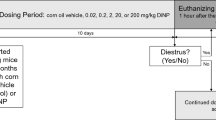
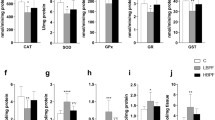
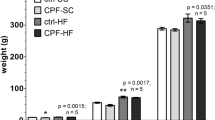
Abstract
To obtain accurate results from experiments in animal models, all potential confounding variables must be identified and controlled. The authors examined the effects of Helicobacter infection on developmental toxicity resulting from exposure to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD), a persistent and ubiquitous environmental contaminant. They administered different doses of TCDD to timed pregnant Helicobacter-positive and Helicobacter-negative Holtzman rats and evaluated fetal and neonatal viability. They also assessed hepatic cytochrome P450 induction and activity of the gene Cyp1a1, which are classic indicators of TCDD exposure. All rats were affected by TCDD, and Helicobacter infection seemed to have little influence on rats' susceptibility to the compound.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
We are sorry, but there is no personal subscription option available for your country.
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mandal, P.K. Dioxin: a review of its environmental effects and its aryl hydrocarbon receptor biology. J. Comp. Physiol. [B] 175, 221–230 (2005).
Birnbaum, L.S. Developmental effects of dioxins. Environ. Health Perspect. 103 Suppl 7, 89–94 (1995).
Boverhof, D.R. et al. Comparative toxicogenomic analysis of the hepatotoxic effects of TCDD in Sprague Dawley rats and C57BL/6 mice. Toxicol. Sci. 94, 398–416 (2006).
Hanlon, P.R. et al. Identification of novel TCDD-regulated genes by microarray analysis. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 202, 215–228 (2005).
Ovando, B.J., Vezina, C.M., McGarrigle, B.P. & Olson, J.R. Hepatic gene downregulation following acute and subchronic exposure to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Toxicol. Sci. 94, 428–438 (2006).
Tijet, N. et al. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor regulates distinct dioxin-dependent and dioxin-independent gene batteries. Mol. Pharmacol. 69, 140–153 (2006).
Vezina, C.M., Walker, N.J. & Olson, J.R. Subchronic exposure to TCDD, PeCDF, PCB126, and PCB153: effect on hepatic gene expression. Environ. Health Perspect. 112, 1636–1644 (2004).
Birnbaum, L.S. & Tuomisto, J. Non-carcinogenic effects of TCDD in animals. Food Addit. Contam. 17, 275–288 (2000).
National Toxicology Program. Toxicology and Carcinogenesis Studies of 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) (CAS No. 1746-01-6) in Female Harlan Sprague-Dawley Rats (Gavage Studies). Technical Report 521, 4–232 (National Toxicology Program, Research Triangle Park, 2006).
Marshall, B.J. & Warren, J.R. Unidentified curved bacilli in the stomach of patients with gastritis and peptic ulceration. Lancet 1, 1311–1315 (1984).
Fox, J.G. The non-H pylori helicobacters: their expanding role in gastrointestinal and systemic diseases. Gut 50, 273–283 (2002).
García, A., Xu, S., Dewhirst, F.E., Nambiar, P.R. & Fox, J.G. Enterohepatic Helicobacter species isolated from the ileum, liver and colon of a baboon with pancreatic islet amyloidosis. J. Med. Microbiol. 55, 1591–1595 (2006).
Kusters, J.G., van Vliet, A.H. & Kuipers, E.J. Pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 19, 449–490 (2006).
Ward, J.M. et al. Chronic active hepatitis and associated liver tumors in mice caused by a persistent bacterial infection with a novel Helicobacter species. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 86, 1222–1227 (1994).
Zenner, L. Pathology, diagnosis and epidemiology of the rodent Helicobacter infection. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 22, 41–61 (1999).
Solnick, J.V. & Schauer, D.B. Emergence of diverse Helicobacter species in the pathogenesis of gastric and enterohepatic diseases. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 14, 59–97 (2001).
Solnick, J.V. Clinical significance of Helicobacter species other than Helicobacter pylori. Clin. Infect. Dis. 36, 349–354 (2003).
Kanbay, M., Kanbay, A. & Boyacioglu, S. Helicobacter pylori infection as a possible risk factor for respiratory system disease: a review of the literature. Respir. Med. 101, 203–209 (2006).
Wu, X.Z. & Chen, D. Helicobacter pylori and hepatocellular carcinoma: correlated or uncorrelated? J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 21, 345–347 (2006).
Hailey, J.R. et al. Impact of Helicobacter hepaticus infection in B6C3F1 mice from twelve National Toxicology Program two-year carcinogenesis studies. Toxicol. Pathol. 26, 602–611 (1998).
Kransler, K.M., McGarrigle, B.P. & Olson, J.R. Comparative developmental toxicity of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in the hamster, rat and guinea pig. Toxicology 229, 214–225 (2007).
Peterson, R.E., Theobald, H.M. & Kimmel, G.L. Developmental and reproductive toxicity of dioxins and related compounds: cross-species comparisons. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 23, 283–335 (1993).
Kransler, K.M., Tonucci, D.A., McGarrigle, B.P., Napoli, J.L. & Olson, J.R. Gestational exposure to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin alters retinoid homeostasis in maternal and perinatal tissues of the Holtzman rat. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 224, 29–38 (2007).
Whitlock, J.P. Jr. Induction of cytochrome P4501A1. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 39, 103–125 (1999).
Greig, J.B. & De Matteis, F. Effects of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin on drug metabolism and hepatic microsomes of rats and mice. Environ. Health Perspect. 5, 211–219 (1973).
Hill, M. UNSW Embryology (Version 6.1), An educational resource for learning concepts in embryological development. 2007. http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryo.htm
Drahushuk, A.T. et al. Validation of precision-cut liver slices in dynamic organ culture as an in vitro model for studying CYP1A1 and CYP1A2 induction. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 140, 393–403 (1996).
Omura, T. & Sato, R. The carbon monoxide-binding pigment of liver microsomes. I. Evidence for its hemoprotein nature. J. Biol. Chem. 239, 2370–2378 (1964).
Prough, R.A., Burke, M.D. & Mayer, R.T. Direct fluorometric methods for measuring mixed function oxidase activity. Methods Enzymol. 52, 372–377 (1978).
Zenner, L. Pathology, diagnosis and epidemiology of the rodent Helicobacter infection. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 22, 41–61 (1999).
Whary, M.T. & Fox, J.G. Detection, eradication, and research implications of Helicobacter infections in laboratory rodents. Lab Anim. (NY) 35, 25–27, 30–36 (2006).
O'Rourke, J.L. & Lee, A. Animal models of Helicobacter pylori infection and disease. Microbes Infect. 5, 741–748 (2003).
Kodama, M. et al. Helicobacter pylori-infected animal models are extremely suitable for the investigation of gastric carcinogenesis. World J. Gastroenterol. 11, 7063–7071 (2005).
Gonciarz, M., Wloch, M. & Gonciarz, Z. Helicobacter pylori in liver diseases. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 57 Suppl 3, 155–161 (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare competing financial interests. At the time of the study, R.J.R. was employed by Harlan Sprague Dawley, Inc., which provided the rats as a gift.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kransler, K., McGarrigle, B., Russell, R. et al. Effects of Helicobacter infection on developmental toxicity of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in Holtzman rats. Lab Anim 37, 171–175 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/laban0408-171
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/laban0408-171