Abstract
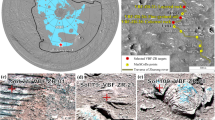
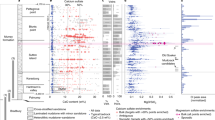
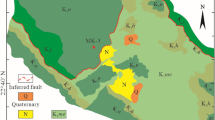
Gusev crater was selected as the landing site for the Spirit rover because of the possibility that it once held a lake. Thus one of the rover's tasks was to search for evidence of lake sediments1. However, the plains at the landing site were found to be covered by a regolith composed of olivine-rich basaltic rock and windblown ‘global’ dust2. The analyses of three rock interiors exposed by the rock abrasion tool showed that they are similar to one another, consistent with having originated from a common lava flow3,4,5,6,7,8. Here we report the investigation of soils, rock coatings and rock interiors by the Spirit rover from sol (martian day) 1 to sol 156, from its landing site to the base of the Columbia hills. The physical and chemical characteristics of the materials analysed provide evidence for limited but unequivocal interaction between water and the volcanic rocks of the Gusev plains. This evidence includes the softness of rock interiors that contain anomalously high concentrations of sulphur, chlorine and bromine relative to terrestrial basalts and martian meteorites9; sulphur, chlorine and ferric iron enrichments in multilayer coatings on the light-toned rock Mazatzal; high bromine concentration in filled vugs and veins within the plains basalts; positive correlations between magnesium, sulphur and other salt components in trench soils; and decoupling of sulphur, chlorine and bromine concentrations in trench soils compared to Gusev surface soils, indicating chemical mobility and separation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Squyres, S. W. et al. Athena Mars rover science investigation. J. Geophys. Res. 108(E12), 8062, doi:10.1029/2003JE002121 (2003)
Squyres, S. W. et al. The Spirit Rover's Athena science investigation at Gusev Crater, Mars. Science 305, 794–799 (2004)
Bell, J. F. III et al. Pancam multispectral imaging results from the Spirit Rover at Gusev Crater. Science 305, 800–806 (2004)
Herkenhoff, K. E. et al. Texture of the soils and rocks at Gusev Crater from Spirit's microscopic imager. Science 305, 824–826 (2004)
Gellert, R. et al. Chemistry of rocks and soils in Gusev Crater from the alpha particle X-ray spectrometer. Science 305, 829–832 (2004)
Morris, R. V. et al. Mineralogy at Gusev Crater from the Mössbauer spectrometer on the Spirit Rover. Science 305, 833–836 (2004)
Christensen, P. R. et al. Initial results from the mini-TES experiment in Gusev Crater from the Spirit Rover. Science 305, 837–842 (2004)
McSween, H. Y. et al. Basaltic rocks analyzed by the Spirit Rover in Gusev Crater. Science 305, 842–845 (2004)
McSween, H. Y. Jr & Treiman, A. in Planetary Materials (ed. Papike, J.) Ch. 6 (Mineralogical Society of America, Washington DC, 1998)
Hunten, D. M. Possible oxidant sources in the atmosphere and surface of Mars. J. Mol. Evol. 14, 71–78 (1979)
Settle, M. Formation and deposition of volcanic sulfate aerosols on Mars. J. Geophys. Res. 84, 8343–8354 (1979)
Arvidson, R. E. et al. Localization and physical properties experiments conducted by Spirit at Gusev Crater. Science 305, 821–824 (2004)
Richardson, M. & Mischna, M. Long-term evolution of transient liquid water on Mars. J. Geophys. Res. 110, doi:10.1029/2004JE002367 (2005)
Greeley, R. et al. Wind-related processes detected by the Spirit Rover at Gusev crater, Mars. Science 305, 810–821 (2004)
Govindaraju, K. Geostandards Newsletter 18 (Special Issue), App. 1, 01–02 (1994)
Bartlett, P. W. et al. Summary of Rock Abrasion Tool (RAT) results pertinent to the Mars Exploration Rover science data set. Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf. XXXVI, abstr. 2292 (2005)
Morris, R. V. et al. Abundance and speciation of water and sulfate at Gusev crater and Meridiani planum. Lunar Planet. Sci. Conf. XXXVI, abstr. 2239 (2005)
Morris, R. V. et al. Mineralogy, composition, and alteration of Mars Pathfinder rocks and soils: Evidence from multispectral, elemental, and magnetic data on terrestrial analogue, SNC meteorite, and Pathfinder samples. J. Geophys. Res. 105, 1757–1817 (2000)
Clark, B. C. et al. Chemical composition of Martian fines. J. Geophys. Res. 87, 10059–10067 (1982)
Grant, J. A. et al. Surficial deposits at Gusev Crater along Spirit Rover traverses. Science 305, 807–809 (2004)
Wang, A. et al. Raman spectroscopic characterization of a highly weathered basalt: igneous mineralogy, alteration products, and a microorganism. J. Geophys. Res. 104, 27067–27077 (1999)
Lide, D. R. Handbook of Chemistry and Physics 82nd edn 4–84 (CRC Press, New York, 2001)
Gooding, J. L. & Keil, K. Alteration of glass as a possible source of clay minerals on Mars. Geophys. Res. Lett. 5, 727–730 (1978)
Gooding, J. L. Soil mineralogy and chemistry on Mars: Possible clues from salts and clays in SNC meteorites. Icarus 99, 28–41 (1992)
Yen, A. et al. An integrated view of the chemistry and mineralogy of martian soils. Nature doi:10.1038/nature03637 (this issue)
Clark, B. C. Geochemical components in Martian soils. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 57, 4575–4581 (1993)
Haskin, L. A. et al. On estimating ejecta deposit thicknesses and proportions of materials from distant basins at lunar highland sites. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 38, 13–33 (2003)
Gorevan, S. P. et al. Rock Abrasion Tool: Mars Exploration Rover mission. J. Geophys. Res. 108, 8068, doi:10.1029/2003JE002061 (2003)
Acknowledgements
Larry A. Haskin, the lead author of this manuscript, died on 24 March 2005. Larry will be remembered by the Athena Science Team for his dedication since the start of the Athena Science Instrument Payload, for his leadership in developing the Mars Microbeam Raman Spectrometer, and for his contributions during the Mars Exploration Rover mission. We thank the NASA Mars programme for support of our participations in the Mars Exploration Rover mission. We thank the Jet Propulsion Laboratory management and the engineering teams for their handling of the rover, sometimes under trying circumstances. We thank K. Kuebler, L. Keszthelyi, M. Blinder and V. Thomas-Holmes for special assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Reprints and permissions information is available at npg.nature.com/reprintsandpermissions. The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haskin, L., Wang, A., Jolliff, B. et al. Water alteration of rocks and soils on Mars at the Spirit rover site in Gusev crater. Nature 436, 66–69 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03640
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03640
This article is cited by
-
Young volcanic terrains are windows into early microbial colonization
Communications Earth & Environment (2024)
-
The InSight HP3 Penetrator (Mole) on Mars: Soil Properties Derived from the Penetration Attempts and Related Activities
Space Science Reviews (2022)
-
Geology of the InSight landing site on Mars
Nature Communications (2020)
-
Natural variation among Arabidopsis thaliana accessions in tolerance to high magnesium supply
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
A Pre-Landing Assessment of Regolith Properties at the InSight Landing Site
Space Science Reviews (2018)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.