Abstract
Objective:
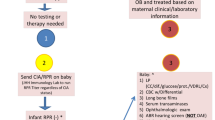
Infants whose mothers had syphilis during pregnancy were studied to determine how often exposed newborns with normal physical examinations and nonreactive nontreponemal serologic tests had abnormal laboratory or radiographic studies.
Study Design:
Retrospective analysis of prospectively collected data from infants born to mothers with syphilis and had a normal examination and a nonreactive nontreponemal test. Some infants had IgM immunoblotting, PCR testing or rabbit infectivity testing (RIT) performed.
Results:
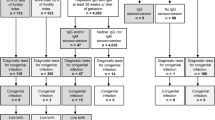
From 1984 to 2002, 115 infants had a nonreactive serum Venereal Disease Research Laboratory (VDRL)/rapid plasma reagin (RPR) test and a normal physical examination at birth. Among 87 infants born to mothers who had untreated syphilis, 4 had a positive serum IgM immunoblot or PCR test, but none had spirochetes recovered by RIT. Two infants had anemia, one had an elevated serum alanine aminotransferase concentration and one with Down’s syndrome had direct hyperbilirubinemia. Among 14 infants born to mothers treated <4 weeks before delivery, none had abnormal laboratory or radiographic tests, although 1 of 11 had a reactive serum IgM immunoblot. Among 14 infants born to mothers treated ⩾4 weeks before delivery, none had abnormal laboratory or radiographic tests.
Conclusion:
Newborns with normal physical examination and nonreactive nontreponemal test results are unlikely to have abnormalities detected on conventional laboratory and radiographic testing.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Binnicker MJ, Jespersen DJ, Rollins LO . Direct comparison of the traditional and reverse syphilis screening algorithms in a population with a low prevalence of syphilis. J Clin Microbiol 2012; 50 (1): 148–150.
Radolf JD, Bolan G, Park IU, Chow JM, Schillinger JA, Pathela P et al. Discordant results from reverse sequence syphilis screening—five laboratories, United States, 2006–2010. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2011; 60 (5): 133–137.
Sanchez PJ, Wendel GD Jr, Grimprel E, Goldberg M, Hall M, Arencibia-Mireles O et al. Evaluation of molecular methodologies and rabbit infectivity testing for the diagnosis of congenital syphilis and neonatal central nervous system invasion by Treponema pallidum. J Infect Dis 1993; 167 (1): 148–157.
Sanchez PJ, McCracken GH Jr, Wendel GD, Olsen K, Threlkeld N, Norgard MV . Molecular analysis of the fetal IgM response to Treponema pallidum antigens: implications for improved serodiagnosis of congenital syphilis. J Infect Dis 1989; 159 (3): 508–517.
Sanchez PJ, Wendel GD, Norgard MV . IgM antibody to Treponema pallidum in cerebrospinal fluid of infants with congenital syphilis. Am J Dis Child 1992; 146 (10): 1171–1175.
Grimprel E, Sanchez PJ, Wendel GD, Burstain JM, McCracken GH Jr, Radolf JD et al. Use of polymerase chain reaction and rabbit infectivity testing to detect Treponema pallidum in amniotic fluid, fetal and neonatal sera, and cerebrospinal fluid. J Clin Microbiol 1991; 29 (8): 1711–1718.
Wiedmeier SE, Henry E, Sola-Visner MC, Christensen RD . Platelet reference ranges for neonates, defined using data from over 47,000 patients in a multihospital healthcare system. J Perinatol 2009; 29 (2): 130–136.
Jopling J, Henry E, Wiedmeier SE, Christensen RD . Reference ranges for hematocrit and blood hemoglobin concentration during the neonatal period: data from a multihospital health care system. Pediatrics 2009; 123 (2): e333–e337.
Peterman TA, Newman DR, Davis D, Su JR . Do women with persistently negative nontreponemal test results transmit syphilis during pregnancy? Sex Transm Dis 2013; 40 (4): 311–315.
Sanchez PJ, Wendel GD, Norgard MV . Congenital syphilis associated with negative results of maternal serologic tests at delivery. Am J Dis Child 1991; 145 (9): 967–969.
Dorfman DH, Glaser JH . Congenital syphilis presenting in infants after the newborn period. N Engl J Med 1990; 323 (19): 1299–1302.
Workowski KA, Bolan GA . Sexually transmitted diseases treatment guidelines. 2015 MMWR Recomm Rep 2015; 64 (RR-03): 1–137.
Mmeje O, Chow JM, Davidson L, Shieh J, Schapiro JM, Park IU . Discordant syphilis immunoassays in pregnancy: perinatal outcomes and implications for clinical management. Clin Infect Dis 2015; 61 (7): 1049–1053.
Thorley JD, Kaplan JM, Holmes RK, McCracken GH Jr., Sanford JP . Passive transfer of antibodies of maternal origin from blood to cerebrospinal fluid in infants. Lancet 1975; 1 (7908): 651–653.
Michelow IC, Wendel GD Jr., Norgard MV, Zeray F, Leos NK, Alsaadi R et al. Central nervous system infection in congenital syphilis. N Engl J Med 2002; 346 (23): 1792–1798.
Chhabra RS, Brion LP, Castro M, Freundlich L, Glaser JH . Comparison of maternal sera, cord blood, and neonatal sera for detecting presumptive congenital syphilis: relationship with maternal treatment. Pediatrics 1993; 91 (1): 88–91.
Brion LP, Manuli M, Rai B, Kresch MJ, Pavlov H, Glaser J . Long-bone radiographic abnormalities as a sign of active congenital syphilis in asymptomatic newborns. Pediatrics 1991; 88 (5): 1037–1040.
Cooper JM, Michelow IC, Wozniak PS, Sanchez PJ . In time: the persistence of congenital syphilis in Brazil— more progress needed!. Rev Paul Pediatr 2016; 34 (3): 251–253.
Bowen V, Su J, Torrone E, Kidd S, Weinstock H . Increase in incidence of congenital syphilis—United States, 2012–2014. Morb Mort Wly Rep 2015; 64 (44): 1241–1245.
Acknowledgements
We thank Michael V Norgard, PhD, Professor and Chair of Microbiology at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX for superb mentorship (PJS) as well as guidance and supervision of the research methodologies used in this study. This study was presented, in part, at the Pediatric Academics Societies Meetings, 25 to 28 April 2015 in San Diego, California. This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health (1 R29 AI 34932-01 to PJS) and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (C1000 689 to PJS, GDW).
Author contributions
PSW helped to conceptualize and design the study, analyzed the data, draft the initial manuscript and approved the final manuscript as submitted.
JBC helped to conceptualize and design the study, analyzed the data, reviewed and revised the manuscript and approved the final manuscript as submitted.
FZ helped to design the study, collected and analyzed the data, reviewed the manuscript draft and approved the final manuscript as submitted.
NKL helped to design the study, performed laboratory testing, analyzed the data and approved the final manuscript as submitted.
JSS helped to design the study, analyzed the data, reviewed the manuscript draft and approved the final manuscript as submitted.
GDW helped to conceptualize and design the study, performed the laboratory testing, analyzed the data, reviewed the manuscript draft and approved the final manuscript as submitted.
PJS helped to conceptualize and design the study, collected and analyzed the data, performed the laboratory testing, reviewed and revised the manuscript and approved the final manuscript as submitted.
All authors approved the final manuscript as submitted and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wozniak, P., Cantey, J., Zeray, F. et al. Congenital syphilis in neonates with nonreactive nontreponemal test results. J Perinatol 37, 1112–1116 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2017.103
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2017.103