Abstract
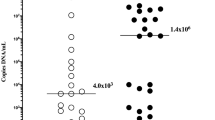
Intrauterine infection and inflammation are recognized as major contributors to the onset of preterm labor. We describe two cases of severe preterm labor with bulging membrane that were treated by intravenous injection of Sivelestat, a neutrophil elastase inhibitor. Ritodrine hydrochloride and magnesium sulfate were intravenously administered for tocolysis, and ampicillin was provided as an antibiotic. Urinary trypsin inhibitor (UTI) was administered transvaginally. Sivelestat was infused intravenously at 4.8 mg kg−1 day−1 through the maternal vein. No side effects were observed. Levels of interleukin (IL)-6 and IL-8 in amniotic fluid decreased, and gestations were prolonged without complications for >1 week. Two healthy infants were delivered. Our experience suggests that multidrug therapy with Sivelestat offers a new therapeutic strategy for preterm labor, but further investigations of the indications, administration period and dosage are required.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Romero R, Mazor M . Infection and preterm labor. Clin Obstet Gynecol 1998; 31: 553–584.
Fonseca EB, Celik E, Parra M, Singh M, Nicolaides KH . Fetal medicine foundation second trimester screening group. Progesterone and the risk of preterm birth among women with a short cervix. N Engl J Med 2007; 357: 462–469.
Haga Y, Ogawa M . Neutrophil elastase inhibitor(ONO-5046.Na) decreases production of proinflammatory cytokines by lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human monocytes. Res Commun Mol Pathol Pharmacol 1997; 98: 243–248.
Iams JD, Creasy RK . Preterm labor and delivery In: Creasym RK, Resnik R, Iams JD (eds). Maternal-Fetal Medicine Principles and Practice, 5th edn. Saunders: Pennsylvania, 2004, pp 623–662.
Chauleur C, Rochigneux S, Seffert P, Chene G, Billiemaz K, Collet F . Neonatal outcomes and four-year follow-up after spontaneous or iatrogenic preterm prelabor rupture of membranes before 24 weeks. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2009; 88: 801–806.
King J, Flenady V . Prophylactic antibiotics for inhibiting preterm labour with intact membranes. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2002; (4): CD000246.
Hutzal CE, Boyle EM, Kenyon SL, Nash JV, Winsor S, Taylor DJ et al. Use of antibiotics for the treatment of preterm parturition and prevention of neonatal morbidity: a metaanalysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2008; 199: 620.e1–620.e8.
Matsuda Y, Kouno S, Nakano H . The significance of interleukin-6 concentrations in cervicovaginal fluid: its relation to umbilical cord plasma and the influence of antibiotic treatment. J Perinat Med 2000; 28: 129–132.
Kanayama N, el Maradny E, Yamamoto N, Tokunaga N, Maehara K, Terao T . Urinary trypsin inhibitor: a new drug to treat preterm labor: a comparative study with ritodrine. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1996; 67: 133–138.
Matsuda Y, Yunohara N . Effects of urinary trypsin inhibitor in patients at risk for premature labor with a bulging fetal membrane. Fetal Diagn Ther 2002; 17: 69–74.
Helmig BR, Romero R, Espinoza J, Chaiworapongsa T, Bujold E, Gomez R et al. Neutrophil elastase and secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor in prelabor rupture of membranes, parturition and intra-amniotic infection. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2002; 12: 237–246.
Tromp G, Kuivaniemi H, Romero R, Chaiworapongsa T, Kim YM, Kim MR et al. Genome-wide expression profiling of fetal membranes reveals a deficient expression of proteinase inhibitor 3 in premature rupture of membranes. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2004; 191: 1331–1338.
Chowdhury MA, Kuivaniemi H, Romero R, Edwin S, Chaiworapongsa T, Tromp G . Identification of novel functional sequence variants in the gene for peptidase inhibitor 3. BMC Med Genet 2006; 23 7: 49.
Tamakuma S, Ogawa M, Aikawa N, Kubota T, Hirasawa H, Ishizaka A et al. Relationship between neutrophil elastase and acute lung injury in humans. Pulm Pharmacol Ther 2004; 17: 271–279.
Masaoka N, Watanabe M, Nakajima Y . The effects of sivelestat sodium hydrate on uterine contraction and the concentration of maternal and fetal blood cytokines in a sheep model of intra-amniotic infection induced by lipopolysaccharide. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2011; 24: 1013–1018.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakajima, Y., Masaoka, N. Initial experience using Sivelestat to manage preterm labor with a bulging fetal membrane in pregnant women. J Perinatol 32, 466–468 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2011.132
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2011.132