Abstract
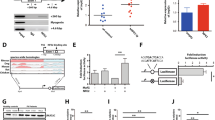
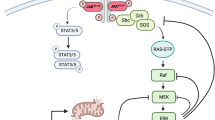
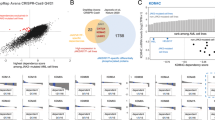
Janus kinase 2 (JAK2)V617F-activating mutations (JAK2mu) occur in myeloproliferative disorders (MPDs) and myelodysplastic syndromes (MDSs). Cell lines MB-02, MUTZ-8, SET-2 and UKE-1 carry JAK2V617F and derive from patients with MPD/MDS histories. Challenging the consensus that expression of JAK2V617F is the sole precondition for cytokine independence in class I cytokine receptor-positive cells, two of four of the JAK2mu cell lines were growth factor-dependent. These cell lines resembled JAK2wt cells regarding JAK2/STAT5 activation: cytokine deprivation effected dephosphorylation, whereas erythropoetin or granulocyte colony-stimulating factor induced phosphorylation of JAK2 and STAT5. Cytokine independence correlated with low expression and cytokine dependence with high expression of the JAK/STAT pathway inhibitor suppressor of cytokine signaling 2 (SOCS2) suggesting a two-step mechanism for cytokine independence of MPD cells: (i) activation of the oncogene JAK2V617F and (ii) inactivation of the tumor suppressor gene SOCS2. Confirming that SOCS2 operates as a negative JAK2V617F regulator, SOCS2 knockdown induced constitutive STAT5 phosphorylation in JAK2mu cells. CpG island hypermethylation is reported to promote SOCS gene silencing in malignant diseases. Accordingly, in one of two cytokine-independent cell lines and in two of seven MPD patients, we found SOCS2 hypermethylation associated with reduced promoter access to transcription factors. Our results provide solid evidence that SOCS2 epigenetic downregulation might be an important second step in the genesis of cytokine-independent MPD clones.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Starr R, Willson TA, Viney EM, Murray LJL, Rayner JR, Jenkins BJ et al. A family of cytokine-inducible inhibitors of signalling. Nature 1997; 387: 917–921.
Endo TA, Masuhara M, Yokouchi M, Suzuki R, Sakamoto H, Mitsui K et al. A new protein containing an SH2 domain that inhibits JAK kinases. Nature 1997; 387: 921–924.
Naka T, Narazaki M, Hirata M, Matsumoto T, Minamoto S, Aono A et al. Structure and function of a new STAT-induced STAT inhibitor. Nature 1997; 387: 924–929.
Sutherland KD, Lindeman GJ, Choong DYH, Wittlin S, Brentzell L, Phillips W et al. Differential hypermethylation of SOCS genes in ovarian and breast carcinomas. Oncogene 2004; 23: 7726–7733.
Galm O, Wilop S, Reichelt J, Jost E, Gehbauer G, Herman JG et al. DNA methylation changes in multiple myeloma. Leukemia 2004; 18: 1687–1692.
Marini A, Mirmohammadsadegh A, Nambiar S, Gustrau A, Ruzicka T, Hengge UR . Epigenetic inactivation of tumor suppressor genes in serum of patients with cutaneous melanoma. J Invest Dermatol 2006; 126: 422–431.
Lee TL, Yeh J, van Waes C, Chen Z . Epigenetic modification of SOCS-1 differentially regulates STAT3 activation in response to interleukin-6 receptor and epidermal growth factor receptor signaling through JAK and/or MEK in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Mol Cancer Ther 2006; 5: 8–19.
Niwa Y, Kanda H, Shikauchi Y, Saiura Y, Matsubara K, Kitagawa T et al. Methylation silencing of SOCS-3 promotes cell growth and migration by enhancing JAK/STAT and FAK signalings in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 2006; 24: 6404–6417.
Brakensiek K, Länger F, Schlegelberger B, Kreipe H, Lehmann U . Hypermethylation of the suppressor of cytokine signalling-1 (SOCS-1) in myelodysplastic syndrome. Br J Haematol 2005; 130: 209–217.
Jost E, do ÓN, Dahl E, Maintz CE, Jousten P, Habets L et al. Epigenetic alterations complement mutation of JAK2 tyrosine kinase in patients with BCR/ABL1-negative myeloproliferative disorders. Leukemia 2007; 21: 505–510.
Etienne A, Carbuccia N, Adelaide J, Bekhouche I, Remy V, Sohn C et al. Rearrangements involving 12q in myeloproliferative disorders: possible role of HMGA2 and SOCS2 genes. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 2007; 176: 80–88.
Lu X, Levine R, Tong W, Wernig G, Pikman Y, Zarnegar S et al. Expression of a homodimeric type I cytokine receptor is required for JAK2V617F-mediated transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 18962–18967.
Lu X, Huang LJS, Lodish HF . Dimerization by a cytokine receptor is necessary for constitutive activation of JAK2V617F. J Biol Chem 2008; 283: 5258–5266.
Quentmeier H, MacLeod RAF, Zaborski M, Drexler HG . JAK2V617F tyrosine kinase mutation in cell lines derived from myeloproliferative disorders. Leukemia 2006; 20: 471–476.
Morgan DA, Gumucio DL, Brodsky I . Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor-dependent growth and erythropoietin-induced differentiation of a human cell line MB-02. Blood 1991; 78: 2860–2871.
Hu ZB, MacLeod RAF, Meyer C, Quentmeier H, Drexler HG . New acute myeloid leukemia-derived cell line: MUTZ-8 with 5q-. Leukemia 2002; 16: 1556–1561.
Matozaki S, Nakagawa T, Kawaguchi R, Aozaki R, Tsutsumi M, Murayama T et al. Establishment of a myeloid leukaemic cell line (SKNO-1) from a patient with t(8;21) who acquired monosomy 17 during disease progression. Br J Haematol 1995; 89: 805–811.
Fiedler W, Henke RP, Ergün S, Schumacher U, Gehling UM, Vohwinkel G et al. Derivation of a new hematopoietic cell line with endothelial features from a patient with transformed myeloproliferative syndrome. Cancer 2000; 88: 344–351.
Drexler HG . The Leukemia-Lymphoma Cell Line Factsbook. Academic Press: San Diego, CA, 2000.
Quentmeier H, Drexler HG, Fleckenstein D, Zaborski M, Armstrong A, Sims JE et al. Cloning of human thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) and signaling mechanisms leading to proliferation. Leukemia 2001; 15: 1286–1292.
MacLeod RAF, Kaufmann M, Drexler HG . Cytogenetic harvesting of commonly used tumor cell lines. Nat Protoc 2007; 2: 372–382.
Scherr M, Battmer K, Ganser A, Eder M . Modulation of gene expression by lentiviral-mediated delivery of small interfering RNA. Cell Cycle 2003; 3: 251–257.
Scherr M, Battmer K, Blömer U, Schiedlmeier B, Ganser A, Grez M et al. Lentiviral gene transfer into peripheral blood-derived CD34+ NOD/SCID-repopulating cells. Blood 2002; 99: 709–712.
Levine RL, Madleigh M, Cools J, Ebert BL, Wernig G, Huntly BJP et al. Activating mutation in the tyrosine kinase JAK2 in polycythemia vera, essential thrombocythemia, and myeloid metaplasia with myelofibrosis. Cancer Cell 2005; 7: 387–397.
Larsen L, Röpke C . Suppressors of cytokine signalling: SOCS. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand 2002; 110: 833–844.
Usenko T, Eskinazi D, Correa PN, Amato D, Ben-David Y, Axelrad AA . Overexpression of SOCS-2 and SOCS-3 genes reverses erythorid overgrowth and IGF-I hypersensitivity of primary polycythemia vera (PV) cells. Leuk Lymphoma 2007; 48: 134–146.
Tannahill GM, Elliott J, Barry AC, Hibbert L, Cacalano NA, Johnston JA . SOCS2 can enhance interleukin-2 (IL-2) and IL-3 signaling by accelerating SOCS3 degradation. Mol Cell Biol 2005; 25: 9115–9126.
Hookham MB, Elliott J, Suessmuth Y, Staerk J, Ward AC, Vainchenker W et al. The myeloproliferative disorder-associated JAK2 V617F mutant escapes negative regulation by suppressor of cytokine signaling 3. Blood 2007; 109: 4924–4929.
Jegalian AG, Wu H . Differential roles of SOCS family members in EpoR signal transduction. J Interferon Cytokine Res 2002; 22: 853–860.
Rice KL, Hormaeche I, Licht JD . Epigenetic regulation of normal and malignant hematopoiesis. Oncogene 2007; 26: 6697–6714.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Leukemia website (http://www.nature.com/leu)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Quentmeier, H., Geffers, R., Jost, E. et al. SOCS2: inhibitor of JAK2V617F-mediated signal transduction. Leukemia 22, 2169–2175 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2008.226
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2008.226
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Evolving cognition of the JAK-STAT signaling pathway: autoimmune disorders and cancer
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2023)
-
MicroRNA-101 expression is associated with JAK2V617F activity and regulates JAK2/STAT5 signaling
Leukemia (2018)
-
SOCS proteins in regulation of receptor tyrosine kinase signaling
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2014)
-
SOCS2 is dispensable for BCR/ABL1-induced chronic myeloid leukemia-like disease and for normal hematopoietic stem cell function
Leukemia (2013)
-
Repression of STAT3, STAT5A, and STAT5B expressions in chronic myelogenous leukemia cell line K–562 with unmodified or chemically modified siRNAs and induction of apoptosis
Annals of Hematology (2013)