Abstract
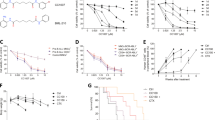
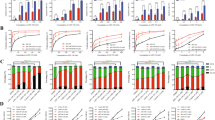
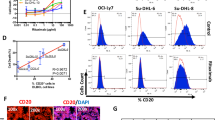
Histone deacetylases (HDACs) have been identified as therapeutic targets due to their regulatory function in chromatin structure and organization. Here, we analyzed the therapeutic effect of LBH589, a class I–II HDAC inhibitor, in acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). In vitro, LBH589 induced dose-dependent antiproliferative and apoptotic effects, which were associated with increased H3 and H4 histone acetylation. Intravenous administration of LBH589 in immunodeficient BALB/c-RAG2−/−γc−/− mice in which human-derived T and B-ALL cell lines were injected induced a significant reduction in tumor growth. Using primary ALL cells, a xenograft model of human leukemia in BALB/c-RAG2−/−γc−/− mice was established, allowing continuous passages of transplanted cells to several mouse generations. Treatment of mice engrafted with T or B-ALL cells with LBH589 induced an in vivo increase in the acetylation of H3 and H4, which was accompanied with prolonged survival of LBH589-treated mice in comparison with those receiving vincristine and dexamethasone. Notably, the therapeutic efficacy of LBH589 was significantly enhanced in combination with vincristine and dexamethasone. Our results show the therapeutic activity of LBH589 in combination with standard chemotherapy in pre-clinical models of ALL and suggest that this combination may be of clinical value in the treatment of patients with ALL.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Pui CH, Robison LL, Look AT . Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Lancet 2008; 371: 1030–1043.
Moorman AV, Ensor HM, Richards SM, Chilton L, Schwab C, Kinsey SE et al. Prognostic effect of chromosomal abnormalities in childhood B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: results from the UK Medical Research Council ALL97/99 randomised trial. Lancet Oncol 2010; 11: 429–438.
Ribera JM, Oriol A, Gonzalez M, Vidriales B, Brunet S, Esteve J et al. Concurrent intensive chemotherapy and imatinib before and after stem cell transplantation in newly diagnosed Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Final results of the CSTIBES02 trial. Haematologica 2010; 95: 87–95.
Stam RW, den Boer ML, Schneider P, Nollau P, Horstmann M, Beverloo HB et al. Targeting FLT3 in primary MLL-gene-rearranged infant acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2005; 106: 2484–2490.
Real PJ, Tosello V, Palomero T, Castillo M, Hernando E, de Stanchina E et al. Gamma-secretase inhibitors reverse glucocorticoid resistance in T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Nat Med 2009; 15: 50–58.
Esteller M . Epigenetics in cancer. N Engl J Med 2008; 358: 1148–1159.
Garcia-Manero G, Yang H, Kuang SQ, O'Brien S, Thomas D, Kantarjian H . Epigenetics of acute lymphocytic leukemia. Semin Hematol 2009; 46: 24–32.
Agirre X, Vilas-Zornoza A, Jimenez-Velasco A, Martin-Subero JI, Cordeu L, Garate L et al. Epigenetic silencing of the tumor suppressor microRNA Hsa-miR-124a regulates CDK6 expression and confers a poor prognosis in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 4443–4453.
Agirre X, Roman-Gomez J, Jimenez-Velasco A, Garate L, Montiel-Duarte C, Navarro G et al. ASPP1, a common activator of TP53, is inactivated by aberrant methylation of its promoter in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Oncogene 2006; 25: 1862–1870.
Roman-Gomez J, Agirre X, Jimenez-Velasco A, Arqueros V, Vilas-Zornoza A, Rodriguez-Otero P et al. Epigenetic regulation of microRNAs in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27: 1316–1322.
Roman-Gomez J, Cordeu L, Agirre X, Jimenez-Velasco A, San Jose-Eneriz E, Garate L et al. Epigenetic regulation of Wnt-signaling pathway in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2007; 109: 3462–3469.
Kuang SQ, Bai H, Fang ZH, Lopez G, Yang H, Tong W et al. Aberrant DNA methylation and epigenetic inactivation of Eph receptor tyrosine kinases and ephrin ligands in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2010; 115: 2412–2419.
Prince HM, Bishton M, Harrison S . The potential of histone deacetylase inhibitors for the treatment of multiple myeloma. Leuk Lymphoma 2008; 49: 385–387.
Piekarz RL, Bates SE . Epigenetic modifiers: basic understanding and clinical development. Clin Cancer Res 2009; 15: 3918–3926.
Prince HM, Bishton MJ, Johnstone RW . Panobinostat (LBH589): a potent pan-deacetylase inhibitor with promising activity against hematologic and solid tumors. Future Oncol 2009; 5: 601–612.
San Jose-Eneriz E, Agirre X, Jimenez-Velasco A, Cordeu L, Martin V, Arqueros V et al. Epigenetic down-regulation of BIM expression is associated with reduced optimal responses to imatinib treatment in chronic myeloid leukaemia. Eur J Cancer 2009; 45: 1877–1889.
Nielaender I, Martin-Subero JI, Wagner F, Martinez-Climent JA, Siebert R . Partial uniparental disomy: a recurrent genetic mechanism alternative to chromosomal deletion in malignant lymphoma. Leukemia 2006; 20: 904–905.
Mestre-Escorihuela C, Rubio-Moscardo F, Richter JA, Siebert R, Climent J, Fresquet V et al. Homozygous deletions localize novel tumor suppressor genes in B-cell lymphomas. Blood 2007; 109: 271–280.
Ocio EM, Vilanova D, Atadja P, Maiso P, Crusoe E, Fernandez-Lazaro D et al. In vitro and in vivo rationale for the triple combination of panobinostat (LBH589) and dexamethasone with either bortezomib or lenalidomide in multiple myeloma. Haematologica 2010; 95: 794–803.
Thiriet C, Hayes JJ . Chromatin in need of a fix: phosphorylation of H2AX connects chromatin to DNA repair. Mol Cell 2005; 18: 617–622.
Espinosa L, Cathelin S, D'Altri T, Trimarchi T, Statnikov A, Guiu J et al. The Notch/Hes1 pathway sustains NF-kappaB activation through CYLD repression in T cell leukemia. Cancer Cell 2010; 18: 268–281.
Yang X, Feng M, Jiang X, Wu Z, Li Z, Aau M et al. miR-449a and miR-449b are direct transcriptional targets of E2F1 and negatively regulate pRb-E2F1 activity through a feedback loop by targeting CDK6 and CDC25A. Genes Dev 2009; 23: 2388–2393.
Lize M, Pilarski S, Dobbelstein M . E2F1-inducible microRNA 449a/b suppresses cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 2010; 17: 452–458.
Duan H, Jiang Y, Zhang H, Wu Y . MiR-320 and miR-494 affect cell cycles of primary murine bronchial epithelial cells exposed to benzo[a]pyrene. Toxicol In Vitro 2010; 24: 928–935.
Richter-Larrea JA, Robles EF, Fresquet V, Beltran E, Rullan AJ, Agirre X et al. Reversion of epigenetically mediated BIM silencing overcomes chemoresistance in Burkitt lymphoma. Blood 2010; 116: 2531–2542.
Pui CH . Toward a total cure for acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27: 5121–5123.
Kuang SQ, Tong WG, Yang H, Lin W, Lee MK, Fang ZH et al. Genome-wide identification of aberrantly methylated promoter associated CpG islands in acute lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 2008; 22: 1529–1538.
Sakajiri S, Kumagai T, Kawamata N, Saitoh T, Said JW, Koeffler HP . Histone deacetylase inhibitors profoundly decrease proliferation of human lymphoid cancer cell lines. Exp Hematol 2005; 33: 53–61.
Garcia-Manero G . Demethylating agents in myeloid malignancies. Curr Opin Oncol 2008; 20: 705–710.
Yanez L, Bermudez A, Richard C, Bureo E, Iriondo A . Successful induction therapy with decitabine in refractory childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 2009; 23: 1342–1343.
Younes A . Novel treatment strategies for patients with relapsed classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program 2009; 1: 507–519.
Yokoyama S, Feige E, Poling LL, Levy C, Widlund HR, Khaled M et al. Pharmacologic suppression of MITF expression via HDAC inhibitors in the melanocyte lineage. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res 2008; 21: 457–463.
Gridelli C, Rossi A, Maione P . The potential role of histone deacetylase inhibitors in the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 2008; 68: 29–36.
LaBonte MJ, Wilson PM, Fazzone W, Groshen S, Lenz HJ, Ladner RD . DNA microarray profiling of genes differentially regulated by the histone deacetylase inhibitors vorinostat and LBH589 in colon cancer cell lines. BMC Med Genomics 2009; 2: 67.
Prystowsky MB, Adomako A, Smith RV, Kawachi N, McKimpson W, Atadja P et al. The histone deacetylase inhibitor LBH589 inhibits expression of mitotic genes causing G2/M arrest and cell death in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. J Pathol 2009; 218: 467–477.
Yu C, Friday BB, Yang L, Atadja P, Wigle D, Sarkaria J et al. Mitochondrial Bax translocation partially mediates synergistic cytotoxicity between histone deacetylase inhibitors and proteasome inhibitors in glioma cells. Neuro Oncol 2008; 10: 309–319.
Zhang B, Strauss AC, Chu S, Li M, Ho Y, Shiang KD et al. Effective targeting of quiescent chronic myelogenous leukemia stem cells by histone deacetylase inhibitors in combination with imatinib mesylate. Cancer Cell 2010; 17: 427–442.
Fiskus W, Pranpat M, Bali P, Balasis M, Kumaraswamy S, Boyapalle S et al. Combined effects of novel tyrosine kinase inhibitor AMN107 and histone deacetylase inhibitor LBH589 against Bcr-Abl-expressing human leukemia cells. Blood 2006; 108: 645–652.
Scuto A, Kirschbaum M, Kowolik C, Kretzner L, Juhasz A, Atadja P et al. The novel histone deacetylase inhibitor, LBH589, induces expression of DNA damage response genes and apoptosis in Ph- acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Blood 2008; 111: 5093–5100.
Muhlenberg T, Zhang Y, Wagner AJ, Grabellus F, Bradner J, Taeger G et al. Inhibitors of deacetylases suppress oncogenic KIT signaling, acetylate HSP90, and induce apoptosis in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 6941–6950.
Nicholson L, Hall AG, Redfern CP, Irving J . NFkappaB modulators in a model of glucocorticoid resistant, childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leuk Res 2010; 34: 1366–1373.
Einsiedel HG, Kawan L, Eckert C, Witt O, Fichtner I, Henze G et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitors have antitumor activity in two NOD/SCID mouse models of B-cell precursor childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 2006; 20: 1435–1436.
Crazzolara R, Cisterne A, Thien M, Hewson J, Baraz R, Bradstock KF et al. Potentiating effects of RAD001 (Everolimus) on vincristine therapy in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2009; 113: 3297–3306.
Liem NL, Papa RA, Milross CG, Schmid MA, Tajbakhsh M, Choi S et al. Characterization of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia xenograft models for the preclinical evaluation of new therapies. Blood 2004; 103: 3905–3914.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by grants from the Spanish Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovacion and Instituto de Salud Carlos III (ISCIII) PI07/0602, PI10/00110, PI10/01691, PI08/0440 and RTICC RD06/0020, Contrato Miguel Servet CP07/00215, European FEDER funds Interreg IVA (CITTIL), Programa Tu Eliges, Tu Decides (CAN), Gobierno de Navarra, Departamento de Salud, Beca Ortiz de Landázuri 2009 (6/2009) and funds from the ‘UTE project CIMA’, collaborative project of the Asociación Española Contra el Cáncer and Junta de Andalucía 0004/2007 and 0206/2009. AV-Z is supported by Ministerio Ciencia e Innovación (AP2008/03686).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Leukemia website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vilas-Zornoza, A., Agirre, X., Abizanda, G. et al. Preclinical activity of LBH589 alone or in combination with chemotherapy in a xenogeneic mouse model of human acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 26, 1517–1526 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2012.31
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2012.31
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Developing Targeted Therapies for T Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia/Lymphoma
Current Hematologic Malignancy Reports (2023)
-
Panobinostat (LBH589) increase survival in adult xenografic model of acute lymphoblastic leukemia with t(4;11) but promotes antagonistic effects in combination with MTX and 6MP
Medical Oncology (2022)
-
The HDAC inhibitor panobinostat (LBH589) exerts in vivo anti-leukaemic activity against MLL-rearranged acute lymphoblastic leukaemia and involves the RNF20/RNF40/WAC-H2B ubiquitination axis
Leukemia (2018)
-
Epigenetic targeting of Notch1-driven transcription using the HDACi panobinostat is a potential therapy against T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Leukemia (2018)
-
Discovery of first-in-class reversible dual small molecule inhibitors against G9a and DNMTs in hematological malignancies
Nature Communications (2017)