Abstract
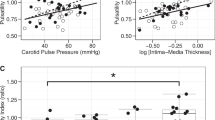
South Asians (SA) suffer from a higher burden of heart disease and stroke compared with White Caucasians (CA). We hypothesized that increased arterial stiffness in older adults of SA origin would be associated with greater cerebrovascular pulsatile pressure and flow characteristics compared with CA older adults. Forty-four SA and CA older adults, free of known cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, were assessed. Vascular ageing was characterized by brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity, carotid pulse pressure, compliance coefficient (CC) and intima-media thickness (IMT). Duplex ultrasonography of the internal carotid arteries estimated anterior cerebral blood flow (aCBF) and cerebrovascular resistance (aCVR), and transcranial Doppler ultrasound quantified middle cerebral artery blood flow velocity, resistive index (RI) and pulsatility index (PI). Fasting blood samples were collected to assess glycaemic status, lipid profile and C-reactive protein. SA had higher carotid pulse pressure and lower CC indicating stiffer arteries compared with CA. Multiple regression analyses revealed that ethnic differences in arterial stiffness were associated with glycated haemoglobin level in SA. Among SA, an inverse association was observed between carotid CC and aCVR. In turn, aCVR was associated with a steeper reduction in aCBF in SA than in CA. IMT was strongly associated with greater PI and RI (r>0.81, P<0.001) in SA, whereas a weaker relationship for PI (r=0.46, P=0.03) and no significant relationship for RI were found in CA. The study found stronger associations between pulsatile cerebrovascular haemodynamics and structural and functional alterations in central arteries in SA that may underlie the elevated risk for cerebrovascular disease.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sutton-Tyrrell K, Najjar SS, Boudreau RM, Venkitachalam L, Kupelian V, Simonsick EM et al. Elevated aortic pulse wave velocity, a marker of arterial stiffness, predicts cardiovascular events in well-functioning older adults. Circulation 2005; 111: 3384–3390.
Robertson AD, Tessmer C, Hughson R . Association between arterial stiffness and cerebrovascular resistance in the elderly. J Hum Hyper 2010; 24: 190–196.
Hatanaka R, Obara T, Watabe D, Ishikawa T, Kondo T, Ishikura K et al. Association of arterial stiffness with silent cerebrovascular lesions: the Ohasama study. Cerebrovasc Dis 2011; 31: 329–337.
Mitchell GF, van Buchem MA, Sigurdsson S, Gotal JD, Jonsdottir MK, Kjartansson Ó et al. Arterial stiffness, pressure and flow pulsatility and brain structure and function: the age, gene/environment susceptibility-Reykjavik study. Brain 2011; 134: 3398–3407.
Xu T, Staessen J, Wei F, Xu J, Li F, Fan W et al. Blood flow pattern in the middle cerebral artery in relation to indices of arterial stiffness in the systemic circulation. Am J Hyper 2012; 25: 319–324.
Scheel P, Ruge C, Petruch U, Schoning M . Color duplex measurement of cerebral blood flow volume in healthy adults. Stroke 2000; 31: 147–150.
Sheth T, Nair C, Nargundkar M, Anand S, Yusuf S . Cardiovascular and cancer mortality among Canadians of European, south Asian and Chinese origin from 1979 to 1993: an analysis of 1.2 million deaths. CMAJ 1999; 161: 132–138.
Rambihar VS, Rambihar SP, Rambihar VS . Race, ethnicity, and heart disease: a challenge for cardiology for the 21st century. Am Heart J 2010; 159: 1–14.
Gunarathne A, Patel JV, Gammon B, Gill PS, Hughes EA, Lip GYH . Ischemic stroke in South Asians: a review of the epidemiology, pathophysiology, and ethnicity-related clinical features. Stroke 2009; 40: e415–e423.
Anand S, Yusuf S, Vuksan V, Devanesen S, Teo K, Montague P et al. Differences in risk factors, atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease between ethnic groups in Canada: the study of health assessment and risk in ethnic groups (SHARE). Indian Heart J 2000; 52: S35–S43.
Din J, Ashman O, Aftab S, Jubb A, Newby D, Flapan A . Increased arterial stiffness in healthy young South Asian men. J Hum Hyper 2006; 20: 163–165.
Gunarathne A, Patel JV, Gammon B, Hughes EA, Lip GYH . Impact of mean arterial blood pressure on higher arterial stiffness indices in South Asians compared to white Europeans. J Hyper 2008; 26: 1420–1426.
Webb DR, Khunti K, Lacy P, Gray LJ, Mostafa S, Talbot D et al. Conduit vessel stiffness in British south Asians of Indian descent relates to 25-hydroxyvitamin D status. J Hyper 2012; 30: 1588–1596.
De Silva DA, Woon F-P, Gan H-Y, Chen CP, Chang H-M, Koh T-H et al. Arterial stiffness is associated with intracranial large artery disease among ethnic Chinese and South Asian ischemic stroke patients. J Hyper 2009; 27: 1453–1458.
Van Bortel L, Duprez D, Starmans-Kool M, Safar M, Giannattasio C, Cockcroft J et al. Clinical applications of arterial stiffness, task force III: Recommendations for user procedures. Am J Hyper 2002; 15: 445–452.
Reneman R, Meinders J, Hoeks A . Non-invasive ultrasound in arterial wall dynamics in humans: what have we learned and what remains to be solved. Eur Heart J 2005; 26: 960–966.
Aaslid R, Markwalder T, Nornes H . Noninvasive transcranial Doppler ultrasound recording of flow velocity in basal cerebral arteries. J Neurosurg 1982; 57: 769–774.
Hughson RL, Edwards MR, O’Leary DD, Shoemaker JK . Critical analysis of cerebrovascular autoregulation during repeated head-up tilt. Stroke 2001; 32: 2403–2408.
Ide K, Eliasziw M, Poulin MJ . Relationship between middle cerebral artery blood velocity and end-tidal PCO2 in the hypocapnic-hypercapnic range in humans. J Appl Physiol 2003; 95: 129–137.
Grundy SM, Cleeman JI, Daniels SR, Donato KA, Eckel RH, Franklin BA et al. Diagnosis and management of the metabolic syndrome: an American Heart Association/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Scientific Statement. Circulation 2005; 112: 2735–2752.
Bathula R, Hughes AD, Panerai RB, Potter JF, McG Thom SA, Tillin T et al. South Asians have adverse cerebrovascular haemodynamics, despite equivalent blood pressure, compared with Europeans. This is due to their greater hyperglycaemia. Int J Epidemiol 2011; 40: 1490–1498.
Lee K, Sohn Y, Baik J, Kim G, Kim J . Arterial pulsatility as an index of cerebral microangiopathy in diabetes. Stroke 2000; 31: 1111–1115.
Mostafa SA, Davies MJ, Webb DR, Srinivasan BT, Gray LJ, Khunti K . Independent effect of ethnicity on glycemia in South Asians and white Europeans. Diabetes Care 2012; 35: 1746–1748.
Van Popele NM, Elizabeth HA, Mattace-Raso FUS, Bots ML, van der Kuip DAM, Reneman RS et al. Impaired fasting glucose is associated with increased arterial stiffness in elderly people without diabetes mellitus: the Rotterdam Study. J Am Geriatr Soc 2006; 54: 397–404.
Liang J, Zhou N, Teng F, Zou C, Xue Y, Yang M et al. Hemoglobin A1c levels and aortic arterial stiffness: the Cardiometabolic Risk in Chinese (CRC) study. PLoS One 2012; 7: e38485.
Gunarathne A, Patel JV, Kausar S, Gammon B, Hughes EA, Lip GYH . Glycemic status underlies increased arterial stiffness and impaired endothelial function in migrant South Asian stroke survivors compared to European Caucasians: pathophysiological insights from the West Birmingham Stroke Project. Stroke 2009; 40: 2298–2306.
Chambless L, Folsom A, Clegg L, Sharrett A, Shahar E, Nieto F et al. Carotid wall thickness is predictive of incident clinical stroke: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study. Am J Epidemiol 2000; 151: 478–487.
Webb A, Simoni M, Mazzucco S, Kuker W, Schulz U, Rothwell PM . Increased cerebral arterial pulsatility in patients with leukoaraiosis: arterial stiffness enhances transmission of aortic pulsatility. Stroke 2012; 43: 2631–2636.
Serrador J, Picot P, Rutt B, Shoemaker J, Bondar R . MRI measures of middle cerebral artery diameter in conscious humans during simulated orthostasis. Stroke 2000; 31: 1672–1678.
Williams E, Nazroo J, Kooner J, Steptoe A . Subgroup differences in psychosocial factors relating to coronary heart disease in the UK South Asian population. J Psychosom Res 2010; 69: 379–387.
Peebles K, Celi L, McGrattan K, Murrell C, Thomas K, Ainslie PN . Human cerebrovascular and ventilatory CO2 reactivity to end-tidal, arterial and internal jugular vein PCO2. J Physiol 2007; 584: 347–357.
Gates PE, Tanaka H, Hiatt WR, Seals DR . Dietary sodium restriction rapidly improves large elastic artery compliance in older adults with systolic hypertension. Hypertension 2004; 44: 35–41.
Chan H-T, Chan Y-H, Yiu KH, Li S-W, Tam S, Lau C-P et al. Worsened arterial stiffness in high-risk cardiovascular patients with high habitual carbohydrate intake: a cross-sectional vascular function study. BMC Cardiovasc Disord 2014; 14: 24–32.
Van Bortel LM, Laurent S, Boutouyrie P, Chowienczyk P, Cruickshank JK, De Backer T et al. Expert consensus document on the measurement of aortic stiffness in daily practice using carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity. J Hyper 2012; 30: 445–458.
Yamashina A, Tomiyama H, Takeda K, Tsuda H, Arai T, Hirose K et al. Validity, reproducibility, and clinical significance of noninvasive brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity measurement. Hyper Res 2002; 25: 359–364.
Yu W-C, Chuang S-Y, Lin Y-P, Chen C-H . Brachial-ankle vs carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity as a determinant of cardiovascular structure and function. J Hum Hypertens 2008; 22: 24–31.
Tanaka H, Munakata M, Kawano Y, Ohishi M, Shoji T, Sugawara J . Comparison between carotid-femoral and brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity as measures of arterial stiffness. J Hyper 2009; 27: 2022–2027.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the participants for volunteering their time in this study, as well as Jing Ouyang, Danielle Greaves and Katelyn Fraser for their technical assistance. This research was supported in part by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (Grant No. 196261). Richard L Hughson is supported as Schlegel Research Chair in Vascular Aging and Brain Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brar, I., Robertson, A. & Hughson, R. Increased central arterial stiffness and altered cerebrovascular haemodynamic properties in South Asian older adults. J Hum Hypertens 30, 309–314 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2015.76
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2015.76