Abstract
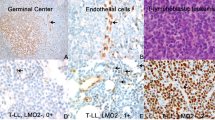
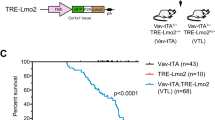
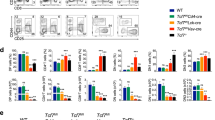
T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) results from leukemic transformation of T-cell precursors arrested at specific differentiation stages, including an ‘early-cortical’ thymic maturation arrest characterized by expression of cytoplasmic TCRβ but no surface T-cell receptor (TCR) and frequent ectopic expression of the TLX1/3 NK-like homeotic proteins (NKL). We designed a TCRα VJC PCR to identify clonal TCRα rearrangements in 32% of 127 T-ALLs, including 0/52 immature/TCRγδ lineage cases and 41/75 (55%) TCRαβ lineage cases. Amongst the latter, TCRα rearrangements were not identified in 30/54 (56%) of IMβ/pre-αβ early-cortical T-ALLs, of which the majority (21/30) expressed TLX1/3. We reasoned that the remaining T-ALLs might express other NKL proteins, so compared transcript levels of 46 NKL in T-ALL and normal thymic subpopulations. Ectopic overexpression of 10 NKL genes, of which six are unreported in T-ALL (NKX2-3, BARHL1, BARX2, EMX2, LBX2 and MSX2), was detectable in 17/104 (16%) T-ALLs. Virtually all NKL overexpressing T-ALLs were TCRα unrearranged and ectopic NKL transcript expression strongly repressed Eα activity, suggesting that ectopic NKL expression is the major determinant in early-cortical thymic T-ALL maturation arrest. This immunogenetic T-ALL subtype, defined by TCRβ VDJ but no TCRα VJ rearrangement, is associated with a favorable outcome in GRAALL-treated adult T-ALLs.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Spits H . Development of alphabeta T cells in the human thymus. Nat Rev Immunol 2002; 2: 760–772.
Dik WA, Pike-Overzet K, Weerkamp F, de Ridder D, de Haas EF, Baert MR et al. New insights on human T cell development by quantitative T cell receptor gene rearrangement studies and gene expression profiling. J Exp Med 2005; 201: 1715–1723.
Cieslak A, Le Noir S, Trinquand A, Lhermitte L, Franchini DM, Villarese P et al. RUNX1-dependent RAG1 deposition instigates human TCR-delta locus rearrangement. J Exp Med 2014; 211: 1821–1832.
von Boehmer H, Aifantis I, Azogui O, Feinberg J, Saint-Ruf C, Zober C et al. Crucial function of the pre-T-cell receptor (TCR) in TCR beta selection, TCR beta allelic exclusion and alpha beta versus gamma delta lineage commitment. Immunol Rev 1998; 165: 111–119.
Krangel MS, Hernandez-Munain C, Lauzurica P, McMurry M, Roberts JL, Zhong XP . Developmental regulation of V(D)J recombination at the TCR alpha/delta locus. Immunol Rev 1998; 165: 131–147.
Bassing CH, Tillman RE, Woodman BB, Canty D, Monroe RJ, Sleckman BP et al. T cell receptor (TCR) alpha/delta locus enhancer identity and position are critical for the assembly of TCR delta and alpha variable region genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003; 100: 2598–2603.
Sleckman BP, Bardon CG, Ferrini R, Davidson L, Alt FW . Function of the TCR alpha enhancer in alphabeta and gammadelta T cells. Immunity 1997; 7: 505–515.
Ho IC, Yang LH, Morle G, Leiden JM . A T-cell-specific transcriptional enhancer element 3' of C alpha in the human T-cell receptor alpha locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1989; 86: 6714–6718.
Ho IC, Bhat NK, Gottschalk LR, Lindsten T, Thompson CB, Papas TS et al. Sequence-specific binding of human Ets-1 to the T cell receptor alpha gene enhancer. Science 1990; 250: 814–818.
Giese K, Kingsley C, Kirshner JR, Grosschedl R . Assembly and function of a TCR alpha enhancer complex is dependent on LEF-1-induced DNA bending and multiple protein-protein interactions. Genes Dev 1995; 9: 995–1008.
Roberts JL, Lauzurica P, Krangel MS . Developmental regulation of VDJ recombination by the core fragment of the T cell receptor alpha enhancer. J Exp Med 1997; 185: 131–140.
Asnafi V, Radford-Weiss I, Dastugue N, Bayle C, Leboeuf D, Charrin C et al. CALM-AF10 is a common fusion transcript in T-ALL and is specific to the TCRgammadelta lineage. Blood 2003; 102: 1000–1006.
Ferrando AA, Neuberg DS, Staunton J, Loh ML, Huard C, Raimondi SC et al. Gene expression signatures define novel oncogenic pathways in T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Cell 2002; 1: 75–87.
Aifantis I, Raetz E, Buonamici S . Molecular pathogenesis of T-cell leukaemia and lymphoma. Nat Rev Immunol 2008; 8: 380–390.
Garcia-Fernandez J . Hox, ParaHox, ProtoHox: facts and guesses. Heredity 2005; 94: 145–152.
Qian YQ, Billeter M, Otting G, Muller M, Gehring WJ, Wuthrich K . The structure of the Antennapedia homeodomain determined by NMR spectroscopy in solution: comparison with prokaryotic repressors. Cell 1989; 59: 573–580.
Holland PW, Booth HA, Bruford EA . Classification and nomenclature of all human homeobox genes. BMC Biol 2007; 5: 47.
Dadi S, Le Noir S, Payet-Bornet D, Lhermitte L, Zacarias-Cabeza J, Bergeron J et al. TLX homeodomain oncogenes mediate T cell maturation arrest in T-ALL via interaction with ETS1 and suppression of TCRalpha gene expression. Cancer Cell 2012; 21: 563–576.
Gabert J, Beillard E, van der Velden VH, Bi W, Grimwade D, Pallisgaard N et al. Standardization and quality control studies of 'real-time' quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction of fusion gene transcripts for residual disease detection in leukemia - a Europe Against Cancer program. Leukemia 2003; 17: 2318–2357.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD . Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001; 25: 402–408.
Ferrando AA, Herblot S, Palomero T, Hansen M, Hoang T, Fox EA et al. Biallelic transcriptional activation of oncogenic transcription factors in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2004; 103: 1909–1911.
Asnafi V, Beldjord K, Boulanger E, Comba B, Le Tutour P, Estienne MH et al. Analysis of TCR, pT alpha, and RAG-1 in T-acute lymphoblastic leukemias improves understanding of early human T-lymphoid lineage commitment. Blood 2003; 101: 2693–2703.
Asnafi V, Beldjord K, Libura M, Villarese P, Millien C, Ballerini P et al. Age-related phenotypic and oncogenic differences in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemias may reflect thymic atrophy. Blood 2004; 104: 4173–4180.
Homminga I, Pieters R, Langerak AW, de Rooi JJ, Stubbs A, Verstegen M et al. Integrated transcript and genome analyses reveal NKX2-1 and MEF2C as potential oncogenes in T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Cell 2011; 19: 484–497.
Le Noir S, Ben Abdelali R, Lelorch M, Bergeron J, Sungalee S, Payet-Bornet D et al. Extensive molecular mapping of TCRalpha/delta- and TCRbeta-involved chromosomal translocations reveals distinct mechanisms of oncogene activation in T-ALL. Blood 2012; 120: 3298–3309.
Przybylski GK, Dik WA, Grabarczyk P, Wanzeck J, Chudobska P, Jankowski K et al. The effect of a novel recombination between the homeobox gene NKX2-5 and the TRD locus in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia on activation of the NKX2-5 gene. Haematologica 2006; 91: 317–321.
Haga SB, Fu S, Karp JE, Ross DD, Williams DM, Hankins WD et al. BP1, a new homeobox gene, is frequently expressed in acute leukemias. Leukemia 2000; 14: 1867–1875.
Homminga I, Pieters R, Meijerink JP . NKL homeobox genes in leukemia. Leukemia 2012; 26: 572–581.
Coustan-Smith E, Mullighan CG, Onciu M, Behm FG, Raimondi SC, Pei D et al. Early T-cell precursor leukaemia: a subtype of very high-risk acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Lancet 2009; 10: 147–156.
Armstrong SA, Look AT . Molecular genetics of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Oncol 2005; 23: 6306–6315.
De Keersmaecker K, Marynen P, Cools J . Genetic insights in the pathogenesis of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica 2005; 90: 1116–1127.
Graux C, Cools J, Michaux L, Vandenberghe P, Hagemeijer A . Cytogenetics and molecular genetics of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia: from thymocyte to lymphoblast. Leukemia 2006; 20: 1496–1510.
Van Vlierberghe P, Pieters R, Beverloo HB, Meijerink JP . Molecular-genetic insights in paediatric T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Br J Haematol 2008; 143: 153–168.
Soulier J, Clappier E, Cayuela JM, Regnault A, Garcia-Peydro M, Dombret H et al. HOXA genes are included in genetic and biologic networks defining human acute T-cell leukemia (T-ALL). Blood 2005; 106: 274–286.
Merabet S, Pradel J, Graba Y . Getting a molecular grasp on Hox contextual activity. Trends Genet 2005; 21: 477–480.
Shen WF, Krishnan K, Lawrence HJ, Largman C . The HOX homeodomain proteins block CBP histone acetyltransferase activity. Mol Cell Biol 2001; 21: 7509–7522.
Mann RS, Lelli KM, Joshi R . Hox specificity unique roles for cofactors and collaborators. Curr Top Dev Biol 2009; 88: 63–101.
Owens BM, Zhu YX, Suen TC, Wang PX, Greenblatt JF, Goss PE et al. Specific homeodomain-DNA interactions are required for HOX11-mediated transformation. Blood 2003; 101: 4966–4974.
Bergeron J, Clappier E, Radford I, Buzyn A, Millien C, Soler G et al. Prognostic and oncogenic relevance of TLX1/HOX11 expression level in T-ALLs. Blood 2007; 110: 2324–2330.
Bernard OA, Busson-LeConiat M, Ballerini P, Mauchauffe M, Della Valle V, Monni R et al. A new recurrent and specific cryptic translocation, t(5;14)(q35;q32), is associated with expression of the Hox11L2 gene in T acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 2001; 15: 1495–1504.
Nagel S, Kaufmann M, Drexler HG, MacLeod RA . The cardiac homeobox gene NKX2-5 is deregulated by juxtaposition with BCL11B in pediatric T-ALL cell lines via a novel t(5;14)(q35.1;q32.2). Cancer Res 2003; 63: 5329–5334.
Dunwell TL, Hesson LB, Pavlova T, Zabarovska V, Kashuba V, Catchpoole D et al. Epigenetic analysis of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Epigenetics 2009; 4: 185–193.
Kusy S, Gerby B, Goardon N, Gault N, Ferri F, Gerard D et al. NKX3.1 is a direct TAL1 target gene that mediates proliferation of TAL1-expressing human T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Exp Med 2010; 207: 2141–2156.
Bell A, Bell D, Weber RS, El-Naggar AK . CpG island methylation profiling in human salivary gland adenoid cystic carcinoma. Cancer 2011; 117: 2898–2909.
Furuta J, Nobeyama Y, Umebayashi Y, Otsuka F, Kikuchi K, Ushijima T . Silencing of Peroxiredoxin 2 and aberrant methylation of 33 CpG islands in putative promoter regions in human malignant melanomas. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 6080–6086.
Kuang SQ, Tong WG, Yang H, Lin W, Lee MK, Fang ZH et al. Genome-wide identification of aberrantly methylated promoter associated CpG islands in acute lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 2008; 22: 1529–1538.
Okamoto J, Hirata T, Chen Z, Zhou HM, Mikami I, Li H et al. EMX2 is epigenetically silenced and suppresses growth in human lung cancer. Oncogene 2010; 29: 5969–5975.
Stevens TA, Meech R . BARX2 and estrogen receptor-alpha (ESR1) coordinately regulate the production of alternatively spliced ESR1 isoforms and control breast cancer cell growth and invasion. Oncogene 2006; 25: 5426–5435.
Tellez CS, Shen L, Estecio MR, Jelinek J, Gershenwald JE, Issa JP . CpG island methylation profiling in human melanoma cell lines. Melanoma Res 2009; 19: 146–155.
Robles EF, Mena-Varas M, Barrio L, Merino-Cortes SV, Balogh P, Du MQ et al. Homeobox NKX2-3 promotes marginal-zone lymphomagenesis by activating B-cell receptor signalling and shaping lymphocyte dynamics. Nat Commun 2015; 7: 11889.
Tanaka Y, Era T, Nishikawa S, Kawamata S . Forced expression of Nanog in hematopoietic stem cells results in a gammadeltaT-cell disorder. Blood 2007; 110: 107–115.
van Dongen JJ, Langerak AW, Bruggemann M, Evans PA, Hummel M, Lavender FL et al. Design and standardization of PCR primers and protocols for detection of clonal immunoglobulin and T-cell receptor gene recombinations in suspect lymphoproliferations: report of the BIOMED-2 Concerted Action BMH4-CT98-3936. Leukemia 2003; 17: 2257–2317.
Bruggemann M, White H, Gaulard P, Garcia-Sanz R, Gameiro P, Oeschger S et al. Powerful strategy for polymerase chain reaction-based clonality assessment in T-cell malignancies Report of the BIOMED-2 Concerted Action BHM4 CT98-3936. Leukemia 2007; 21: 215–221.
Sherwood AM, Desmarais C, Livingston RJ, Andriesen J, Haussler M, Carlson CS et al. Deep sequencing of the human TCRgamma and TCRbeta repertoires suggests that TCRbeta rearranges after alphabeta and gammadelta T cell commitment. Sci Transl Med 2011; 3: 90ra–61.
Ben Abdelali R, Asnafi V, Petit A, Micol JB, Callens C, Villarese P et al. The prognosis of CALM-AF10-positive adult T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemias depends on the stage of maturation arrest. Haematologica 2013; 98: 1711–1717.
Acknowledgements
We thank all French, Swiss and Belgian participants, clinicians, biologists and clinical research assistants, in the GRAALL 2003-2005 trials for collecting and providing data and samples. We thank the IBiSA ‘Transcriptomics and Genomics Marseille-Luminy (TGML)’ platform for sequencing of RNAseq samples. We thank the tumorothèque plateform of Necker’s hospital APHP.
Author contributions
PV, EAM and VA wrote the manuscript. PV, CL, SLN, RBA, AC, AT, MB, ML, MT, AL and SP performed research and/or data analysis. NI, HD, AP and NB provided clinical material and data analysis from the GRAALL trials. VA oversaw conceptual development of the project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Leukemia website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Villarese, P., Lours, C., Trinquand, A. et al. TCRα rearrangements identify a subgroup of NKL-deregulated adult T-ALLs associated with favorable outcome. Leukemia 32, 61–71 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2017.176
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2017.176
This article is cited by
-
The LL-100 panel: 100 cell lines for blood cancer studies
Scientific Reports (2019)