Abstract
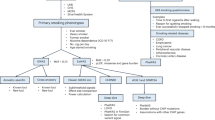
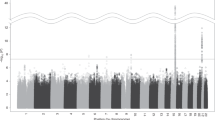
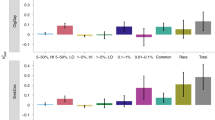
Genetic and functional studies have revealed that both common and rare variants of several nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunits are associated with nicotine dependence (ND). In this study, we identified variants in 30 candidate genes including nicotinic receptors in 200 sib pairs selected from the Mid-South Tobacco Family population with equal numbers of African Americans (AAs) and European Americans (EAs). We selected 135 of the rare and common variants and genotyped them in the Mid-South Tobacco Case–Control (MSTCC) population, which consists of 3088 AAs and 1430 EAs. None of the genotyped common variants showed significant association with smoking status (smokers vs non-smokers), Fagerström Test for ND scores or indexed cigarettes per day after Bonferroni correction. Rare variants in NRXN1, CHRNA9, CHRNA2, NTRK2, GABBR2, GRIN3A, DNM1, NRXN2, NRXN3 and ARRB2 were significantly associated with smoking status in the MSTCC AA sample, with weighted sum statistic (WSS) P-values ranging from 2.42 × 10−3 to 1.31 × 10−4 after 106 phenotype rearrangements. We also observed a significant excess of rare nonsynonymous variants exclusive to EA smokers in NRXN1, CHRNA9, TAS2R38, GRIN3A, DBH, ANKK1/DRD2, NRXN3 and CDH13 with WSS P-values between 3.5 × 10−5 and 1 × 10−6. Variants rs142807401 (A432T) and rs139982841 (A452V) in CHRNA9 and variants V132L, V389L, rs34755188 (R480H) and rs75981117 (N549S) in GRIN3A are of particular interest because they are found in both the AA and EA samples. A significant aggregate contribution of rare and common coding variants in CHRNA9 to the risk for ND (SKAT-C: P=0.0012) was detected by applying the combined sum test in MSTCC EAs. Together, our results indicate that rare variants alone or combined with common variants in a subset of 30 biological candidate genes contribute substantially to the risk of ND.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
TAG. Genome-wide meta-analyses identify multiple loci associated with smoking behavior. Nat Genet 2010; 42: 441–447.
Thorgeirsson TE, Gudbjartsson DF, Surakka I, Vink JM, Amin N, Geller F et al. Sequence variants at CHRNB3-CHRNA6 and CYP2A6 affect smoking behavior. Nat Genet 2010; 42: 448–453.
Liu JZ, Tozzi F, Waterworth DM, Pillai SG, Muglia P, Middleton L et al. Meta-analysis and imputation refines the association of 15q25 with smoking quantity. Nat Genet 2010; 42: 436–440.
Gelernter J, Yu Y, Weiss R, Brady K, Panhuysen C, Yang BZ et al. Haplotype spanning TTC12 and ANKK1, flanked by the DRD2 and NCAM1 loci, is strongly associated to nicotine dependence in two distinct American populations. Hum Mol Genet 2006; 15: 3498–3507.
Huang W, Payne TJ, Ma JZ, Beuten J, Dupont RT, Inohara N et al. Significant association of ANKK1 and detection of a functional polymorphism with nicotine dependence in an African-American sample. Neuropsychopharmacology 2009; 34: 319–330.
Tobacco-and-Genetics-Consortium. Genome-wide meta-analyses identify multiple loci associated with smoking behavior. Nat Genet 2010; 42: 441–447.
Beuten J, Ma JZ, Payne TJ, Dupont RT, Quezada P, Huang W et al. Significant association of BDNF haplotypes in European-American male smokers but not in European-American female or African-American smokers. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 2005; 139: 73–80.
Bierut LJ, Madden PA, Breslau N, Johnson EO, Hatsukami D, Pomerleau OF et al. Novel genes identified in a high-density genome wide association study for nicotine dependence. Hum Mol Genet 2007; 16: 24–35.
Nussbaum J, Xu Q, Payne TJ, Ma JZ, Huang W, Gelernter J et al. Significant association of the neurexin-1 gene (NRXN1) with nicotine dependence in European- and African-American smokers. Hum Mol Genet 2008; 17: 1569–1577.
Thorgeirsson TE, Geller F, Sulem P, Rafnar T, Wiste A, Magnusson KP et al. A variant associated with nicotine dependence, lung cancer and peripheral arterial disease. Nature 2008; 452: 638–642.
Rivas MA, Beaudoin M, Gardet A, Stevens C, Sharma Y, Zhang CK et al. Deep resequencing of GWAS loci identifies independent rare variants associated with inflammatory bowel disease. Nat Genet 2011; 43: 1066–1073.
Asselbergs FW, Guo Y, van Iperen EP, Sivapalaratnam S, Tragante V, Lanktree MB et al. Large-scale gene-centric meta-analysis across 32 studies identifies multiple lipid loci. Am J Hum Genet 2012; 91: 823–838.
Diogo D, Kurreeman F, Stahl EA, Liao KP, Gupta N, Greenberg JD et al. Rare, low-frequency, and common variants in the protein-coding sequence of biological candidate genes from GWASs contribute to risk of rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Hum Genet 2013; 92: 15–27.
Wessel J, McDonald SM, Hinds DA, Stokowski RP, Javitz HS, Kennemer M et al. Resequencing of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor genes and association of common and rare variants with the Fagerstrom test for nicotine dependence. Neuropsychopharmacology 2010; 35: 2392–2402.
Xie P, Kranzler HR, Krauthammer M, Cosgrove KP, Oslin D, Anton RF et al. Rare nonsynonymous variants in alpha-4 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor gene protect against nicotine dependence. Biol Psychiatry 2011; 70: 528–536.
Haller G, Druley T, Vallania FL, Mitra RD, Li P, Akk G et al. Rare missense variants in CHRNB4 are associated with reduced risk of nicotine dependence. Hum Mol Genet 2012; 21: 647–655.
Madsen BE, Browning SR . A groupwise association test for rare mutations using a weighted sum statistic. PLoS Genet 2009; 5: e1000384.
Ionita-Laza I, Lee S, Makarov V, Buxbaum JD, Lin X . Sequence kernel association tests for the combined effect of rare and common variants. Am J Hum Genet 2013; 92: 841–853.
Shi G, Rao DC . Optimum designs for next-generation sequencing to discover rare variants for common complex disease. Genet Epidemiol 2011; 35: 572–579.
Li MD, Beuten J, Ma JZ, Payne TJ, Lou XY, Garcia V et al. Ethnic- and gender-specific association of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha4 subunit gene (CHRNA4) with nicotine dependence. Hum Mol Genet 2005; 14: 1211–1219.
Ma JZ, Beuten J, Payne TJ, Dupont RT, Elston RC, Li MD . Haplotype analysis indicates an association between the DOPA decarboxylase (DDC) gene and nicotine dependence. Hum Mol Genet 2005; 14: 1691–1698.
Beuten J, Ma JZ, Payne TJ, Dupont RT, Crews KM, Somes G et al. Single- and multilocus allelic variants within the gabab receptor subunit 2 (GABAB2) gene are significantly associated with nicotine dependence. Am J Hum Genet 2005; 76: 859–864.
Wang S, Yang Z, Ma JZ, Payne TJ, Li MD . Introduction to deep sequencing and its application to drug addiction research with a focus on rare variants. Mol Neurobiol 2014; 49: 601–614.
Li H, Durbin R . Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009; 25: 1754–1760.
Kumar P, Henikoff S, Ng PC . Predicting the effects of coding non-synonymous variants on protein function using the SIFT algorithm. Nat Protoc 2009; 4: 1073–1081.
Adzhubei IA, Schmidt S, Peshkin L, Ramensky VE, Gerasimova A, Bork P et al. A method and server for predicting damaging missense mutations. Nat Methods 2010; 7: 248–249.
Pollard KS, Hubisz MJ, Rosenbloom KR, Siepel A . Detection of nonneutral substitution rates on mammalian phylogenies. Genome Res 2010; 20: 110–121.
Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K, Thomas L, Ferreira MA, Bender D et al. PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet 2007; 81: 559–575.
Morgenthaler S, Thilly WG . A strategy to discover genes that carry multi-allelic or mono-allelic risk for common diseases: a cohort allelic sums test (CAST). Mutation Res 2007; 615: 28–56.
Li B, Leal SM . Methods for detecting associations with rare variants for common diseases: application to analysis of sequence data. Am J Hum Genet 2008; 83: 311–321.
Lee S, Emond MJ, Bamshad MJ, Barnes KC, Rieder MJ, Nickerson DA et al. Optimal unified approach for rare-variant association testing with application to small-sample case-control whole-exome sequencing studies. Am J Hum Genet 2012; 91: 224–237.
Li Y, Vinckenbosch N, Tian G, Huerta-Sanchez E, Jiang T, Jiang H et al. Resequencing of 200 human exomes identifies an excess of low-frequency non-synonymous coding variants. Nat Genet 2010; 42: 969–972.
Saccone NL, Schwantes-An TH, Wang JC, Grucza RA, Breslau N, Hatsukami D et al. Multiple cholinergic nicotinic receptor genes affect nicotine dependence risk in African and European Americans. Genes Brain Behav 2010; 9: 741–750.
Chen LS, Saccone NL, Culverhouse RC, Bracci PM, Chen CH, Dueker N et al. Smoking and genetic risk variation across populations of European, Asian, and African American ancestry–a meta-analysis of chromosome 15q25. Genet Epidemiol 2012; 36: 340–351.
Bierut LJ, Stitzel JA, Wang JC, Hinrichs AL, Grucza RA, Xuei X et al. Variants in nicotinic receptors and risk for nicotine dependence. Am J Psychiatry 2008; 165: 1163–1171.
Fowler CD, Lu Q, Johnson PM, Marks MJ, Kenny PJ . Habenular alpha5 nicotinic receptor subunit signalling controls nicotine intake. Nature 2011; 471: 597–601.
Lustig LR, Peng H . Chromosome location and characterization of the human nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunit alpha (alpha) 9 (CHRNA9) gene. Cytogenet Genome Res 2002; 98: 154–159.
Marchler-Bauer A, Lu S, Anderson JB, Chitsaz F, Derbyshire MK, DeWeese-Scott C et al. CDD: a conserved domain database for the functional annotation of proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 2011; 39: D225–D229.
Sgard F, Charpantier E, Bertrand S, Walker N, Caput D, Graham D et al. A novel human nicotinic receptor subunit, alpha10, that confers functionality to the alpha9-subunit. Mol Pharmacol 2002; 61: 150–159.
Nguyen VT, Ndoye A, Grando SA . Novel human alpha9 acetylcholine receptor regulating keratinocyte adhesion is targeted by Pemphigus vulgaris autoimmunity. Am J Pathol 2000; 157: 1377–1391.
Peng H, Ferris RL, Matthews T, Hiel H, Lopez-Albaitero A, Lustig LR . Characterization of the human nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunit alpha (alpha) 9 (CHRNA9) and alpha (alpha) 10 (CHRNA10) in lymphocytes. Life Sci 2004; 76: 263–280.
Lips KS, Pfeil U, Kummer W . Coexpression of alpha 9 and alpha 10 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. Neuroscience 2002; 115: 1–5.
Greenbaum L, Kanyas K, Karni O, Merbl Y, Olender T, Horowitz A et al. Why do young women smoke? I. Direct and interactive effects of environment, psychological characteristics and nicotinic cholinergic receptor genes. Mol Psychiatry 2006; 11: 312–322, 223.
Rigbi A, Kanyas K, Yakir A, Greenbaum L, Pollak Y, Ben-Asher E et al. Why do young women smoke? V. Role of direct and interactive effects of nicotinic cholinergic receptor gene variation on neurocognitive function. Genes Brain Behav 2008; 7: 164–172.
Chikova A, Bernard HU, Shchepotin IB, Grando SA . New associations of the genetic polymorphisms in nicotinic receptor genes with the risk of lung cancer. Life Sci 2012; 91: 1103–1108.
Andersson O, Stenqvist A, Attersand A, von Euler G . Nucleotide sequence, genomic organization, and chromosomal localization of genes encoding the human NMDA receptor subunits NR3A and NR3B. Genomics 2001; 78: 178–184.
Lipton SA, Choi YB, Takahashi H, Zhang D, Li W, Godzik A et al. Cysteine regulation of protein function–as exemplified by NMDA-receptor modulation. Trends Neurosci 2002; 25: 474–480.
Ciabarra AM, Sullivan JM, Gahn LG, Pecht G, Heinemann S, Sevarino KA . Cloning and characterization of chi-1: a developmentally regulated member of a novel class of the ionotropic glutamate receptor family. J Neurosci 1995; 15: 6498–6508.
Sucher NJ, Akbarian S, Chi CL, Leclerc CL, Awobuluyi M, Deitcher DL et al. Developmental and regional expression pattern of a novel NMDA receptor-like subunit (NMDAR-L) in the rodent brain. J Neurosci 1995; 15: 6509–6520.
Perez-Otano I, Schulteis CT, Contractor A, Lipton SA, Trimmer JS, Sucher NJ et al. Assembly with the NR1 subunit is required for surface expression of NR3A-containing NMDA receptors. J Neurosci 2001; 21: 1228–1237.
Sasaki YF, Rothe T, Premkumar LS, Das S, Cui J, Talantova MV et al. Characterization and comparison of the NR3A subunit of the NMDA receptor in recombinant systems and primary cortical neurons. J Neurophysiol 2002; 87: 2052–2063.
Eriksson M, Nilsson A, Froelich-Fabre S, Akesson E, Dunker J, Seiger A et al. Cloning and expression of the human N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit NR3A. Neurosci Lett 2002; 321: 177–181.
Ma JZ, Payne TJ, Nussbaum J, Li MD . Significant association of glutamate receptor, ionotropic N-methyl-D-aspartate 3A (GRIN3A), with nicotine dependence in European- and African-American smokers. Hum Genet 2010; 127: 503–512.
Liu HP, Lin WY, Liu SH, Wang WF, Tsai CH, Wu BT et al. Genetic variation in N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit NR3A but not NR3B influences susceptibility to Alzheimer's disease. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 2009; 28: 521–527.
Takata A, Iwayama Y, Fukuo Y, Ikeda M, Okochi T, Maekawa M et al. A population-specific uncommon variant in GRIN3A associated with schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 2013; 73: 532–539.
Marco S, Giralt A, Petrovic MM, Pouladi MA, Martinez-Turrillas R, Martinez-Hernandez J et al. Suppressing aberrant GluN3A expression rescues synaptic and behavioral impairments in Huntington's disease models. Nat Med 2013; 19: 1030–1038.
Li MD, Ma JZ, Payne TJ, Lou XY, Zhang D, Dupont RT et al. Genome-wide linkage scan for nicotine dependence in European Americans and its converging results with African Americans in the Mid-South Tobacco Family sample. Mol Psychiatry 2008; 13: 407–416.
Li MD, Payne TJ, Ma JZ, Lou XY, Zhang D, Dupont RT et al. A genomewide search finds major susceptibility Loci for nicotine dependence on chromosome 10 in african americans. Am J Hum Genet 2006; 79: 745–751.
Abecasis GR, Auton A, Brooks LD, DePristo MA, Durbin RM, Handsaker RE et al. An integrated map of genetic variation from 1092 human genomes. Nature 2012; 491: 56–65.
Huang W, Payne TJ, Ma JZ, Li MD . A functional polymorphism, rs6280, in DRD3 is significantly associated with nicotine dependence in European-American smokers. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 2008; 147B: 1109–1115.
Huang W, Ma JZ, Payne TJ, Beuten J, Dupont RT, Li MD . Significant association of DRD1 with nicotine dependence. Hum Genet 2008; 123: 133–140.
Mangold JE, Payne TJ, Ma JZ, Chen G, Li MD . Bitter taste receptor gene polymorphisms are an important factor in the development of nicotine dependence in African Americans. J Med Genet 2008; 45: 578–582.
Cui WY, Wang S, Yang J, Yi SG, Yoon D, Kim YJ et al. Significant association of CHRNB3 variants with nicotine dependence in multiple ethnic populations. Mol Psychiatry 2013; 18: 1149–1151.
Beuten J, Ma JZ, Payne TJ, Dupont RT, Lou XY, Crews KM et al. Association of specific haplotypes of neurotrophic tyrosine kinase receptor 2 gene (NTRK2) with vulnerability to nicotine dependence in African-Americans and European-Americans. Biol Psychiatry 2007; 61: 48–55.
Beuten J, Ma JZ, Payne TJ, Dupont RT, Crews KM, Somes G et al. Single- and multilocus allelic variants within the GABA(B) receptor subunit 2 (GABAB2) gene are significantly associated with nicotine dependence. Am J Hum Genet 2005; 76: 859–864.
Xu Q, Huang W, Payne TJ, Ma JZ, Li MD . Detection of genetic association and a functional polymorphism of dynamin 1 gene with nicotine dependence in European and African Americans. Neuropsychopharmacology 2009; 34: 1351–1359.
Wei J, Ma JZ, Payne TJ, Cui W, Ray R, Mitra N et al. Replication and extension of association of choline acetyltransferase with nicotine dependence in European and African American smokers. Hum Genet 2010; 127: 691–698.
Sun D, Ma JZ, Payne TJ, Li MD . Beta-arrestins 1 and 2 are associated with nicotine dependence in European American smokers. Mol Psychiatry 2008; 13: 398–406.
Li MD, Xu Q, Lou XY, Payne TJ, Niu T, Ma JZ . Association and interaction analysis of variants in CHRNA5/CHRNA3/CHRNB4 gene cluster with nicotine dependence in African and European Americans. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 2010; 153B: 745–756.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the invaluable contributions of personal information and blood samples by all participants in the study. This project was supported by National Institutes of Health grant R01 DA012844 to MDL.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Molecular Psychiatry website
Supplementary information
PowerPoint slides
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, J., Wang, S., Yang, Z. et al. The contribution of rare and common variants in 30 genes to risk nicotine dependence. Mol Psychiatry 20, 1467–1478 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2014.156
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2014.156
This article is cited by
-
Polymorphisms of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review and data analysis
Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics (2022)
-
Deconstructing the neurobiology of cannabis use disorder
Nature Neuroscience (2020)
-
Structural features in the glycine-binding sites of the GluN1 and GluN3A subunits regulate the surface delivery of NMDA receptors
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Earlier smoking after waking and the risk of asthma: a cross-sectional study using NHANES data
BMC Pulmonary Medicine (2018)
-
Implication of Genes for the N-Methyl-d-Aspartate (NMDA) Receptor in Substance Addictions
Molecular Neurobiology (2018)