Abstract
Objective:
Report clinical response to recombinant factor VIIa in a cohort of critically ill infants.
Study Design:
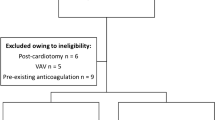
We identified all infants who received factor VIIa in the Duke Neonatal Intensive Care Unit between January 2005 and July 2008. Hematological data and volume of blood transfusions before and after factor VIIa treatment were compared. The precipitating diagnosis for each factor VIIa use, and the ensuing clinical outcomes of bleeding, thrombosis and mortality were noted.
Result:
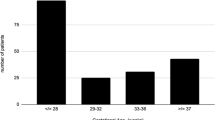
We identified 18 infants with median birth weight of 880 g and median gestational age of 26 weeks. One to six doses of factor VIIa (90 mcg kg−1 per dose) were administered, with 13 (72%) infants receiving a single dose. Hemostasis was achieved in 13 (72%) of the infants. Prothrombin time and activated partial thromboplastin time significantly decreased following treatment with factor VIIa. Volume of plasma transfusions significantly decreased following treatment with factor VIIa (P=0.02). Thrombosis occurred in one (11%) infant. Six (33%) infants died within 72 h of treatment, and overall mortality was 10/18 (56%).
Conclusion:
Treatment with factor VIIa at doses of 90 mcg kg−1 improved coagulation studies and decreased the need for plasma transfusions in a group of critically ill infants without significant risk. Factor VIIa may be an effective addition to current treatment modalities for refractory hemorrhage in infants.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lindley CM, Sawyer WT, Macik BG, Lusher J, Harrison JF, Baird-Cox K et al. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of recombinant Factor VIIa. Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics 1994; 55 (6): 638–648.
Walsh MC, Kliegman RM . Necrotizing enterocolitis: treatment based on staging criteria. Pediatr Clin North Am 1986; 33 (1): 179–201.
Agarwal HS, Bennett JE, Churchwell KB, Christian KG, Drinkwater Jr DC, He Y et al. Recombinant factor seven therapy for postoperative bleeding in neonatal and pediatric cardiac surgery. Ann Thorac Surg 2007; 84 (1): 168–169.
Alten JA, Benner K, Green K, Toole B, Tofil NM, Winkler MK . Pediatric off-label use of recombinant factor VIIa. Pediatrics 2009; 123 (3): 1066–1072.
Veldman A, Neuhaeuser C, Akintuerk H, Thul J, Gehron J, Schranz D et al. rFVIIa in the treatment of persistent hemorrhage in pediatric patients on ECMO following surgery for congenital heart disease. Paediatr Anaesth 2007; 17 (12): 1123–1125.
Heller M, Lau W, Pazmino-Canizares J, Brandao LR, Carcao M . A comprehensive review of rFVIIa use in a tertiary care pediatric center. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2008; 50 (5): 1013–1017.
Guzzetta NA, Huch S, Fernandez JD, Tosone SR, Miller BE . Use of recombinant factor VIIa for uncontrolled bleeding in neonates after cardiopulmonary bypass. Paediatr Anaesth 2009; 19 (4): 364–370.
Yilmaz D, Karapinar B, Balkan C, Akisu M, Kavakli K . Single-center experience: use of recombinant factor VIIa for acute life-threatening bleeding in children without congenital hemorrhagic disorder. Pediatr Hematol Oncol 2008; 25 (4): 301–311.
Grizelj R, Vukovic J, Filipovic-Grcic B, Saric D, Luetic T . Successful use of recombinant activated FVIIa and aminocaproic acid in four neonates with life-threatening hemorrhage. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 2006; 17 (5): 413–415.
Jen H, Shew S . Recombinant activated factor VII use in critically ill infants with active hemorrhage. J Pediatr Surg 2008; 43 (12): 2235–2238.
Tancabelic J, Haun SE . Management of coagulopathy with recombinant factor VIIa in a neonate with echovirus type 7. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2004; 43 (2): 170–176.
Ekert H, Brizard C, Eyers R, Cochrane A, Henning R . Elective administration in infants of low-dose recombinant activated factor VII (rFVIIa) in cardiopulmonary bypass surgery for congenital heart disease does not shorten time to chest closure or reduce blood loss and need for transfusions: a randomized, double-blind, parallel group, placebo-controlled study of rFVIIa and standard haemostatic replacement therapy versus standard hemostatic replacement therapy. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 2006; 17 (5): 389–395.
Razon Y, Erez E, Vidne B, Birk E, Katz J, Tamari H et al. Recombinant factor VIIa (Novoseven®) as a hemostatic agent after surgery for congenital heart disease. Pediatric Anesth 2005; 15: 235–240.
Velik-Salchner C, Sergi C, Fries D, Moser P, Streif W, Kolbitsch C . Use of recombinant factor VIIa (Novoseven) in combination with other products led to a thrombotic occlusion of the truncus brachiocephalicus in a neonate supported by extracorporal membrane oxygenation. Anesth Analg 2005; 101: 924.
Wittenstein B, Ng C, Ravn H, Goldmann A . Recombinant factor VII for severe bleeding during extracorporeal membrane oxygenation following open heart surgery. Pediatr Crit Care Med 2005; 6: 473–476.
Cetin H, Yalaz M, Akisu M, Karapinar DY, Kavakli K, Kultursay N . The use of recombinant activated factor VII in the treatment of massive pulmonary hemorrhage in a preterm infant. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 2006; 17 (3): 213–216.
Olomu N, Kulkarni R, Manco-Johnson M . Treatment of Severe Pulmonary Hemorrhage with activated recombinant factor VII (rFVIIa) in very low birth weight infants. J Perinatol 2002; 22: 672–674.
Hunseler C, Kribs A, Eifinger F, Roth B . Recombinant activated factor VII in acute life-threatening bleeding neonates: report on three cases and review of the literature. J Perinatol 2006; 26: 706–713.
Filan PM, Mills JF, Clarnette TD, Ekert H, Ekert P . Spontaneous liver hemorrhage during laparotomy for necrotizing enterocolitis: a potential role for recombinant factor VIIa. J Pediatr 2005; 147: 857–859.
Brady KM, Easley RB, Tobias JD . Recombinant activated factor VII treatment in infants with hemorrhage. Ped Anesthesia 2006; 16: 1042–1046.
Girisch M, Rauch R, Carbon R, Habash T, Hofbeck M . Refractory bleeding following major surgery of a giant sacrococcygeal teratoma in a premature infant: successful use of recombinant factor VIIa. Eur J Pediatr 2004; 163 (2): 118–119.
Fischer D, Schloesser R, Buxmann H, Veldman A . Recombinant activated factor VII as a hemostatic agent in very low birth weight preterms with gastrointestinal hemorrhage and disseminated intravascular coagulation. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 2008; 5: 337–342.
Mitsiakos G, Papaioannou G, Giougi E, Karagianni P, Garipidou V, Nikolaidis N . Is the use of rFVIIa safe and effective in bleeding neonates? A retrospective series of 8 cases. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 2007; 29 (3): 145–150.
Yilmaz D, Karapinar B, Balkan C, Akisu M, Kavakli K . Single-center experience: use of recombinant factor VIIa for acute life-threatening bleeding in children without congenital hemorrhagic disorder. Pediatr Hematol Oncol 2008; 25 (4): 301–311.
Altuncu E, Berrak S, Bilgen H, Yurdakul Z, Canpolat C, Ozek E . Use of recombinant factor VIIa in a preterm infant with coagulopathy and subdural hematoma. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2007; 20 (8): 627–629.
Abdullah F, Hunter C, Hargrove C, Arnold M, Stein J . Recombinant factor VIIa for treatment of massive liver fracture in a premature infant. J Pediatr Surg 2006; 41 (10): 1764–1767.
Young G, Wicklund B, Neff P, Johnson C, Nugent DJ . Off-label use of rFVIIa in children with excessive bleeding: a consecutive study of 153 off-label uses in 139 children. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2009; 53: 178–183.
Manco-Johnson M, Nuss R . Hemostasis in neonates. Neoreviews 2000; 1: e191–e195.
Tripodi A, Ramenghi LA, Chantarangkul V, De Carli A, Clerici M, Groppo M et al. Normal thrombin generation in neonates in spite of prolonged conventional coagulation tests. Haematologica 2008; 93: 1256–1259.
O’Connell KA, Wood JJ, Wise RP, Lozier JN, Braun MM . Thromboembolic adverse events after use of recombinant human coagulation factor VIIa. JAMA 2006; 295: 293–298.
Puetz J, Darling G, Brabec P, Blatny J, Mathew P . Thrombotic events in neonates receiving recombinant factor VIIa or fresh frozen plasma. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2009; 53: 1074–1078.
Acknowledgements
We thank Kimberley A Fisher, RN, PhD and Sandra Grimes, RN for their expert technical contributions. The Jean and George W Brumley, Jr Neonatal Perinatal Research Institute provided financial support for this study. Dr Smith received support from NIH-1K23HD060040-01.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dang, C., Katakam, L., Smith, P. et al. Recombinant activated factor VIIa treatment for refractory hemorrhage in infants. J Perinatol 31, 188–192 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2010.85
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2010.85
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Neonatal thrombocytopenia: Thrombin generation in presence of reduced platelet counts and effects of rFVIIa in cord blood
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Recombinant Activated Factor VIIa (rFVIIa) Treatment in Very-Low-Birth-Weight (VLBW) Premature Infants with Acute Pulmonary Hemorrhage: A Single-Center, Retrospective Study
Pediatric Drugs (2017)