Abstract
Objective:
We studied whether cerebral blood pressure autoregulation and kidney and liver injuries are associated in neonatal encephalopathy (NE).
Study design:
We monitored autoregulation of 75 newborns who received hypothermia for NE in the neonatal intensive care unit to identify the mean arterial blood pressure with optimized autoregulation (MAPOPT). Autoregulation parameters and creatinine, aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) were analyzed using adjusted regression models.
Results:
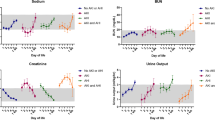
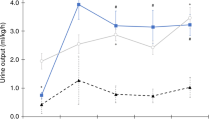
Greater time with blood pressure within MAPOPT during hypothermia was associated with lower creatinine in girls. Blood pressure below MAPOPT related to higher ALT and AST during normothermia in all neonates and boys. The opposite occurred in rewarming when more time with blood pressure above MAPOPT related to higher AST.
Conclusions:
Blood pressures that optimize cerebral autoregulation may support the kidneys. Blood pressures below MAPOPT and liver injury during normothermia are associated. The relationship between MAPOPT and AST during rewarming requires further study.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dammann O, Ferriero D, Gressens P . Neonatal encephalopathy or hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy? Appropriate terminology matters. Pediatr Res 2011; 70 (1): 1–2.
Gupta C, Massaro AN, Ray PE . A new approach to define acute kidney injury in term newborns with hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy. Pediatr Nephrol 2016; 31 (7): 1167–1178.
Choudhary M, Sharma D, Dabi D, Lamba M, Pandita A, Shastri S . Hepatic dysfunction in asphyxiated neonates: prospective case-controlled study. Clin Med Insights Pediatr 2015; 9: 1–6.
Burton VJ, Gerner G, Cristofalo E, Chung SE, Jennings JM, Parkinson C et al. A pilot cohort study of cerebral autoregulation and 2-year neurodevelopmental outcomes in neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy who received therapeutic hypothermia. BMC Neurol 2015; 15: 209–015-0464-4.
Howlett JA, Northington FJ, Gilmore MM, Tekes A, Huisman TAGM, Parkinson C et al. Cerebrovascular autoregulation and neurologic injury in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Pediatr Res 2013; 74 (5): 525–535.
Tekes A, Poretti A, Scheurkogel MM, Huisman TA, Howlett JA, Alqahtani E et al. Apparent diffusion coefficient scalars correlate with near-infrared spectroscopy markers of cerebrovascular autoregulation in neonates cooled for perinatal hypoxic-ischemic injury. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2015; 36 (1): 188–193.
Massaro AN, Govindan RB, Vezina G, Chang T, Andescavage NN, Wang Y et al. Impaired cerebral autoregulation and brain injury in newborns with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy treated with hypothermia. J Neurophysiol 2015; 114 (2): 818–824.
Chalak LF, Tian F, Tarumi T, Zhang R . Cerebral hemodynamics in asphyxiated newborns undergoing hypothermia therapy: pilot findings using a multiple-time-scale analysis. Pediatr Neurol 2016; 55: 30–36.
Lee JK, Poretti A, Perin J, Huisman TA, Parkinson C, Chavez-Valdez R et al. Optimizing cerebral autoregulation may decrease neonatal regional hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Dev Neurosci 2016;doi:10.1159/000452833.
Lee JK, Kibler KK, Benni PB, Easley RB, Czosnyka M, Smielewski P et al. Cerebrovascular reactivity measured by near-infrared spectroscopy. Stroke 2009; 40 (5): 1820–1826.
Cohen SS, Stonestreet BS . Sex differences in behavioral outcome following neonatal hypoxia ischemia: insights from a clinical meta-analysis and a rodent model of induced hypoxic ischemic injury. Exp Neurol 2014; 256: 70–73.
Smith AL, Alexander M, Rosenkrantz TS, Sadek ML, Fitch RH . Sex differences in behavioral outcome following neonatal hypoxia ischemia: insights from a clinical meta-analysis and a rodent model of induced hypoxic ischemic brain injury. Exp Neurol 2014; 254: 54–67.
Shankaran S, Laptook AR, Ehrenkranz RA, Tyson JE, McDonald SA, Donovan EF et al. Whole-body hypothermia for neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. N Engl J Med 2005; 353 (15): 1574–1584.
Chavez-Valdez R, O'Connor M, Perin J, Reyes M, Armstrong J, Parkinson C et al. Associations between cerebrovascular blood pressure autoregulation and cardiopulmonary injury may be sex-specific in neonates treated with therapeutic hypothermia for hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Pediatr Res 2017;doi:10.1038/pr.2017.23 (in press).
Larson AC, Jamrogowicz JL, Kulikowicz E, Wang B, Yang ZJ, Shaffner DH et al. Cerebrovascular autoregulation after rewarming from hypothermia in a neonatal swine model of asphyxic brain injury. J Appl Physiol 2013; 115 (10): 1433–1442.
Armstead WM, Kiessling JW, Kofke WA, Vavilala MS . Impaired cerebral blood flow autoregulation during posttraumatic arterial hypotension after fluid percussion brain injury is prevented by phenylephrine in female but exacerbated in male piglets by extracellular signal-related kinase mitogen-activated protein kinase upregulation. Crit Care Med 2010; 38 (9): 1868–1874.
Siriussawakul A, Sharma D, Sookplung P, Armstead W, Vavilala MS . Gender differences in cerebrovascular reactivity to carbon dioxide during sevoflurane anesthesia in children: preliminary findings. Paediatr Anaesth 2011; 21 (2): 141–147.
Pappas A, Shankaran S, Laptook AR, Langer JC, Bara R, Ehrenkranz RA et al. Hypocarbia and adverse outcome in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. J Pediatr 2011; 158 (5): 752–758.e1.
Ono M, Arnaoutakis GJ, Fine DM, Brady K, Easley RB, Zheng Y et al. Blood pressure excursions below the cerebral autoregulation threshold during cardiac surgery are associated with acute kidney injury. Crit Care Med 2013; 41 (2): 464–471.
Karlsson M, Wiberg-Itzel E, Chakkarapani E, Blennow M, Winbladh B, Thoresen M . Lactate dehydrogenase predicts hypoxic ischaemic encephalopathy in newborn infants: a preliminary study. Acta Paediatr 2010; 99 (8): 1139–1144.
Acknowledgements
Support was provided by the NIH R01HD070996 (FJN), R01HD074593 (FJN), K08NS080984 (JKL) and R21HD072845 (JKL); Johns Hopkins University Clinician Scientist Award (JKL); American Heart Association Grant-in-Aid (JKL); and the Sutland-Pakula Endowment for Neonatal Research (RC-V). Funding for the study described in this manuscript was provided in part by Medtronic. JKL was the principal investigator of this grant. The funding was used to support research effort by RC-V, FJN, JP, CP and MR.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
JKL was a paid advisory board member for Medtronic. This arrangement has been reviewed and approved by the Johns Hopkins University in accordance with its conflict of interest policies. In addition, JKL and FJN have been funded by the NIH. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
We dedicate this manuscript to the Poretti family in loving memory of Dr Andrea Poretti.
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Journal of Perinatology website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, J., Perin, J., Parkinson, C. et al. Relationships between cerebral autoregulation and markers of kidney and liver injury in neonatal encephalopathy and therapeutic hypothermia. J Perinatol 37, 938–942 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2017.64
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2017.64