Abstract
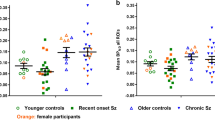
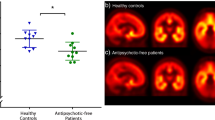
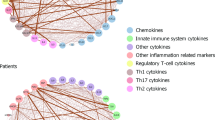
Positron emission tomography (PET) imaging of the 18 kDa translocator protein (TSPO) has been used to investigate whether microglial activation, an indication of neuroinflammation, is evident in the brain of adults with schizophrenia. Interpretation of these studies is confounded by potential modulatory effects of antipsychotic medication on microglial activity. In the first such study in antipsychotic-free schizophrenia, we have used [11C](R)-PK11195 PET to compare TSPO availability in a predominantly antipsychotic-naive group of moderate-to-severely symptomatic unmedicated patients (n=8), similarly symptomatic medicated patients with schizophrenia taking risperidone or paliperidone by regular intramuscular injection (n=8), and healthy comparison subjects (n=16). We found no evidence for increased TSPO availability in antipsychotic-free patients compared with healthy controls (mean difference 4%, P=0.981). However, TSPO availability was significantly elevated in medicated patients (mean increase 88%, P=0.032) across prefrontal (dorsolateral, ventrolateral, orbital), anterior cingulate and parietal cortical regions. In the patients, TSPO availability was also strongly correlated with negative symptoms measured using the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale across all the brain regions investigated (r=0.651–0.741). We conclude that the pathophysiology of schizophrenia is not associated with microglial activation in the 2–6 year period following diagnosis. The elevation in the medicated patients may be a direct effect of the antipsychotic, although this study cannot exclude treatment resistance and/or longer illness duration as potential explanations. It also remains to be determined whether it is present only in a subset of patients, represents a pro- or anti-inflammatory state, its association with primary negative symptoms, and whether there are significant differences between antipsychotics.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
McGrath J, Saha S, Welham J, El Saadi O, MacCauley C, Chant D . A systematic review of the incidence of schizophrenia: the distribution of rates and the influence of sex, urbanicity, migrant status and methodology. BMC Med 2004; 2: 13.
Brown AS, Derkits EJ . Prenatal infection and schizophrenia: a review of epidemiologic and translational studies. Am J Psychiatry 2010; 167: 261–280.
Chaudhry IB, Hallak J, Husain N, Minhas F, Stirling J, Richardson P et al. Minocycline benefits negative symptoms in early schizophrenia: a randomised double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial in patients on standard treatment. J Psychopharmacol 2012; 26: 1185–1193.
Ghanizadeh A, Dehbozorgi S, OmraniSigaroodi M, Rezaei Z . Minocycline as add-on treatment decreases the negative symptoms of schizophrenia; a randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial. Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov 2014; 8: 211–215.
Levkovitz Y, Mendlovich S, Riwkes S, Braw Y, Levkovitch-Verbin H, Gal G et al. A double-blind, randomized study of minocycline for the treatment of negative and cognitive symptoms in early-phase schizophrenia. J Clin Psychiatry 2010; 71: 138–149.
Eaton WW, Byrne M, Ewald H, Mors O, Chen CY, Agerbo E et al. Association of schizophrenia and autoimmune diseases: linkage of Danish national registers. Am J Psychiatry 2006; 163: 521–528.
Irani SR, Bera K, Waters P, Zuliani L, Maxwell S, Zandi MS et al. N-methyl-D-aspartate antibody encephalitis: temporal progression of clinical and paraclinical observations in a predominantly non-paraneoplastic disorder of both sexes. Brain 2010; 133: 1655–1667.
Purcell SM, Wray NR, Stone JL, Visscher PM, O'Donovan MC, Sullivan PF et al. Common polygenic variation contributes to risk of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Nature 2009; 460: 748–752.
Shi J, Levinson DF, Duan J, Sanders AR, Zheng Y, Pe'er I et al. Common variants on chromosome 6p22.1 are associated with schizophrenia. Nature 2009; 460: 753–757.
Stefansson H, Ophoff RA, Steinberg S, Andreassen OA, Cichon S, Rujescu D et al. Common variants conferring risk of schizophrenia. Nature 2009; 460: 744–747.
Potvin S, Stip E, Sepehry AA, Gendron A, Bah R, Kouassi E . Inflammatory cytokine alterations in schizophrenia: a systematic quantitative review. Biol Psychiatry 2008; 63: 801–808.
Miller BJ, Buckley P, Seabolt W, Mellor A, Kirkpatrick B . Meta-analysis of cytokine alterations in schizophrenia: clinical status and antipsychotic effects. Biol Psychiatry 2011; 70: 663–671.
Upthegrove R, Manzanares-Teson N, Barnes NM . Cytokine function in medication-naive first episode psychosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Schizophr Res 2014; 155: 101–108.
Radewicz K, Garey LJ, Gentleman SM, Reynolds R . Increase in HLA-DR immunoreactive microglia in frontal and temporal cortex of chronic schizophrenics. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2000; 59: 137–150.
Fillman SG, Cloonan N, Catts VS, Miller LC, Wong J, McCrossin T et al. Increased inflammatory markers identified in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of individuals with schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 2013; 18: 206–214.
Bayer TA, Buslei R, Havas L, Falkai P . Evidence for activation of microglia in patients with psychiatric illnesses. Neurosci Lett 1999; 271: 126–128.
van Berckel BN, Bossong MG, Boellaard R, Kloet R, Schuitemaker A, Caspers E et al. Microglia activation in recent-onset schizophrenia: a quantitative (R)-[11C]PK11195 positron emission tomography study. Biol Psychiatry 2008; 64: 820–822.
Doorduin J, de Vries EF, Willemsen AT, de Groot JC, Dierckx RA, Klein HC . Neuroinflammation in schizophrenia-related psychosis: a PET study. J Nucl Med 2009; 50: 1801–1807.
Bloomfield PS, Selvaraj S, Veronese M, Rizzo G, Bertoldo A, Owen DR et al. Microglial activity in people at ultra high risk of psychosis and in schizophrenia: an [(11)C]PBR28 PET brain imaging study. Am J Psychiatry 2016; 173: 44–52.
Takano A, Arakawa R, Ito H, Tateno A, Takahashi H, Matsumoto R et al. Peripheral benzodiazepine receptors in patients with chronic schizophrenia: a PET study with [11C]DAA1106. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 2010; 13: 943–950.
Kenk M, Selvanathan T, Rao N, Suridjan I, Rusjan P, Remington G et al. Imaging neuroinflammation in gray and white matter in schizophrenia: an in vivo PET study with [18F]-FEPPA. Schizophr Bull 2015; 41: 85–93.
Coughlin JM, Wang Y, Ambinder EB, Ward RE, Minn I, Vranesic M et al. In vivo markers of inflammatory response in recent-onset schizophrenia: a combined study using [(11)C]DPA-713 PET and analysis of CSF and plasma. Transl Psychiatry 2016; 6: e777.
Monji A, Kato TA, Mizoguchi Y, Horikawa H, Seki Y, Kasai M et al. Neuroinflammation in schizophrenia especially focused on the role of microglia. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2013; 42: 115–121.
Kluge M, Schuld A, Schacht A, Himmerich H, Dalal MA, Wehmeier PM et al. Effects of clozapine and olanzapine on cytokine systems are closely linked to weight gain and drug-induced fever. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2009; 34: 118–128.
Danovich L, Veenman L, Leschiner S, Lahav M, Shuster V, Weizman A et al. The influence of clozapine treatment and other antipsychotics on the 18 kDa translocator protein, formerly named the peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptor, and steroid production. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 2008; 18: 24–33.
Cotel MC, Lenartowicz EM, Natesan S, Modo MM, Cooper JD, Williams SC et al. Microglial activation in the rat brain following chronic antipsychotic treatment at clinically relevant doses. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 2015; 25: 2098–2107.
Perry VH, Nicoll JA, Holmes C . Microglia in neurodegenerative disease. Nat Rev Neurol 2010; 6: 193–201.
Knegtering R, Baselmans P, Castelein S, Bosker F, Bruggeman R, van den Bosch RJ . Predominant role of the 9-hydroxy metabolite of risperidone in elevating blood prolactin levels. Am J Psychiatry 2005; 162: 1010–1012.
Vita A, De Peri L, Deste G, Sacchetti E . Progressive loss of cortical gray matter in schizophrenia: a meta-analysis and meta-regression of longitudinal MRI studies. Transl Psychiatry Psychiatry 2012; 2: e190.
First MB, Spitzer RL, Gibbon M, Williams JBW . Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV-TR Axis I Disorders, Research Version, Patient Edition. (SCID-I/P). Biometrics Research, New York State Psychiatric Institute: New York, NY, USA, 2002.
Kay SR, Fiszbein A, Opler LA . The positive and negative syndrome scale (PANSS) for schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 1987; 13: 261–276.
Talbot PS, Bradley S, Clarke CP, Babalola KO, Philipp AW, Brown G et al. Brain serotonin transporter occupancy by oral sibutramine dosed to steady state: a PET study using (11)C-DASB in healthy humans. Neuropsychopharmacology 2010; 35: 741–751.
Shah F, Hume SP, Pike VW, Ashworth S, McDermott J . Synthesis of the enantiomers of [N-methyl-11C]PK 11195 and comparison of their behaviours as radioligands for PK binding sites in rats. Nucl Med Biol 1994; 21: 573–581.
Su Z, Herholz K, Gerhard A, Roncaroli F, Du Plessis D, Jackson A et al. [11C]-(R)PK11195 tracer kinetics in the brain of glioma patients and a comparison of two referencing approaches. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2013; 40: 1406–1419.
Hudson HM, Larkin RS . Accelerated image reconstruction using ordered subsets of projection data. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 1994; 13: 601–609.
Hong IK, Chung ST, Kim HK, Kim YB, Son YD, Cho ZH . Ultra fast symmetry and SIMD-based projection-backprojection (SSP) algorithm for 3-D PET image reconstruction. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 2007; 26: 789–803.
Cizek J, Herholz K, Vollmar S, Schrader R, Klein J, Heiss WD . Fast and robust registration of PET and MR images of human brain. Neuroimage 2004; 22: 434–442.
Ashburner J, Friston KJ . Unified segmentation. Neuroimage 2005; 26: 839–851.
Hammers A, Allom R, Koepp MJ, Free SL, Myers R, Lemieux L et al. Three-dimensional maximum probability atlas of the human brain, with particular reference to the temporal lobe. Hum Brain Mapp 2003; 19: 224–247.
Gousias IS, Rueckert D, Heckemann RA, Dyet LE, Boardman JP, Edwards AD et al. Automatic segmentation of brain MRIs of 2-year-olds into 83 regions of interest. Neuroimage 2008; 40: 672–684.
Innis RB, Cunningham VJ, Delforge J, Fujita M, Gjedde A, Gunn RN et al. Consensus nomenclature for in vivo imaging of reversibly binding radioligands. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2007; 27: 1533–1539.
Lammertsma AA, Hume SP . Simplified reference tissue model for PET receptor studies. Neuroimage 1996; 4: 153–158.
Gunn RN, Lammertsma AA, Hume SP, Cunningham VJ . Parametric imaging of ligand-receptor binding in PET using a simplified reference region model. Neuroimage 1997; 6: 279–287.
Doble A, Malgouris C, Daniel M, Daniel N, Imbault F, Basbaum A et al. Labelling of peripheral-type benzodiazepine binding sites in human brain with [3H]PK 11195: anatomical and subcellular distribution. Brain Res Bull 1987; 18: 49–61.
Kumar A, Muzik O, Shandal V, Chugani D, Chakraborty P, Chugani HT . Evaluation of age-related changes in translocator protein (TSPO) in human brain using (11)C-[R]-PK11195 PET. J Neuroinflammation 2012; 9: 232.
Narendran R, Frankle WG . Comment on analyses and conclusions of "microglial activity in people at ultra high risk of psychosis and in schizophrenia: an [(11)C]PBR28 PET brain imaging study". Am J Psychiatry 2016; 173: 536–537.
Kapur S, VanderSpek SC, Brownlee BA, Nobrega JN . Antipsychotic dosing in preclinical models is often unrepresentative of the clinical condition: a suggested solution based on in vivo occupancy. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2003; 305: 625–631.
Dickens AM, Vainio S, Marjamaki P, Johansson J, Lehtiniemi P, Rokka J et al. Detection of microglial activation in an acute model of neuroinflammation using PET and radiotracers 11C-(R)-PK11195 and 18F-GE-180. J Nucl Med 2014; 55: 466–472.
Varga B, Marko K, Hadinger N, Jelitai M, Demeter K, Tihanyi K et al. Translocator protein (TSPO 18kDa) is expressed by neural stem and neuronal precursor cells. Neurosci Lett 2009; 462: 257–262.
Cazzullo CL, Sacchetti E, Galluzzo A, Panariello A, Adorni A, Pegoraro M et al. Cytokine profiles in schizophrenic patients treated with risperidone: a 3-month follow-up study. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2002; 26: 33–39.
Kato T, Monji A, Hashioka S, Kanba S . Risperidone significantly inhibits interferon-gamma-induced microglial activation in vitro. Schizophr Res 2007; 92: 108–115.
Zhang XY, Zhou DF, Cao LY, Zhang PY, Wu GY, Shen YC . Changes in serum interleukin-2, -6, and -8 levels before and during treatment with risperidone and haloperidol: relationship to outcome in schizophrenia. J Clin Psychiatry 2004; 65: 940–947.
Sugino H, Futamura T, Mitsumoto Y, Maeda K, Marunaka Y . Atypical antipsychotics suppress production of proinflammatory cytokines and up-regulate interleukin-10 in lipopolysaccharide-treated mice. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2009; 33: 303–307.
Kim DJ, Kim W, Yoon SJ, Go HJ, Choi BM, Jun TY et al. Effect of risperidone on serum cytokines. Int J Neurosci 2001; 111: 11–19.
Fusar-Poli P, Smieskova R, Kempton MJ, Ho BC, Andreasen NC, Borgwardt S . Progressive brain changes in schizophrenia related to antipsychotic treatment? A meta-analysis of longitudinal MRI studies. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2013; 37: 1680–1691.
Dorph-Petersen KA, Pierri JN, Perel JM, Sun Z, Sampson AR, Lewis DA . The influence of chronic exposure to antipsychotic medications on brain size before and after tissue fixation: a comparison of haloperidol and olanzapine in macaque monkeys. Neuropsychopharmacology 2005; 30: 1649–1661.
Vernon AC, Natesan S, Modo M, Kapur S . Effect of chronic antipsychotic treatment on brain structure: a serial magnetic resonance imaging study with ex vivo and postmortem confirmation. Biol Psychiatry 2011; 69: 936–944.
Vernon AC, Natesan S, Crum WR, Cooper JD, Modo M, Williams SC et al. Contrasting effects of haloperidol and lithium on rodent brain structure: a magnetic resonance imaging study with postmortem confirmation. Biol Psychiatry 2012; 71: 855–863.
Vernon AC, Crum WR, Lerch JP, Chege W, Natesan S, Modo M et al. Reduced cortical volume and elevated astrocyte density in rats chronically treated with antipsychotic drugs-linking magnetic resonance imaging findings to cellular pathology. Biol Psychiatry 2014; 75: 982–990.
Agid O, Mamo D, Ginovart N, Vitcu I, Wilson AA, Zipursky RB et al. Striatal vs extrastriatal dopamine D2 receptors in antipsychotic response—a double-blind PET study in schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology 2007; 32: 1209–1215.
Kegeles LS, Slifstein M, Frankle WG, Xu X, Hackett E, Bae SA et al. Dose-occupancy study of striatal and extrastriatal dopamine D2 receptors by aripiprazole in schizophrenia with PET and [18F]fallypride. Neuropsychopharmacology 2008; 33: 3111–3125.
Mondelli V, Ciufolini S, Belvederi Murri M, Bonaccorso S, Di Forti M, Giordano A et al. Cortisol and inflammatory biomarkers predict poor treatment response in first episode psychosis. Schizophr Bull 2015; 41: 1162–1170.
Dodel R, Spottke A, Gerhard A, Reuss A, Reinecker S, Schimke N et al. Minocycline 1-year therapy in multiple-system-atrophy: effect on clinical symptoms and [(11)C] (R)-PK11195 PET (MEMSA-trial). Mov Disord 2010; 25: 97–107.
Tynan RJ, Weidenhofer J, Hinwood M, Cairns MJ, Day TA, Walker FR . A comparative examination of the anti-inflammatory effects of SSRI and SNRI antidepressants on LPS stimulated microglia. Brain Behav Immun 2012; 26: 469–479.
Singh SP, Singh V, Kar N, Chan K . Efficacy of antidepressants in treating the negative symptoms of chronic schizophrenia: meta-analysis. Br J Psychiatry 2010; 197: 174–179.
Setiawan E, Wilson AA, Mizrahi R, Rusjan PM, Miler L, Rajkowska G et al. Role of translocator protein density, a marker of neuroinflammation, in the brain during major depressive episodes. JAMA Psychiatry 2015; 72: 268–275.
Kalk NJ, Owen DR, Tyacke RJ, Reynolds R, Rabiner EA, Lingford-Hughes AR et al. Are prescribed benzodiazepines likely to affect the availability of the 18 kDa translocator protein (TSPO) in PET studies? Synapse 2013; 67: 909–912.
Kropholler MA, Boellaard R, van Berckel BN, Schuitemaker A, Kloet RW, Lubberink MJ et al. Evaluation of reference regions for (R)-[(11)C]PK11195 studies in Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2007; 27: 1965–1974.
Drake C, Boutin H, Jones MS, Denes A, McColl BW, Selvarajah JR et al. Brain inflammation is induced by co-morbidities and risk factors for stroke. Brain Behav Immun 2011; 25: 1113–1122.
Su Z, Roncaroli F, Durrenberger PF, Coope DJ, Karabatsou K, Hinz R et al. The 18-kDa mitochondrial translocator protein in human gliomas: an 11C-(R)PK11195 PET imaging and neuropathology study. J Nucl Med 2015; 56: 512–517.
Hunter HJA, Hinz R, Gerhard A, Talbot PS, Su Z, Holland G et al. Brain inflammation and psoriasis: a [11C]-(R)-PK11195 positron emission tomography study. Br J Dermatol 2016; doi:10.1111/bjd.13788.
Acknowledgements
This study was partly funded by the award of the Margaret Temple grant from the British Medical Association’s Board of Science to SEH, and financial support was provided by Professor Karl Herholz and the University of Manchester’s Magnetic Resonance Imaging Facility (MRIF). AG and RH have received funding from the European Union’s Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007-2013) under Grant Agreement Number HEALTH-F2-2011-278850 (INMiND). The authors acknowledge the contributions of operational staff at the Wolfson Molecular Imaging Centre, including Elizabeth Barnett and Carrie-Anne Mellor for processing of blood samples; Michael Green, Team Leader for Radiochemistry Production; PET radiographers Mike Godfrey, Eleanor Duncan-Rouse and Gerrit Helms van der Vegte; and MR Radiographers Amy Watkins and Barry Whitnall. Recruitment was supported by staff of the National Institute for Health Research Clinical Research Network: Greater Manchester.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Molecular Psychiatry website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Holmes, S., Hinz, R., Drake, R. et al. In vivo imaging of brain microglial activity in antipsychotic-free and medicated schizophrenia: a [11C](R)-PK11195 positron emission tomography study. Mol Psychiatry 21, 1672–1679 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2016.180
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2016.180
This article is cited by
-
Microglia sequelae: brain signature of innate immunity in schizophrenia
Translational Psychiatry (2022)
-
The utility of PET imaging in the diagnosis and management of psychosis: a brief review
Clinical and Translational Imaging (2022)
-
Increased levels of midbrain immune-related transcripts in schizophrenia and in murine offspring after maternal immune activation
Molecular Psychiatry (2021)
-
Haploinsufficiency of the schizophrenia and autism risk gene Cyfip1 causes abnormal postnatal hippocampal neurogenesis through microglial and Arp2/3 mediated actin dependent mechanisms
Translational Psychiatry (2021)
-
Neuroinflammation as measured by positron emission tomography in patients with recent onset and established schizophrenia: implications for immune pathogenesis
Molecular Psychiatry (2021)