typically rigid and massive) without compromising the mechanical or optical properties of either. A second, and more fundamental, challenge is to read out the mechanical element’s energy eigenstate. Displacement measurements (no matter how sensitive) cannot determine an oscillator’s energy eigenstate13, and measurements coupling to quantities other than displacement14,15,16 have been difficult to realize in practice. Here we present an optomechanical system that has the potential to resolve both of these challenges. We demonstrate a cavity which is detuned by the motion of a 50-nm-thick dielectric membrane placed between two macroscopic, rigid, high-finesse mirrors. This approach segregates optical and mechanical functionality to physically distinct structures and avoids compromising either. It also allows for direct measurement of the square of the membrane’s displacement, and thus in principle the membrane’s energy eigenstate. We estimate that it should be practical to use this scheme to observe quantum jumps of a mechanical system, an important goal in the field of quantum measurement.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fabre, C. et al. Quantum-noise reduction using a cavity with a movable mirror. Phys. Rev. A. 49, 1337–1343 (1994)
Giovannetti, V., Mancini, S. & Tombesi, P. Radiation pressure induced Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen paradox. Europhys. Lett. 54, 559–565 (2001)
Vitali, D. et al. Optomechanical entanglement between a movable mirror and a cavity field. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 030405 (2007)
Pinard, M. et al. Entangling movable mirrors in a double-cavity system. Europhys. Lett. 72, 747–753 (2005)
Bose, S., Jacobs, K. & Knight, P. L. Scheme to probe the decoherence of a macroscopic object. Phys. Rev. A. 59, 3204–3210 (1999)
Marshall, W., Simon, C., Penrose, R. & Bouwmeester, D. Towards quantum superpositions of a mirror. Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 130401 (2003)
Fereira, A., Geirreiro, A. & Vedral, V. Macroscopic thermal entanglement due to radiation pressure. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 060407 (2006)
Höhberger, C. & Karrai, K. Cavity cooling of a microlever. Nature 432, 1002–1005 (2004)
Gigan, S. et al. Self cooling of a micromirror by radiation pressure. Nature 444, 67–70 (2006)
Arcizet, O., Cohadon, P.-F., Briant, T., Pinard, M. & Heidmann, A. Radiation-pressure cooling and optomechanical instability of a micromirror. Nature 444, 71–74 (2006)
Corbitt, T. et al. An all-optical trap for a gram-scale mirror. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 150802 (2007)
Schliesser, A., Del’Haye, P., Nooshi, N., Vahala, K. J. & Kippenberg, T. J. Radiation pressure cooling of a micromechanical oscillator using dynamical backaction. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 243905 (2006)
Braginsky, V. B., Vorontsov, Y. I. & Thorne, K. S. Quantum nondemolition measurements. Science 209, 547–557 (1980)
Santamore, D. H., Doherty, A. C. & Cross, M. C. Quantum nondemolition measurements of Fock states of mesoscopic mechanical oscillators. Phys. Rev. B 70, 144301 (2004)
Martin, I. & Zurek, W. H. Measurement of energy eigenstates by a slow detector. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 120401 (2007)
Jacobs, K., Lougovski, P. & Blencowe, M. Continuous measurement of the energy eigenstates of a nanomechanical resonator without a nondemolition probe. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 147201 (2007)
Harry, G. M. et al. Thermal noise in interferometric gravitational wave detectors due to dielectric optical coatings. Class. Quantum Grav. 19, 897–917 (2002)
Hood, C. J., Kimble, H. J. & Ye, J. Characterization of high-finesse mirrors: Loss, phase shifts, and mode structure in an optical cavity. Phys. Rev. A. 64, 033804 (1999)
Kleckner, D. et al. High finesse opto-mechanical cavity with a movable thirty-micron-size mirror. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 173901 (2006)
Brune, M., Haroche, S., Lefevre, V., Raimond, J. M. & Zagury, N. Quantum nondemolition measurement of small photon numbers by Rydberg-atom phase-sensitive detection. Phys. Rev. Lett. 65, 976–979 (1990)
Wallraff, A. et al. Strong coupling of a single photon to a superconducting qubit using circuit quantum electrodynamics. Nature 431, 162–167 (2004)
Meystre, P., Wright, E. M., McCullen, J. D. & Vignes, E. Theory of radiation-pressure-driven interferometers. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 2, 1830–1840 (1985)
Poenar, D. P. & Wolffenbuttel, R. F. Optical properties of thin-film silicon-compatible materials. Appl. Opt. 36, 5122–5128 (1997)
Müller-Seydlitz, T. et al. Atoms in the lowest motional band of a three-dimensional optical lattice. Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 1038–1041 (1997)
Marquardt, F., Chen, J. P., Clerk, A. A. & Girvin, S. M. Quantum theory of cavity-assisted sideband cooling of mechanical motion. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 093902 (2007)
Black, E. D. An introduction to Pound-Drever-Hall laser frequency stabilization. Am. J. Phys. 69, 79–87 (2001)
Bleszynski, A. C., Shanks, W. E. & Harris, J. G. E. Noise thermometry and electron thermometry of a sample-on-cantilever system below 1 Kelvin. Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 013123 (2008)
Kilic, O. et al. Photonic crystal slabs demonstrating strong broadband supression of transmission in the presence of disorders. Opt. Lett. 29, 2782–2784 (2004)
Stipe, B. C., Rezaei, M. A. & Ho, W. A variable-temperature scanning tunneling microscope capable of single-molecule vibrational spectroscopy. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 70, 137–143 (1999)
Wilson-Rae, I., Nooshi, N., Zwerger, W. & Kippenberg, T. J. Theory of ground state cooling of a mechanical oscillator using dynamical backaction. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 093901 (2007)
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge funding by the NSF, the DFG NIM network and Emmy Noether programme (F.M.), and a fellowship from the Sloane Research Foundation (J.H.). We thank W. Shanks for the microscopy and cryogenic measurements, and C. Yang for assistance with the laser-cooling measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
The file contains Supplementary Notes with Supplementary Equations and additional references. (PDF 273 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thompson, J., Zwickl, B., Jayich, A. et al. Strong dispersive coupling of a high-finesse cavity to a micromechanical membrane. Nature 452, 72–75 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06715
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06715
This article is cited by
-
Direct laser-written optomechanical membranes in fiber Fabry-Perot cavities
Nature Communications (2024)
-
Ultrahigh-quality-factor micro- and nanomechanical resonators using dissipation dilution
Nature Nanotechnology (2024)
-
Intracavity-squeezed Cooling in the via Quadratic Optomechanical Coupling with the Hybrid Optomechanical System
International Journal of Theoretical Physics (2024)
-
Dynamics of Two-Level Atom in Cavity Optomechanics: Strong Coupling Limit Study
International Journal of Theoretical Physics (2024)
-
Study of optical bistability/multistability and transparency in cavity-assisted-hybrid optomechanical system embedded with quantum dot molecules
Optical and Quantum Electronics (2024)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.