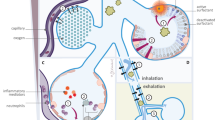
Abstract
In this article we have attempted to review the current pharmacological treatment options for infants with meconium aspiration syndrome with or without persistent pulmonary hypertension. These treatments include ventilatory support, surfactant treatment and inhaled nitric oxide (INO), in addition to older and newer pharmacological treatments. These include sedatives, muscle relaxants, alkali infusion, antibiotics and the newer vasodilators. Many aspects of treatment, including ventilatory care, surfactant treatment and the use of INO, are reviewed in great detail in this issue. On the other hand, many newer pharmacological modalities of treatment described here have not been evaluated with randomized control trials. We have given an overview of these emerging therapies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wiswell TM . Advances in treatment of the meconium aspiration syndrome. Acta Paediatr Suppl 2001; 436: 28–30.
Wiswell TE . Meconium in the Delivery Room Trial Group: delivery room management of the apparently vigorous meconium-stained neonate: results of the multicenter collaborative trial. Pediatrics 2000; 105: 1–7.
Linder N, Aranda JV, Tsur M . Need for endotracheal intubation and suction in meconium-stained neonates. J Pediatr 1988; 112: 613–615.
Bhat R, Chari G, Gulati A, Aldana O, Velamati R, Bhargava H . Pharmacokinetics of Morphine in preterm and term neonates. J Pediatr 1990; 117: 477–481.
Bhat R, Abu-Harb M, Chari G, Gulati A . Morphine metabolism in acutely ill preterm newborn infants. J Pediatr 1992; 120: 795–799.
Walsh-Sukys MC, Tyson JE, Wright LL, Bauer CR, Korones SB, Stevenson DK et al. Persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn in the era before nitric oxide: practice variation and outcomes. Pediatrics 2000; 105: 14–20.
Lyrene RK, Welch KA, Godoy G, Philips III JB . Alkalosis attenuates hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction in neonatal lambs. Pediatr Res 1985; 19: 1268–1271.
Drummond WH, Gregory GA, Heymann MA, Phibbs RA . The independent effects of hyperventilation, tolazoline, and dopamine in infants with persistent pulmonary hypertension. J Pediatr 1981; 98: 608–611.
Hansen NB, Brubakk AM, Bratlid D, Oh W, Stonestreet BS . The effects of variations in PaCO2 on brain blood flow and cardiac output in the newborn piglet. Pediatr Res 1984; 18 (11): 1132–1136.
Ambalavanan N, Carlo WA . Hypocapnia and hypercapnia in respiratory management of newborn infants. Clin Perinatol 2001; 28 (3): 517–531. Review.
Greenough A, Khetriwal B . Pulmonary hypertension in the newborn. Paediatr Respir Rev 2005; 6 (2): 111–116.
Booker PD, Evans C, Franks R . Comparison of the haemodynamic effects of dopamine and dobutamine in young children undergoing cardiac surgery. Br J Anaesth 1995; 74 (4): 419–423.
Stevenson DK, Kasting DS, Darnall Jr RA, Ariagno RL, Johnson JD, Malachowski N et al. Refractory hypoxemia associated with neonatal pulmonary diseases: the use and limitations of tolazoline. J Pediatr 1979; 95: 595–599.
Nuntnarumit P, Korones SB, Yang W, Bada HS . Efficacy and safety of tolazoline for treatment of severe hypoxemia in extremely preterm infants. Pediatrics 2002; 109 (5): 852–856.
Parida SK, Baker S, Kuhn R, Desai N, Pauly TH . Endotracheal tolazoline administration in neonates with persistent pulmonary hypertension. J Perinatol 1997; 17: 461–464.
Tolsa JF, Cotting J, Sekarski N, Payot M, Micheli JL, Calame A . Magensium Sulphate as an alternative and safe treatment for persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 1995; 72: F184–F187.
Islam S, Masiakos P, Schnitzer JJ, Doody DP, Ryan DP . Diltiazem reduces pulmonary arterial pressures in recurrent pulmonary hypertension associated with pulmonary hypoplasia. J Pediatr Surg 1999; 34: 712–714.
Al-Alaiyan S, Al-Omran A, Dyer D . The use of phoshodiestersae inhibitor( dipyridamole) to wean from inhaled nitric oxide. Intensive care med 1996; 22: 1093–1095.
Ivy DD, Kinsella JP, Ziegler JW, Abman SH . Dipyridamole attenuates rebound pulmonary hypertension after inhaled nitric oxide withdrawl in postoperative congenital heart disease. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1998; 115: 875–882.
Kinsella JP, Toricelli F, Ziegler JW, Ivy DD, Abman SH . Dipyridamole augmentation of response to nitric oxide. Lancet 1995; 346: 647–648.
Travadi JN, Patole SK . Phosphodiesterase inhibitors for persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn: a review. Pediatr Pulmonol 2003; 36 (6): 529–535.
Shekerdamien LS, Penny DJ, Ryhammer PK, Reader JA, Ravn HB . Endothelin—a receptor blockade and inhaled nitric oxide in a porcine model of meconium aspiration syndrome. Pediatr Res 2004; 56: 353–358.
Schranz D, Zepp F, Iversen S, Wippermann C, Huth R, Zimmer B et al. Effects of tolazoline and prostacyclin on pulmonary hypertension in infants after cardiac surgery. Crit Care Med 1992; 20 (9): 1243–1249.
Bush A, Busst CM, Knight WB, Shinebourne EA . Comparison of the haemodynamic effects of epoprostenol (prostacyclin) and tolazoline. Br Heart J 1988; 60 (2): 141.
De Jaeger AP, den Anker JN . Endotracheal instillation of prostacyclin in preterm infants with persistent pulmonary hypertension. Eur Respir J 1998; 12: 932–934.
Paradisis M, Jiang X, Mclachlan AJ, Evans N, Kluckow M, Osborn D . Population pharmacokinetics and dosing regimen of milrinone in preterm infants. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 2007; 92: F204–F209.
Baquero H, Soliz A, Neira F, Venegas ME, Sola A . Oral sildenafil in infants with persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn: a pilot randomized blinded study. Pediatrics 2006; 117: 1077–1083.
Erickson S, Reyes J, Bohn D, Adatia I . Sildenafil (Viagra) in childhood and neonatal pulmonary hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol 2002; 39 (Suppl 2): 402–402(1).
McMurray JJV, Teerlink JR, Cotter G, Bourge RC, Cleland JG, Jondeau G et al. Effects of Tezosentan on symptoms and clinical outcomes in patients with acute heart failure. JAMA 2007; 298 (17): 2009–2019.
Konduri GG, Garcia DC, Kazzi NJ, Shankaran S . Adenosine infusion improves oxygenation in term infants with respiratory failure. Pediatrics 1996; 97: 295–300.
Lee TS, Hou X . Dual vasoactive effects of tolazoline on rabbit pulmonary arteries. J Cardiothoc Vasc Anesth 1996; 10: 364–367.
Curtis J, Palacino JJ, O’Neill JT . Production of pulmonary vasodilation by tolazoline, independent of nitric oxide production in neonatal lambs. J Pediatr 1996; 128: 118–124.
Paret G, Eyal O, Mayan H, Ben-Abraham R, Vardi A, Manisterski Y et al. Pharmacokinetics of endobronchial tolazoline administration in dogs. Am J Perinatol 1999; 16: 1–6.
Welch JC, Bridosn JM, Gibbs JL . Endotracheal tolazoline for severe persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn. Br Heart J 1995; 73: 99–100.
Bassler D, Choong K, McNamara P, Kirpalani H . Neonatal persistent pulmonary hypertension treated with milrinone: four case reports. Biol Neonate 2006; 89: 1–5.
Ziegler JW, Ivy DD, Fox JJ, Kinsella JP, Clarke WR, Abman SH et al Dipyridamole, a cGMP phosphodiesterase inhibitor, causes pulmonary vasodilation in the ovine fetus. Am J Physiol 1995; 269: 473–479.
Thusu KG, Morin III FC, Russell JA, Steinhorn RH . The cGMP phosphodiesterase inhibitor zaprinast enhances the effect of nitric oxide. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1995; 152: 1605–1610.
Ichinose F, Adrie C, Hurford WE, Zapol WM . Prolonged pulmonary vasodilator action of inhaled nitric oxide by Zaprinast in awake lambs. J Appl Physiol 1995; 78: 1288–1295.
Ichinose F, Adrie C, Hurford WE, Bloch KD, Zapol WM . Selective pulmonary vasodilation induced by aerosolized zaprinast. Anesthesiology 1998; 88: 410–416.
Newman SP . Aerosol deposition considerations in inhalation therapy. Chest 1985; 88 (2 Suppl): 152S–160S. Review.
Stocker C, Penny DJ, Brizard CP, Cochrane AD, Soto R, Shekerdemian LS . Intravenous sildenafil and inhaled nitric oxide: a randomised trial in infants after cardiac surgery. Intensive Care Med 2003; 29 (11): 1996–2003.
Atz AM, Wessel DL . Sildenafil ameliorates effects of inhaled nitric oxide withdrawl. Anesthesiology 1999; 91: 307–310.
Martell M, Blasina F, Silvera F, Tellechea S, Godoy C, Vaamonde L . Intratracheal sildenafil in the newborn with pulmonary hypertension. Pediatrics 2007; 119: 215–216.
Tamura M, Kurumatani H, Matsushita T . Comparative effects of beraprost, a stable analogue of prostacyclin, with PGE(1), nitroglycerin and nifedipine on canine model of vasoconstrictive pulmonary hypertension. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 2001; 64 (3): 197–202.
Bindl L, Fahnenstich H, Peukert U . Aerosolised prostacyclin for pulmonary hypertension in neonates. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 1994; 71 (3): F214–F216.
Soifer SJ, Clyman RI, Heymann MA . Effects of prostaglandin D2 on pulmonary arterial pressure and oxygenation in newborn infants with persistent pulmonary hypertension. J Pediatr 1998; 112: 774–777.
Buchan KW, Magnusson KW, Rabe KF, Summer MJ, Watts IS . Characterization of the endothelin receptor mediating contraction of human pulmonary artery using BQ123 and Ro46-2005. Eur J Pharmacol 1994; 260: 221–226.
Kuo C, Chen J . Effect of meconium aspiration on plasma endothelin-1 level and pulmonary hemodynamics in a piglet model. Biol Neonate 1999; 76: 228–234.
Kyo CY . Endothelin—a receptor antagonist prevents neonatal pulmonary hypertension in meconium aspiration in piglets. J Formos Med Assoc 2001; 100: 420–423.
Rubin LJ, Badesch DB, Barst RJ, Galie N, Black CM, Keogh A et al. Bosentan therapy for pulmonary arterial hypertension. N Eng J Med 2002; 346: 896–903.
Sitbon O, Badesch DB, Channick RN, Frost A, Robbins IM, Simonneau G et al. Effects of dual endothelin receptor antagonist bosentan in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension: a 1-year follow-up study. Chest 2003; 124: 247–254.
Geiger R, Pajk W, Neu N, Maier S, Kleinsasser A, Fratz S et al. Tezosentan decreases pulmonary artery pressure and improves survival rate in an animal model of meconium aspiration. Pediatr Res 2006; 59: 147–150.
Kappa P, Jahnukainen T, Grinlund J, Rautanen M, Halkola L, Välimäki I . Adenosine triphosphate treatment for meconium aspiration-induced pulmonary hypertension in pigs. Acta Physiol Scand 1997; 160 (3): 283–289.
Wu TJ, Teng RJ, Tsou KI . Persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn treated with magnesium sulfate in premature neonates. Pediatrics 1995; 96: 472–474.
Patole SK, Finer NN . Experimental and clinical effects of magnesium infusion in the treatment of neonatal pulmonary hypertension. Magnes Res 1995; 8 (4): 373–388. Review.
Abu-Osaba YK, Galal O, Mansara K, Rejjal A . Treatment of severe persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn with magnesium sulphate. Arch Dis Child 1992; 67: 31–35.
Palmer RM, Rees DD, Ashton DS, Moncada S . L-arginine is the physiological precursor for the formation of nitric oxide in endothelium-dependent relaxation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1988; 153 (3): 1251–1256.
Steinhorn RH, Albert G, Swartz DD, Russell JA, Levine CR, Davis JM . Recombinant human superoxide dismutase enhances the effect of inhaled nitric oxide in persistent pulmonary hypertension. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2001; 164 (5): 834–839.
Lam BCC, Yeung CY . Surfactant lavage for meconium aspiration syndrome: a pilot study. Pediatrics 1999; 103: 1014–1018.
Rubin BK, Tomkiewicz RP, Patrinos ME, Easa D . The surface and transport properties of meconium and reconstituted meconium solutions. Pediatr Res 1996; 40: 834–838.
Sun B, Curstedt T, Robertson B . Surfactant inhibition in experimental meconium aspiration syndrome. Acta Pediatr 1993; 82: 182–189.
al-Mateen KB, Dailey K, Grimes MM, Gutcher GR . Improved oxygenation with exogenous surfactant administration in experimental meconium aspiration syndrome. Pediatr Pulmonol 1994; 17 (2): 75–80.
Dargaville PA, South M, McDougall PN . Surfactant and surfactant inhibitors in meconium aspiration syndrome. J Pediatr 2001; 138: 113–115.
Findlay RD, Taeusch HW, Walther FJ . Surfactant replacement therapy for meconium aspiration syndrome. Pediatrics 1996; 97: 48–52.
Bryan CS . Enhancement of bacterial infection by meconium. Johns Hopkins Med J 1967; 121: 9–13.
Eidelman AI, Nevet A, Rudensky B, Rabinowitz R, Hammerman C, Raveh D et al. The effect of meconium staining of amniotic fluid on the growth of Escherichia coli and group B Streptococcus. J Perinatol 2002; 22: 467–471.
Lin HC, Su BH, Tsai CH, Lin TW, Yeh TF . Role of antibiotics in management of non-ventilated cases of meconium aspiration syndrome without risk factors for infection. Biol Neonate 2005; 87: 51–55.
Shankar V, Paul VK, Deorari AK, Singh M . Do neonates with meconium aspiration syndrome require antibiotics? Indian J Pediatr 1995; 62: 327–331.
Krishnan L, Nasruddin, Prabhakar P, Bhaskaranand N . Routine antibiotic cover for newborns intubated for aspirating meconium: is it necessary? Indian Pediatr 1995; 32 (5): 529–531.
Khan AM, Elidemir O, Epstein CE, Lally KP, Xue H, Blackburn M et al. Meconium aspiration produces airway hyperresponsiveness and eosinophilic inflammation in a murine model. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Moll Physiol 2002; 283: L785–L790.
Zagariya A, Bhat R, Navale S, Vidyasagar D . Cytokine expression in meconium-induced lungs. Indian J Pediatr 2004; 71 (3): 195–201.
Zagariya A, Bhat R, Uhal B, Navale S, Freidine M, Vidyasagar D . Cell death and lung cell histology in meconium aspirated newborn rabbit lung. Eur J Pediatr 2000; 159: 819–826.
Khan AM, Shabarek FM, Kutchback JW, Lally KP . Effects of dexamethasone on meconium aspiration syndrome in newborn piglets. Pediatr Res 1999; 46 (2): 179–183.
da Costa DE, Nair AK, Pai MG, Al Khusaiby SM . Steroids in full term infants with respiratory failure and pulmonary hypertension due to meconium aspiration syndrome. Eur J Pediatr 2001; 160: 150–153.
Ward M, Sinn J . Steroid therapy for meconium aspiration syndrome in newborn infants. Cochrane Database Syste Rev 2003; (4): CD003485. Review.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Dharmapuri Vidyasagar for his many contributions on the pathophysiology and treatment of MAS during the last 30 years.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Disclosure
R Bhat has lectured while on a speakers bureau. A Asad has declared no financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Asad, A., Bhat, R. Pharmacotherapy for meconium aspiration. J Perinatol 28 (Suppl 3), S72–S78 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2008.160
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2008.160