Abstract
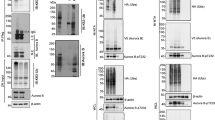
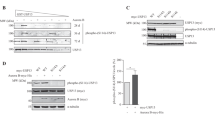
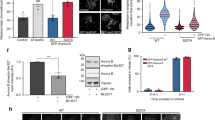
During division of metazoan cells, the nucleus disassembles to allow chromosome segregation, and then reforms in each daughter cell. Reformation of the nucleus involves chromatin decondensation and assembly of the double-membrane nuclear envelope around the chromatin; however, regulation of the process is still poorly understood1,2. In vitro, nucleus formation requires p97 (ref. 3), a hexameric ATPase implicated in membrane fusion and ubiquitin-dependent processes4,5. However, the role and relevance of p97 in nucleus formation have remained controversial. Here we show that p97 stimulates nucleus reformation by inactivating the chromatin-associated kinase Aurora B. During mitosis, Aurora B inhibits nucleus reformation by preventing chromosome decondensation and formation of the nuclear envelope membrane. During exit from mitosis, p97 binds to Aurora B after its ubiquitylation and extracts it from chromatin. This leads to inactivation of Aurora B on chromatin, thus allowing chromatin decondensation and nuclear envelope formation. These data reveal an essential pathway that regulates reformation of the nucleus after mitosis and defines ubiquitin-dependent protein extraction as a common mechanism of Cdc48/p97 activity also during nucleus formation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burke, B. & Ellenberg, J. Remodelling the walls of the nucleus. Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 3, 487–497 (2002)
Hetzer, M. W., Walther, T. C. & Mattaj, I. W. Pushing the envelope: structure, function, and dynamics of the nuclear periphery. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 21, 347–380 (2005)
Hetzer, M. et al. Distinct AAA-ATPase p97 complexes function in discrete steps of nuclear assembly. Nature Cell Biol. 3, 1086–1091 (2001)
Ye, Y. Diverse functions with a common regulator: ubiquitin takes command of an AAA ATPase. J. Struct. Biol. 156, 29–40 (2006)
Jentsch, S. & Rumpf, S. Cdc48 (p97): a “molecular gearbox” in the ubiquitin pathway? Trends Biochem. Sci. 32, 6–11 (2007)
Kondo, H. et al. p47 is a cofactor for p97-mediated membrane fusion. Nature 388, 75–78 (1997)
Burke, B. The nuclear envelope: filling in gaps. Nature Cell Biol. 3, E273–E274 (2001)
Meusser, B., Hirsch, C., Jarosch, E. & Sommer, T. ERAD: the long road to destruction. Nature Cell Biol. 7, 766–772 (2005)
Vagnarelli, P. & Earnshaw, W. C. Chromosomal passengers: the four-dimensional regulation of mitotic events. Chromosoma 113, 211–222 (2004)
Vong, Q. P., Cao, K., Li, H. Y., Iglesias, P. A. & Zheng, Y. Chromosome alignment and segregation regulated by ubiquitination of survivin. Science 310, 1499–1504 (2005)
Hagstrom, K. A., Holmes, V. F., Cozzarelli, N. R. & Meyer, B. J. C. elegans condensin promotes mitotic chromosome architecture, centromere organization, and sister chromatid segregation during mitosis and meiosis. Genes Dev. 16, 729–742 (2002)
Kaitna, S., Pasierbek, P., Jantsch, M., Loidl, J. & Glotzer, M. The aurora B kinase AIR-2 regulates kinetochores during mitosis and is required for separation of homologous Chromosomes during meiosis. Curr. Biol. 12, 798–812 (2002)
Lipp, J. J., Hirota, T., Poser, I. & Peters, J. M. Aurora B controls the association of condensin I but not condensin II with mitotic chromosomes. J. Cell Sci. 120, 1245–1255 (2007)
Takemoto, A. et al. Analysis of the role of Aurora B on the chromosomal targeting of condensin I. Nucleic Acids Res. 35, 2403–2412 (2007)
Hsu, J. Y. et al. Mitotic phosphorylation of histone H3 is governed by Ipl1/aurora kinase and Glc7/PP1 phosphatase in budding yeast and nematodes. Cell 102, 279–291 (2000)
Fischle, W. et al. Regulation of HP1-chromatin binding by histone H3 methylation and phosphorylation. Nature 438, 1116–1122 (2005)
Hirota, T., Lipp, J. J., Toh, B. H. & Peters, J. M. Histone H3 serine 10 phosphorylation by Aurora B causes HP1 dissociation from heterochromatin. Nature 438, 1176–1180 (2005)
Kourmouli, N. et al. Dynamic associations of heterochromatin protein 1 with the nuclear envelope. EMBO J. 19, 6558–6568 (2000)
Sessa, F. et al. Mechanism of Aurora B activation by INCENP and inhibition by hesperadin. Mol. Cell 18, 379–391 (2005)
Hauf, S. et al. The small molecule Hesperadin reveals a role for Aurora B in correcting kinetochore-microtubule attachment and in maintaining the spindle assembly checkpoint. J. Cell Biol. 161, 281–294 (2003)
Sugiyama, K. et al. Aurora-B associated protein phosphatases as negative regulators of kinase activation. Oncogene 21, 3103–3111 (2002)
Ye, Y., Meyer, H. H. & Rapoport, T. A. Function of the p97–Ufd1–Npl4 complex in retrotranslocation from the ER to the cytosol: dual recognition of nonubiquitinated polypeptide segments and polyubiquitin chains. J. Cell Biol. 162, 71–84 (2003)
Kelly, A. E. et al. Chromosomal enrichment and activation of the aurora B pathway are coupled to spatially regulate spindle assembly. Dev. Cell 12, 31–43 (2007)
Poteryaev, D., Squirrell, J. M., Campbell, J. M., White, J. G. & Spang, A. Involvement of the actin cytoskeleton and homotypic membrane fusion in ER dynamics in Caenorhabditis elegans. Mol. Biol. Cell 16, 2139–2153 (2005)
Mouysset, J., Kahler, C. & Hoppe, T. A conserved role of Caenorhabditis elegans CDC-48 in ER-associated protein degradation. J. Struct. Biol. 156, 41–49 (2006)
Severson, A. F., Hamill, D. R., Carter, J. C., Schumacher, J. & Bowerman, B. The aurora-related kinase AIR-2 recruits ZEN-4/CeMKLP1 to the mitotic spindle at metaphase and is required for cytokinesis. Curr. Biol. 10, 1162–1171 (2000)
Kamath, R. S. et al. Systematic functional analysis of the Caenorhabditis elegans genome using RNAi. Nature 421, 231–237 (2003)
Meyer, H. H., Shorter, J. G., Seemann, J., Pappin, D. & Warren, G. A complex of mammalian Ufd1 and Npl4 links the AAA-ATPase, p97, to ubiquitin and nuclear transport pathways. EMBO J. 19, 2181–2192 (2000)
Murray, A. W. Cell cycle extracts. Methods Cell Biol. 36, 581–605 (1991)
Lohka, M. J. Analysis of nuclear envelope assembly using extracts of Xenopus eggs. Methods Cell Biol. 53, 367–395 (1998)
Wang, Y., Satoh, A., Warren, G. & Meyer, H. H. VCIP135 acts as a deubiquitinating enzyme during p97-p47-mediated reassembly of mitotic Golgi fragments. J. Cell Biol. 164, 973–978 (2004)
Audhya, A. et al. A complex containing the Sm protein CAR-1 and the RNA helicase CGH-1 is required for embryonic cytokinesis in Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Cell Biol. 171, 267–279 (2005)
Yamauchi, S., Yamanaka, K. & Ogura, T. Comparative analysis of expression of two p97 homologues in Caenorhabditis elegans. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 345, 746–753 (2006)
Acknowledgements
We thank Y. Zheng for sharing data before publication and for the GST-survivin construct, A. Musacchio for the Aurora B/INCENP construct, K. Oegema for AIR-2 antibodies, P. Jackson for MCM3 antibodies, K. Yamanaka and T. Ogura for CDC-48 antibodies, N. Kraut (Boehringer Ingelheim, Vienna) for hesperadin, and C. Brasseur and C. Zbinden for technical help. This work was supported by grants of the Swiss National Fund, the ETH Zurich, the Bonizzi-Theler Stiftung, the Roche Research Foundations (to K.R.), the Novartis Foundation and the DAAD (to O.P.). R.B., F.M.S. and T.B. were on the Molecular Life Science PhD Program Zurich.
Author Contributions M.G. and F.M.S. performed the C. elegans experiments. H.H.M. wrote the paper. All authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Supplementary Figures
This file contains Supplementary Figures 1-6 with Legends. (PDF 1836 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramadan, K., Bruderer, R., Spiga, F. et al. Cdc48/p97 promotes reformation of the nucleus by extracting the kinase Aurora B from chromatin. Nature 450, 1258–1262 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06388
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06388
This article is cited by
-
Valosin containing protein (VCP): initiator, modifier, and potential drug target for neurodegenerative diseases
Molecular Neurodegeneration (2023)
-
The ubiquitin-dependent ATPase p97 removes cytotoxic trapped PARP1 from chromatin
Nature Cell Biology (2022)
-
The phosphorylation and dephosphorylation switch of VCP/p97 regulates the architecture of centrosome and spindle
Cell Death & Differentiation (2022)
-
K29-linked ubiquitin signaling regulates proteotoxic stress response and cell cycle
Nature Chemical Biology (2021)
-
Understanding the birth of rupture-prone and irreparable micronuclei
Chromosoma (2020)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.