Abstract
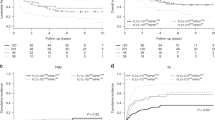
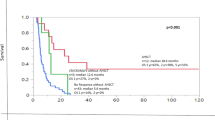
Post-remission treatment (PRT) in patients with cytogenetically normal (CN) acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in first complete remission (CR1) is debated. We studied 521 patients with CN-AML in CR1, for whom mutational status of NPM1 and FLT3-ITD was available, including the FLT3-ITD allelic ratio. PRT consisted of reduced intensity conditioning (RIC) allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (alloHSCT) (n=68), myeloablative conditioning (MAC) alloHSCT (n=137), autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (autoHSCT) (n=168) or chemotherapy (n=148). Favorable overall survival (OS) was found for patients with mutated NPM1 without FLT3-ITD (71±4%). Outcome in patients with a high FLT3-ITD allelic ratio appeared to be very poor with OS and relapse-free survival (RFS) of 23±8% and 12±6%, respectively. Patients with wild-type NPM1 without FLT3-ITD or with a low allelic burden of FLT3-ITD were considered as intermediate-risk group because of similar OS and RFS at 5 years, in which PRT by RIC alloHSCT resulted in better OS and RFS as compared with chemotherapy (hazard ratio (HR) 0.56, P=0.022 and HR 0.50, P=0.004, respectively) or autoHSCT (HR 0.60, P=0.046 and HR 0.60, P=0.043, respectively). The lowest cumulative incidence of relapse (23±4%) was observed following MAC alloHSCT. These results suggest that alloHSCT may be preferred in patients with molecularly intermediate-risk CN-AML, while the choice of conditioning type may be personalized according to risk for non-relapse mortality.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grimwade D, Walker H, Oliver F, Wheatley K, Harrison C, Harrison G et al. The importance of diagnostic cytogenetics on outcome in AML: analysis of 1,612 patients entered into the MRC AML 10 trial. The Medical Research Council Adult and Children's Leukaemia Working Parties. Blood 1998; 92: 2322–2333.
Marcucci G, Haferlach T, Dohner H . Molecular genetics of adult acute myeloid leukemia: prognostic and therapeutic implications. J Clin Oncol 2011; 29: 475–486.
Schlenk RF, Dohner K, Krauter J, Frohling S, Corbacioglu A, Bullinger L et al. Mutations and treatment outcome in cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 2008; 358: 1909–1918.
Dohner H, Estey EH, Amadori S, Appelbaum FR, Buchner T, Burnett AK et al. Diagnosis and management of acute myeloid leukemia in adults: recommendations from an international expert panel, on behalf of the European LeukemiaNet. Blood 2010; 115: 453–474.
Cornelissen JJ, Gratwohl A, Schlenk RF, Sierra J, Bornhauser M, Juliusson G et al. The European LeukemiaNet AML Working Party consensus statement on allogeneic HSCT for patients with AML in remission: an integrated-risk adapted approach. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2012; 9: 579–590.
Port M, Bottcher M, Thol F, Ganser A, Schlenk R, Wasem J et al. Prognostic significance of FLT3 internal tandem duplication, nucleophosmin 1, and CEBPA gene mutations for acute myeloid leukemia patients with normal karyotype and younger than 60 years: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Hematol 2014; 93: 1279–1286.
Gale RE, Green C, Allen C, Mead AJ, Burnett AK, Hils RK et al. The impact of FLT3 internal tandem duplication mutant level, number, size, and interaction with NPM1 mutations in a large cohort of young adult patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2008; 111: 2776–2784.
Thiede C, Steudel C, Mohr B, Schaich M, Schakel U, Platzbecker U et al. Analysis of FLT3-activating mutations in 979 patients with acute myelogenous leukemia: association with FAB subtypes and identification of subgroups with poor prognosis. Blood 2002; 99: 4326–4335.
Linch DC, Hills RK, Burnett AK, Khwaja A, Gale RE . Impact of FLT3(ITD) mutant allele level on relapse risk in intermediate-risk acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2014; 124: 273–276.
Schlenk RF, Kayser S, Bullinger L, Kobbe G, Casper J, Ringhoffer M et al. Differential impact of allelic ratio and insertion site in FLT3-ITD-positive AML with respect to allogeneic transplantation. Blood 2014; 124: 3441–3449.
de Jonge HJ, Valk PJ, de Bont ES, Schuringa JJ, Ossenkoppele G, Vellenga E et al. Prognostic impact of white blood cell count in intermediate risk acute myeloid leukemia: relevance of mutated NPM1 and FLT3-ITD. Haematologica 2011; 96: 1310–1317.
Rollig C, Bornhauser M, Kramer M, Thiede C, Ho AD, Kramer A et al. Allogeneic stem-cell transplantation in patients with NPM1-mutated acute myeloid leukemia: results from a prospective donor versus no-donor analysis of patients after upfront HLA typing within the SAL-AML 2003 trial. J Clin Oncol 2015; 33: 403–410.
Koreth J, Schlenk R, Kopecky KJ, Honda S, Sierra J, Djulbegovic BJ et al. Allogeneic stem cell transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia in first complete remission: systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective clinical trials. JAMA 2009; 301: 2349–2361.
Suciu S, Mandelli F, de Witte T, Zittoun R, Gallo E, Labar B et al. Allogeneic compared with autologous stem cell transplantation in the treatment of patients younger than 46 years with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in first complete remission (CR1): an intention-to-treat analysis of the EORTC/GIMEMAAML-10 trial. Blood 2003; 102: 1232–1240.
Pfirrmann M, Ehninger G, Thiede C, Bornhauser M, Kramer M, Rollig C et al. Prediction of post-remission survival in acute myeloid leukaemia: a post-hoc analysis of the AML96 trial. Lancet Oncol 2012; 13: 207–214.
Slovak ML, Kopecky KJ, Cassileth PA, Harrington DH, Theil KS, Mohamed A et al. Karyotypic analysis predicts outcome of preremission and postremission therapy in adult acute myeloid leukemia: a Southwest Oncology Group/Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Study. Blood 2000; 96: 4075–4083.
Burnett AK, Wheatley K, Goldstone AH, Stevens RF, Hann IM, Rees JH et al. The value of allogeneic bone marrow transplant in patients with acute myeloid leukaemia at differing risk of relapse: results of the UK MRC AML 10 trial. Br J Haematol 2002; 118: 385–400.
Cornelissen JJ, van Putten WL, Verdonck LF, Theobald M, Jacky E, Daenen SM et al. Results of a HOVON/SAKK donor versus no-donor analysis of myeloablative HLA-identical sibling stem cell transplantation in first remission acute myeloid leukemia in young and middle-aged adults: benefits for whom? Blood 2007; 109: 3658–3666.
Ho AD, Schetelig J, Bochtler T, Schaich M, Schafer-Eckart K, Hanel M et al. Allogeneic stem cell transplantation improves survival in patients with acute myeloid leukemia characterized by a high allelic ratio of mutant FLT3-ITD. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2016; 22: 462–469.
Gale RE, Hills R, Kottaridis PD, Srirangan S, Wheatley K, Burnett AK et al. No evidence that FLT3 status should be considered as an indicator for transplantation in acute myeloid leukemia (AML): an analysis of 1135 patients, excluding acute promyelocytic leukemia, from the UK MRC AML 10 and 12 trials. Blood 2005; 106: 3658–3665.
Bornhauser M, Illmer T, Schaich M, Soucek S, Ehninger G, Thiede C . Improved outcome after stem-cell transplantation in FLT3/ITD-positive AML. Blood 2007; 109: 2264–2265.
Lowenberg B, Pabst T, Vellenga E, van Putten W, Schouten HC, Graux C et al. Cytarabine dose for acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 2011; 364: 1027–1036.
Randomized study to assess the added value of Laromustine in combination with standard remission-induction chemotherapy in patients aged 18-65 years with previously untreated acute myeloid leukemia (AML) or myelodysplasia (MDS) (RAEB with IPSS ⩾1.5); Netherlands Trial Register; Main ID: NTR1446. Available from http://www.trialregister.nl/trialreg/admin/rctview.asp?TC=1446 (accessed on 6 July 2016).
Lowenberg B, van Putten W, Theobald M, Gmur J, Verdonck L, Sonneveld P et al. Effect of priming with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor on the outcome of chemotherapy for acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 2003; 349: 743–752.
Willemze R, Suciu S, Meloni G, Labar B, Marie JP, Halkes CJ et al. High-dose cytarabine in induction treatment improves the outcome of adult patients younger than age 46 years with acute myeloid leukemia: results of the EORTC-GIMEMA AML-12 trial. J Clin Oncol 2014; 32: 219–228.
Vellenga E, van Putten W, Ossenkoppele GJ, Verdonck LF, Theobald M, Cornelissen JJ et al. Autologous peripheral blood stem cell transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2011; 118: 6037–6042.
Cornelissen JJ, Versluis J, Passweg JR, van Putten WL, Manz MG, Maertens J et al. Comparative therapeutic value of post-remission approaches in patients with acute myeloid leukemia aged 40-60 years. Leukemia 2015; 29: 1041–1050.
Cornelissen JJ, Breems D, van Putten WL, Gratwohl AA, Passweg JR, Pabst T et al. Comparative analysis of the value of allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation in acute myeloid leukemia with monosomal karyotype versus other cytogenetic risk categories. J Clin Oncol 2012; 30: 2140–2146.
Mantel N, Byar D . Evaluation of response-time data involving transient states: an illustration using heart-transplant data. J Am Stat Assoc 1974; 69: 81–86.
Grambsch PM, Therneau TM . Proportional hazards tests and diagnostics based on weighted residuals. Biometrika 1994; 81: 515–526.
Schmid C, Labopin M, Socie G, Daguindau E, Volin L, Huynh A et al. Outcome and risk factor analysis of molecular subgroups in cytogenetically normal AML treated by allogeneic transplantation. Blood 2015; 126: 2062–2069.
Pratcorona M, Brunet S, Nomdedeu J, Ribera JM, Tormo M, Duarte R et al. Favorable outcome of patients with acute myeloid leukemia harboring a low-allelic burden FLT3-ITD mutation and concomitant NPM1 mutation: relevance to post-remission therapy. Blood 2013; 121: 2734–2738.
Guieze R, Cornillet-Lefebvre P, Lioure B, Blanchet O, Pigneux A, Recher C et al. Role of autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation according to the NPM1/FLT3-ITD molecular status for cytogenetically normal AML patients: a GOELAMS Study. Am J Hematol 2012; 87: 1052–1056.
Stelljes M, Krug U, Beelen DW, Braess J, Sauerland MC, Heinecke A et al. Allogeneic transplantation versus chemotherapy as postremission therapy for acute myeloid leukemia: a prospective matched pairs analysis. J Clin Oncol 2014; 32: 288–296.
Ringden O, Labopin M, Ehninger G, Niederwieser D, Olsson R, Basara N et al. Reduced intensity conditioning compared with myeloablative conditioning using unrelated donor transplants in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27: 4570–4577.
Aoudjhane M, Labopin M, Gorin NC, Shimoni A, Ruutu T, Kolb HJ et al. Comparative outcome of reduced intensity and myeloablative conditioning regimen in HLA identical sibling allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation for patients older than 50 years of age with acute myeloblastic leukaemia: a retrospective survey from the Acute Leukemia Working Party (ALWP) of the European group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT). Leukemia 2005; 19: 2304–2312.
Shimoni A, Hardan I, Shem-Tov N, Yeshurun M, Yerushalmi R, Avigdor A et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation in AML and MDS using myeloablative versus reduced-intensity conditioning: the role of dose intensity. Leukemia 2006; 20: 322–328.
Flynn CM, Hirsch B, Defor T, Barker JN, Miller JS, Wagner JE et al. Reduced intensity compared with high dose conditioning for allotransplantation in acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome: a comparative clinical analysis. Am J Hematol 2007; 82: 867–872.
Alyea EP, Kim HT, Ho V, Cutler C, DeAngelo DJ, Stone R et al. Impact of conditioning regimen intensity on outcome of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for advanced acute myelogenous leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2006; 12: 1047–1055.
Martino R, de Wreede L, Fiocco M, van Biezen A, von dem Borne PA, Hamladji RM et al. Comparison of conditioning regimens of various intensities for allogeneic hematopoietic SCT using HLA-identical sibling donors in AML and MDS with <10% BM blasts: a report from EBMT. Bone Marrow Transplant 2013; 48: 761–770.
Luger SM, Ringden O, Zhang MJ, Perez WS, Bishop MR, Bornhauser M et al. Similar outcomes using myeloablative vs reduced-intensity allogeneic transplant preparative regimens for AML or MDS. Bone Marrow Transplant 2012; 47: 203–211.
Sorror ML, Giralt S, Sandmaier BM, De Lima M, Shahjahan M, Maloney DG et al. Hematopoietic cell transplantation specific comorbidity index as an outcome predictor for patients with acute myeloid leukemia in first remission: combined FHCRC and MDACC experiences. Blood 2007; 110: 4606–4613.
Gratwohl A, Hermans J, Goldman JM, Arcese W, Carreras E, Devergie A et al. Risk assessment for patients with chronic myeloid leukaemia before allogeneic blood or marrow transplantation. Chronic Leukemia Working Party of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Lancet 1998; 352: 1087–1092.
Versluis J, Labopin M, Niederwieser D, Socie G, Schlenk RF, Milpied N et al. Prediction of non-relapse mortality in recipients of reduced intensity conditioning allogeneic stem cell transplantation with AML in first complete remission. Leukemia 2015; 29: 51–57.
Terwijn M, van Putten WL, Kelder A, van der Velden VH, Brooimans RA, Pabst T et al. High prognostic impact of flow cytometric minimal residual disease detection in acute myeloid leukemia: data from the HOVON/SAKK AML 42A Study. J Clin Oncol 2013; 31: 3889–3897.
Walter RB, Gooley TA, Wood BL, Milano F, Fang M, Sorror ML et al. Impact of pretransplantation minimal residual disease, as detected by multiparametric flow cytometry, on outcome of myeloablative hematopoietic cell transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncol 2011; 29: 1190–1197.
Ivey A, Hills RK, Simpson MA, Jovanovic JV, Gilkes A, Grech A et al. Assessment of minimal residual disease in standard-risk AML. N Engl J Med 2016; 374: 422–433.
Burnett AK, Goldstone A, Hills RK, Milligan D, Prentice A, Yin J et al. Curability of patients with acute myeloid leukemia who did not undergo transplantation in first remission. J Clin Oncol 2013; 31: 1293–1301.
Schlenk RF, Taskesen E, van Norden Y, Krauter J, Ganser A, Bullinger L et al. The value of allogeneic and autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in prognostically favorable acute myeloid leukemia with double mutant CEBPA. Blood 2013; 122: 1576–1582.
Jourdan E, Boissel N, Chevret S, Delabesse E, Renneville A, Cornillet P et al. Prospective evaluation of gene mutations and minimal residual disease in patients with core binding factor acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2013; 121: 2213–2223.
Scott BL, Pasquini MC, Logan BR, Wu J, Devine SM, Porter DL et alResults of a Phase III Randomized, Multi-Center Study of allogeneic stem cell transplantation after high versus reduced intensity conditioning in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) or acute myeloid leukemia (AML): Blood and Marrow Transplant Clinical Trials Network (BMT CTN) 0901. 57th ASH Annual Meeting & Exposition; Orlando, FL, USA; 5–8 December 2015.
Sorror ML . How I assess comorbidities before hematopoietic cell transplantation. Blood 2013; 121: 2854–2863.
Acknowledgements
We thank the Leukemia Working Group of the HOVON/SAKK Cooperative Groups and the Leukemia Working Group of the EORTC for conception and design; Martine Testroote, Ine Meulendijks, Christel van Hooije (HOVON) and Christine Biaggi (SAKK) for collection and assembly of data. Stefan Suciu (EORTC) and Myriam Labopin (EBMT) are acknowledged for completing clinical data. Joop H. Jansen (EORTC) is highly acknowledged for molecular analysis of patients.
Author contributions
JV, FEMitH, GH and JJC contributed to the study design; all authors provided study materials or patients; all authors were involved in collection and assembly of clinical data; JV, FEMitH, GH and JJC were involved in analysing and interpreting the data and writing this report; and all authors reviewed and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Presented by the first author as an oral presentation at the 56th Annual Meeting of the American Society of Hematology, 6–9 December 2014, San Francisco, CA, USA; and at the 9th Dutch Hematology Congress, 21–23 January 2015, Arnhem, The Netherlands.
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Leukemia website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Versluis, J., in ‘t Hout, F., Devillier, R. et al. Comparative value of post-remission treatment in cytogenetically normal AML subclassified by NPM1 and FLT3-ITD allelic ratio. Leukemia 31, 26–33 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2016.183
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2016.183
This article is cited by
-
FLT3-targeted treatment for acute myeloid leukemia
International Journal of Hematology (2022)
-
Sorafenib maintenance after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation improves outcome of FLT3–ITD-mutated acute myeloid leukemia
International Journal of Hematology (2022)
-
Post-remission measurable residual disease directs treatment choice and improves outcomes for patients with intermediate-risk acute myeloid leukemia in CR1
International Journal of Hematology (2022)
-
Comparison of HLA-mismatched unrelated donor transplantation with post-transplant cyclophosphamide versus HLA-haploidentical transplantation in patients with active acute myeloid leukemia
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2022)
-
The evolving concept of indications for allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation during first complete remission of acute myeloid leukemia
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2021)