Abstract
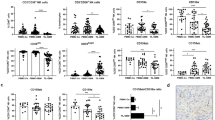
Exploiting the antitumor effect of natural killer (NK) cells has regained interest in light of data from preclinical and clinical work on the potential of alloreactive NK cells. Multiple myeloma (MM) and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) represent the two most prevalent adult hematological malignancies in the western hemisphere. To evaluate the role of NK cells in the immune surveillance and their therapeutic potential for CLL and MM, tumor cell susceptibility to NK-mediated killing was investigated. Results show relative resistance of tumor cells from CLL as well as MM (73 and 70% of the patients, respectively) to NK-mediated killing. To gain insight into molecular mechanisms of this resistance, the expression of the tolerogenic HLA-G molecule in CLL and MM and its relevance to susceptibility to NK-mediated killing were investigated. HLA-G transcript was found in tumor cells from 89% (n=19) of CLL and 100% (n=9) of MM patients examined. HLA-G1 surface expression was observed in CLL and was very low or undetectable in MM. Notably, blocking of HLA-G1 with specific antibody on CLL samples increased their susceptibility to NK-mediated killing, demonstrating that HLA-G participates in protecting CLL cells from NK-mediated killing and may thus contribute to their immune escape in vivo.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hideshima T, Bergsagel PL, Kuehl WM, Anderson KC . Advances in biology of multiple myeloma: clinical applications. Blood 2004; 104: 607–618.
Hamblin TJ . Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: clinical translations of biological features. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 2005; 294: 165–185.
Hideshima T, Richardson P, Anderson KC . Novel therapeutic approaches for multiple myeloma. Immunol Rev 2003; 194: 164–176.
Keating MJ, Chiorazzi N, Messmer B, Damle RN, Allen SL, Rai KR et al. Biology and treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program 2003, 153–175.
Pant S, Copelan EA . Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in multiple myeloma. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2007; 13: 877–885.
Kharfan-Dabaja MA, Anasetti C, Santos ES . Hematopoietic cell transplantation for chronic lymphocytic leukemia: an evolving concept. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2007; 13: 373–385.
Trinchieri G . Biology of natural killer cells. Adv Immunol 1989; 47: 187–376.
Lanier LL . NK cell recognition. Annu Rev Immunol 2005; 23: 225–274.
Lopez-Botet M, Llano M, Navarro F, Bellon T . NK cell recognition of non-classical HLA class I molecules. Semin Immunol 2000; 12: 109–119.
Colonna M . Specificity and function of immunoglobulin superfamily NK cell inhibitory and stimulatory receptors. Immunol Rev 1997; 155: 127–133.
Karre K . NK cells, MHC class I molecules and the missing self. Scand J Immunol 2002; 55: 221–228.
Ruggeri L, Capanni M, Casucci M, Volpi I, Tosti A, Perruccio K et al. Role of natural killer cell alloreactivity in HLA-mismatched hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood 1999; 94: 333–339.
Ruggeri L, Capanni M, Urbani E, Perruccio K, Shlomchik WD, Tosti A et al. Effectiveness of donor natural killer cell alloreactivity in mismatched hematopoietic transplants. Science 2002; 295: 2097–2100.
Parham P, McQueen KL . Alloreactive killer cells: hindrance and help for haematopoietic transplants. Nat Rev Immunol 2003; 3: 108–122.
Cosman D, Fanger N, Borges L, Kubin M, Chin W, Peterson L et al. A novel immunoglobulin superfamily receptor for cellular and viral MHC class I molecules. Immunity 1997; 7: 273–282.
Saverino D, Fabbi M, Ghiotto F, Merlo A, Bruno S, Zarcone D et al. The CD85/LIR-1/ILT-2 inhibitory receptor is expressed by all human T lymphocytes and down regulates their functions. J Immunol 2000; 165: 3742–3755.
Rajagopalan S, Long EO . A human histocompatibility leukocyte antigen (HLA)-G-specific receptor expressed on all natural killer cells. J Exp Med 1999; 189: 1093–1100.
Carosella ED, Moreau P, Le Maoult J, Le Discorde M, Dausset J, Rouas-Freiss N . HLA-G molecules: from maternal–fetal tolerance to tissue acceptance. Adv Immunol 2003; 81: 199–252.
Kovats S, Main EK, Librach C, Stubblebine M, Fisher SJ, DeMars R . A class I antigen, HLA-G, expressed in human trophoblasts. Science 1990; 248: 220–223.
King A, Hiby SE, Verma S, Burrows T, Gardner L, Loke YW . Uterine NK cells and trophoblast HLA class I molecules. Am J Reprod Immunol 1997; 37: 459–462.
Rouas-Freiss N, Moreau P, Ferrone S, Carosella ED . HLA-G proteins in cancer: do they provide tumor cells with an escape mechanism? Cancer Res 2005; 65: 10139–10144.
Paul P, Rouas-Freiss N, Khalil-Daher I, Moreau P, Riteau B, Le Gal FA et al. HLA-G expression in melanoma: a way for tumor cells to escape from immunosurveillance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998; 95: 4510–4515.
Wiendl H, Mitsdoerffer M, Hofmeister V, Wischhusen J, Bornemann A, Meyermann R et al. A functional role of HLA-G expression in human gliomas: an alternative strategy of immune escape. J Immunol 2002; 168: 4772–4780.
Braud VM, Allan DS, O'Callaghan CA, Soderstrom K, D'Andrea A, Ogg GS et al. HLA-E binds to natural killer cell receptors CD94/NKG2A, B and C. Nature 1998; 391: 795–799.
LeMaoult J, Caumartin J, Daouya M, Favier B, Le Rond S, Gonzalez A et al. Immune regulation by pretenders: cell-to-cell transfers of HLA-G make effector T cells act as regulatory cells. Blood 2007; 109: 2040–2048.
Caumartin J, Favier B, Daouya M, Guillard C, Moreau P, Carosella ED et al. Trogocytosis-based generation of suppressive NK cells. EMBO J 2007; 26: 1423–1433.
Gong JH, Maki G, Klingemann HG . Characterization of a human cell line (NK-92) with phenotypical and functional characteristics of activated natural killer cells. Leukemia 1994; 8: 652–658.
Maki G, Klingemann HG, Martinson JA, Tam YK . Factors regulating the cytotoxic activity of the human natural killer cell line, NK-92. J Hematother Stem Cell Res 2001; 10: 369–383.
Lichtenfels R, Biddison WE, Schulz H, Vogt AB, Martin R . CARE-LASS (calcein-release-assay), an improved fluorescence-based test system to measure cytotoxic T lymphocyte activity. J Immunol Methods 1994; 172: 227–239.
Liu L, Chahroudi A, Silvestri G, Wernett ME, Kaiser WJ, Safrit JT et al. Visualization and quantification of T cell-mediated cytotoxicity using cell-permeable fluorogenic caspase substrates. Nat Med 2002; 8: 185–189.
Betts MR, Brenchley JM, Price DA, De Rosa SC, Douek DC, Roederer M et al. Sensitive and viable identification of antigen-specific CD8+ T cells by a flow cytometric assay for degranulation. J Immunol Methods 2003; 281: 65–78.
Bryceson YT, March ME, Barber DF, Ljunggren HG, Long EO . Cytolytic granule polarization and degranulation controlled by different receptors in resting NK cells. J Exp Med 2005; 202: 1001–1012.
Pierson BA, Miller JS . CD56+bright and CD56+dim natural killer cells in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia progressively decrease in number, respond less to stimuli that recruit clonogenic natural killer cells, and exhibit decreased proliferation on a per cell basis. Blood 1996; 88: 2279–2287.
Costello RT, Sivori S, Marcenaro E, Lafage-Pochitaloff M, Mozziconacci MJ, Reviron D et al. Defective expression and function of natural killer cell-triggering receptors in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2002; 99: 3661–3667.
Kiladjian JJ, Bourgeois E, Lobe I, Braun T, Visentin G, Bourhis JH et al. Cytolytic function and survival of natural killer cells are severely altered in myelodysplastic syndromes. Leukemia 2006; 20: 463–470.
Almeida J, Orfao A, Ocqueteau M, Mateo G, Corral M, Caballero MD et al. High-sensitive immunophenotyping and DNA ploidy studies for the investigation of minimal residual disease in multiple myeloma. Br J Haematol 1999; 107: 121–131.
Le Gal FA, Riteau B, Sedlik C, Khalil-Daher I, Menier C, Dausset J et al. HLA-G-mediated inhibition of antigen-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Int Immunol 1999; 11: 1351–1356.
Menier C, Riteau B, Carosella ED, Rouas-Freiss N . MICA triggering signal for NK cell tumor lysis is counteracted by HLA-G1-mediated inhibitory signal. Int J Cancer 2002; 100: 63–70.
Amiot L, Onno M, Drenou B, Monvoisin C, Fauchet R . HLA-G class I gene expression in normal and malignant hematopoietic cells. Hum Immunol 1998; 59: 524–528.
Sebti Y, Le Friec G, Pangault C, Gros F, Drenou B, Guilloux V et al. Soluble HLA-G molecules are increased in lymphoproliferative disorders. Hum Immunol 2003; 64: 1093–1101.
Polakova K, Krcova M, Kuba D, Russ G . Analysis of HLA-G expression in malignant hematopoetic cells from leukemia patients. Leuk Res 2003; 27: 643–648.
Nuckel H, Rebmann V, Durig J, Duhrsen U, Grosse-Wilde H . HLA-G expression is associated with an unfavorable outcome and immunodeficiency in reb. Blood 2005; 105: 1694–1698.
Leleu X, Le Friec G, Facon T, Amiot L, Fauchet R, Hennache B et al. Total soluble HLA class I and soluble HLA-G in multiple myeloma and monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance. Clin Cancer Res 2005; 11: 7297–7303.
Apps R, Gardner L, Sharkey AM, Holmes N, Moffett A . A homodimeric complex of HLA-G on normal trophoblast cells modulates antigen-presenting cells via LILRB1. Eur J Immunol 2007; 37: 1924–1937.
Gonen-Gross T, Achdout H, Arnon TI, Gazit R, Stern N, Horejsi V et al. The CD85J/Leukocyte inhibitory receptor-1 distinguishes between conformed and beta 2-microglobulin-free HLA-G molecules. J Immunol 2005; 175: 4866–4874.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by grants from ‘The Leukemia & Lymphoma Society’ and ‘Grant CLL-63119, Section of Hematology, Rush University Medical Center’.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Leukemia website (http://www.nature.com/leu)
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maki, G., Hayes, G., Naji, A. et al. NK resistance of tumor cells from multiple myeloma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients: implication of HLA-G. Leukemia 22, 998–1006 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2008.15
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2008.15
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Trogocytic intercellular membrane exchanges among hematological tumors
Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2015)
-
Neutralization of (NK-cell-derived) B-cell activating factor by Belimumab restores sensitivity of chronic lymphoid leukemia cells to direct and Rituximab-induced NK lysis
Leukemia (2015)
-
CS1-specific chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-engineered natural killer cells enhance in vitro and in vivo antitumor activity against human multiple myeloma
Leukemia (2014)
-
Impact of HLA-E gene polymorphism on HLA-E expression in tumor cells and prognosis in patients with stage III colorectal cancer
Medical Oncology (2013)
-
Case–control study of HLA-G promoter methylation status, HPV infection and cervical neoplasia in Curitiba, Brazil: a pilot analysis
BMC Cancer (2012)