Abstract
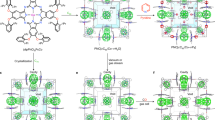
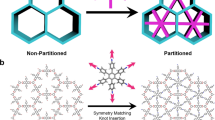
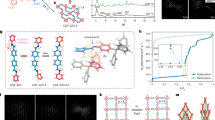
One of the outstanding challenges in the field of porous materials is the design and synthesis of chemical structures with exceptionally high surface areas1. Such materials are of critical importance to many applications involving catalysis, separation and gas storage. The claim for the highest surface area of a disordered structure is for carbon, at 2,030 m2 g-1 (ref. 2). Until recently, the largest surface area of an ordered structure was that of zeolite Y, recorded at 904 m2 g-1 (ref. 3). But with the introduction of metal-organic framework materials, this has been exceeded, with values up to 3,000 m2 g-1 (refs 4–7). Despite this, no method of determining the upper limit in surface area for a material has yet been found. Here we present a general strategy that has allowed us to realize a structure having by far the highest surface area reported to date. We report the design, synthesis and properties of crystalline Zn4O(1,3,5-benzenetribenzoate)2, a new metal-organic framework with a surface area estimated at 4,500 m2 g-1. This framework, which we name MOF-177, combines this exceptional level of surface area with an ordered structure that has extra-large pores capable of binding polycyclic organic guest molecules—attributes not previously combined in one material.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Davis, M. E. Ordered porous materials for emerging applications. Nature 417, 813–821 (2002)
Nijkamp, M. G., Raaymakers, J. E., van Dillen, A. J. & de Jong, K. P. Hydrogen storage using physisorption-materials demands. Appl. Phys. A 72, 619–623 (2001)
Chester, A. W., Clement, P. & Han, S. Faujasite zeolitic materials. US patent 6,136,291A (24 October 2000).
Li, H., Eddaoudi, M., O'Keeffe, M. & Yaghi, O. M. Design and synthesis of an exceptionally stable and highly porous metal-organic framework. Nature 402, 276–279 (1999)
Eddaoudi, M. et al. Systematic design of pore size and functionality in isoreticular MOFs and their application in methane storage. Science 295, 469–472 (2002)
Noro, S. et al. Framework engineering by anions and porous functionalities of Cu(II)/4,4′-bpy coordination polymers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 2568–2583 (2002)
Seki, K., Takamizawa, S. & Mori, W. Design and gas adsorption property of a three-dimensional coordination polymer with a stable and highly porous framework. Chem. Lett. 30, 332–333 (2001)
Connolly, M. L. Solvent accessible surfaces of proteins and nucleic acids. Science 221, 709–713 (1983)
Yaghi, O. M. et al. Reticular synthesis and the design of new materials. Nature 423, 705–714 (2003)
Delgado-Friedrichs, O., O'Keeffe, M. & Yaghi, O. M. Three-periodic nets and tilings: regular and quasiregular nets. Acta Crystallogr. A 59, 22–27 (2003)
Chae, H. K., Kim, J., Delgado-Friedrichs, O., O'Keeffe, M. & Yaghi, O. M. Design of frameworks with mixed triangular and octahedral building blocks exemplified by the structure of Zn4O(TCA)2 having the pyrite topology (TCA = 4,4′,4″ tricarboxytriphenylamine). Angew. Chem. Int. Edn Engl. 42, 3907–3909 (2003)
Chen, B., Eddaoudi, M., Hyde, T., O'Keeffe, M & Yaghi, O. Interwoven metal-organic framework on a periodic minimal surface with extra-large pores. Science 291, 1021–1023 (2001)
De Vos, D. E. & Jacobs, P. A. Zeolite-based supramolecular assemblies. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 137, 957–985 (2001)
Sato, K., Nishimura, Y., Honna, K., Matsubayashi, N. & Shimada, H. Role of HY zeolite mesopores in hydrocracking of heavy oils. J. Catal. 200, 288–297 (2001)
Kahr, B. & Gurney, R. W. Dyeing crystals. Chem. Rev. 101, 893–951 (2001)
Acknowledgements
Initial phases of this work were carried out by H. Li and scale-up was performed by A. Benin. We are grateful to the NSF and the DOE for support of various aspects of this programme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
41586_2004_BFnature02311_MOESM1_ESM.doc
Supplementary information file containing: (1) X-ray crystallographic data for MOF-177;(2) Thermal Gravimetric Analysis (TGA) for MOF-177;(3) Powder X-ray patterns showing the stability of the MOF-177 framework after removal of solvent from the pores by heating. (DOC 12390 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chae, H., Siberio-Pérez, D., Kim, J. et al. A route to high surface area, porosity and inclusion of large molecules in crystals. Nature 427, 523–527 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02311
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02311
This article is cited by
-
Two-dimensional nanomaterials induced nano-bio interfacial effects and biomedical applications in cancer treatment
Journal of Nanobiotechnology (2024)
-
Exploring modern developments in diverse 2D photocatalysts for water oxidation
Journal of Porous Materials (2024)
-
High-throughput screening of hypothetical metal-organic frameworks for thermal conductivity
npj Computational Materials (2023)
-
Chalcogen-bridged coordination polymer for the photocatalytic activation of aryl halides
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Embedded nano spin sensor for in situ probing of gas adsorption inside porous organic frameworks
Nature Communications (2023)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.