Abstract
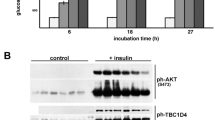
Insulin stimulates glucose transport by promoting exocytosis of the glucose transporter Glut4 (refs 1, 2). The dynamic processes involved in the trafficking of Glut4-containing vesicles, and in their targeting, docking and fusion at the plasma membrane, as well as the signalling processes that govern these events, are not well understood. We recently described tyrosine-phosphorylation events restricted to subdomains of the plasma membrane that result in activation of the G protein TC10 (refs 3, 4). Here we show that TC10 interacts with one of the components of the exocyst complex, Exo70. Exo70 translocates to the plasma membrane in response to insulin through the activation of TC10, where it assembles a multiprotein complex that includes Sec6 and Sec8. Overexpression of an Exo70 mutant blocked insulin-stimulated glucose uptake, but not the trafficking of Glut4 to the plasma membrane. However, this mutant did block the extracellular exposure of the Glut4 protein. So, the exocyst might have a crucial role in the targeting of the Glut4 vesicle to the plasma membrane, perhaps directing the vesicle to the precise site of fusion.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saltiel, A. R. & Kahn, C. R. Insulin signalling and the regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism. Nature 414, 799–806 (2001)
Bryant, N. J., Govers, R. & James, D. E. Regulated transport of the glucose transporter GLUT4. Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 3, 267–277 (2002)
Chiang, S. H. et al. Insulin-stimulated GLUT4 translocation requires the CAP-dependent activation of TC10. Nature 410, 944–948 (2001)
Liu, J., Kimura, A., Baumann, C. A. & Saltiel, A. R. APS facilitates c-Cbl tyrosine phosphorylation and GLUT4 translocation in response to insulin in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 22, 3599–3609 (2002)
Neudauer, C. L., Joberty, G., Tatsis, N. & Macara, I. G. Distinct cellular effects and interactions of the Rho-family GTPase TC10. Curr. Biol. 8, 1151–1160 (1998)
TerBush, D. R., Maurice, T., Roth, D. & Novick, P. The exocyst is a multiprotein complex required for exocytosis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 15, 6483–6494 (1996)
Kee, Y. et al. Subunit structure of the mammalian exocyst complex. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 94, 14438–14443 (1997)
Symons, M. Rho family GTPases: the cytoskeleton and beyond. Trends Biochem. Sci. 21, 178–181 (1996)
Tapon, N. & Hall, A. Rho, Rac, and Cdc42 GTPases regulate the organization of the actin cytoskeleton. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 9, 86–92 (1997)
Van Aelst, L. & D'Souza-Schorey, C. Rho GTPases and signaling networks. Genes Dev. 11, 2295–2322 (1997)
Chiang, S. H., Hou, J. C., Hwang, J., Pessin, J. E. & Saltiel, A. R. Cloning and functional characterization of related TC10 isoforms, a subfamily of Rho proteins involved in insulin-stimulated glucose transport. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 13067–13073 (2002)
Hsu, S. C., Hazuka, C. D., Foletti, D. L. & Scheller, R. H. Targeting vesicles to specific sites on the plasma membrane: the role of the sec6/8 complex. Trends Cell. Biol. 9, 150–153 (1999)
Guo, W., Sacher, M., Barrowman, J., Ferro-Novick, S. & Novick, P. Protein complexes in transport vesicle targeting. Trends Cell Biol. 10, 251–255 (2000)
Lipschutz, J. H. & Mostov, K. E. Exocytosis: the many masters of the exocyst. Curr. Biol. 12, R212–R214 (2002)
Ting, A. E. et al. rSec6 and rSec8, mammalian homologs of yeast proteins essential for secretion. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 92, 9613–9617 (1995)
Yeaman, C., Grindstaff, K. K., Wright, J. R. & Nelson, W. J. Sec6/8 complexes on trans-Golgi network and plasma membrane regulate late stages of exocytosis in mammalian cells. J. Cell Biol. 155, 593–604 (2001)
Kimura, A., Baumann, C. A., Chiang, S. H. & Saltiel, A. R. The sorbin homology domain: a motif for the targeting of proteins to lipid rafts. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 98, 9098–9103 (2001)
Dawson, K., Aviles-Hernandez, A., Cushman, S. W. & Malide, D. Insulin-regulated trafficking of dual-labelled glucose transporter 4 in primary rat adipose cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 287, 445–454 (2001)
Novick, P. & Guo, W. Ras family therapy: Rab, Rho and Ral talk to the exocyst. Trends Cell Biol. 12, 247–249 (2002)
Cheatham, B. GLUT4 and company: SNAREing roles in insulin-regulated glucose uptake. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 11, 356–361 (2000)
Chamberlain, L. H. & Gould, G. W. The v-and t-SNARE proteins that mediate Glut4 vesicle fusion are localised in detergent-insoluble lipid rafts present on distinct intracellular membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 49750–49754 (2002)
Sherman, L. A., Hirshman, M. F., Cormont, M., Le Marchand-Brustel, Y. & Goodyear, L. J. Differential effects of insulin and exercise on Rab4 distribution in rat skeletal muscle. Endocrinology 137, 266–273 (1996)
Cormont, M. et al. Potential role of Rab4 in the regulation of subcellular localization of Glut4 in adipocytes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 16, 6879–6886 (1996)
Shisheva, A. & Czech, M. P. Association of cytosolic Rab4 with GDI isoforms in insulin-sensitive 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Biochemistry 36, 6564–6570 (1997)
Millar, C. A., Shewan, A., Hickson, G. R., James, D. E. & Gould, G. W. Differential regulation of secretory compartments containing the insulin-responsive glucose transporter 4 in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Mol. Biol. Cell 10, 3675–3688 (1999)
Chang, L., Adams, R. D. & Saltiel, A. R. The TC10-interacting protein CIP4/2 is required for insulin-stimulated Glut4 translocation in 3T3L1 adipocytes. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 99, 12835–12840 (2002)
Lin, D. et al. A mammalian PAR-3–PAR-6 complex implicated in Cdc42/Rac1 and aPKC signalling and cell polarity. Nature Cell Biol. 2, 540–547 (2000)
Thurmond, D. C. et al. Regulation of insulin-stimulated GLUT4 translocation by Munc18c in 3T3L1 adipocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 33876–33883 (1998)
Hwang, J. B. & Frost, S. C. Effect of alternative glycosylation on insulin receptor processing. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 22813–22820 (1999)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health. We thank T-H. Chun for helpful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Inoue, M., Chang, L., Hwang, J. et al. The exocyst complex is required for targeting of Glut4 to the plasma membrane by insulin. Nature 422, 629–633 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01533
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01533
This article is cited by
-
Obesity causes mitochondrial fragmentation and dysfunction in white adipocytes due to RalA activation
Nature Metabolism (2024)
-
Exo70 intracellular redistribution after repeated mild traumatic brain injury
Biological Research (2021)
-
An active tethering mechanism controls the fate of vesicles
Nature Communications (2021)
-
TC10 regulates breast cancer invasion and metastasis by controlling membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase at invadopodia
Communications Biology (2021)
-
Proteomic Profiling of Small Extracellular Vesicles Secreted by Human Pancreatic Cancer Cells Implicated in Cellular Transformation
Scientific Reports (2020)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.