Abstract
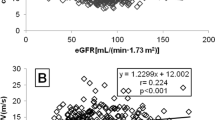
Resistin, a newly discovered protein, promotes endothelial dysfunction and proinflammatory activation, contributing to subclinical atherosclerosis in different clinical settings. In this study we sought to investigate the relationship of increased resistin levels with estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), the most established marker of kidney impairment, in hypertensive subjects. Our population consisted of 132 untreated non-diabetic subjects with stage I–II essential hypertension (49 males, mean age=54 years, office blood pressure (BP)=159/100 mm Hg). In all patients eGFR was assessed by the Modification in Renal Disease equation and venous blood sampling was performed for estimation of resistin concentrations. The distribution of resistin was split by the median (4.63 ng ml−1) and accordingly subjects were stratified into those with high and low values. Hypertensive patients with high (n=66) compared to those with low resistin (n=66) exhibited lower eGFR values (77.1±9.4 vs 89.1±12.2 ml min−1 per 1.73m2, P<0.0001), even after adjustment for established confounders. In the total population, resistin was associated with 24-h systolic BP (r=0.244, P<0.05), serum creatinine (r=0.311, P=0.007) and eGFR (r=−0.519, P<0.0001). Multiple regression analysis revealed that age (b=0.379, P=0.01), body mass index (b=0.158, P=0.022), 24-h systolic BP (b=0.284, P=0.006) and resistin (b=0.429, P<0.0001) were independent predictors of eGFR (R2=0.436, P<0.0001). In essential hypertensive subjects, higher resistin levels are associated with renal function impairment, as reflected by decreased eGFR. Moreover, the independent association of resistin with eGFR suggests involvement of resistin in the progression of kidney damage in the early stages of hypertension.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rangwala SM, Lazar ST, Bhat S, Brown EJ, Banerjee RR, Wright CM et al. The hormone resistin links obesity to diabetes. Nature 2001; 409: 307–312.
Verma S, Li SH, Wang CH, Fedak PW, Li RK, Weisel RD et al. Resistin promotes endothelial cell activation: further evidence of adipokine-endothelial interaction. Circulation 2003; 108: 736–740.
Steppan CM, Lazar MA . The current biology of resistin. J Intern Med 2004; 255: 439–447.
Silha JV, Krsek M, Skrha JV, Sucharda P, Nyomba BL, Murphy LJ . Plasma resistin, adiponectin and leptin levels in lean and obese subjects: correlations with insulin resistance. Eur J Endocrinol 2003; 149: 331–335.
Norata GD, Ongari M, Garlaschelli K, Raselli S, Grigore L, Catapano AL . Plasma resistin levels correlate with determinants of the metabolic syndrome. Eur J Endocrinol 2007; 156: 279–284.
Ohmori R, Momiyama Y, Kato R, Taniguchi H, Ogura M, Ayaori M et al. Associations between serum resistin levels and insulin resistance, inflammation, and coronary artery disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 2005; 46: 379–380.
McTernan CL, McTernan PG, Harte AL, Levick PL, Barnett AH, Kumar S . Resistin, central obesity, and type 2 diabetes. Lancet 2002; 359: 46–47.
Malyszko J, Malyszko JS, Pawlak K, Mysliwiec M . Resistin, a new adipokine, is related to inflammation and renal function in kidney allograft recipients. Transplant Proc 2006; 38: 3434–3436.
Savage DB, Sewter CP, Klenk ES, Segal DG, Vidal-Puig A, Considine RV et al. Resistin/Fizz3 expression in obesity and peroxisome proliferator- activated receptor y in humans. Diabetes 2001; 50: 2199–2202.
Zhang JL, Qin YW, Zheng X, Qiu JL, Zou DJ . Serum resistin level in essential hypertension patients with different glucose tolerance. Diabet Med 2003; 20: 828–831.
Furuhashi M, Ura N, Higashiura K, Murakami H, Shimamoto K . Circulating resistin levels in essential hypertension. Clin Endocrinol 2003; 59: 507–510.
Takata Y, Osawa H, Kurata M, Kurokawa M, Yamauchi J, Ochi M et al. Hyperresistinemia is associated with coexistence of hypertension and type 2 diabetes. Hypertension 2008; 51: 534–539.
Shin HJ, Park S, Yoon SJ, Cho DK, Kim JS, Ko YG et al. Association between serum resistin and carotid intima media thickness in hypertension patients. Int J Cardiol 2008; 125: 79–84.
Axelsson J, Bergsten A, Qureshi AR, Heimbürger O, Bárány P, Lönnqvist F et al. Elevated resistin levels in chronic kidney disease are associated with decreased glomerular filtration rate and inflammation, but not with insulin resistance. Kidney Int 2006; 69: 596–604.
Ellington AA, Malik AR, Klee GG, Turner ST, Rule AD, Mosley Jr TH et al. Association of plasma resistin with glomerular filtration rate and albuminuria in hypertensive adults. Hypertension 2007; 50: 708–714.
Mancia G, De Backer G, Dominiczak A, Cifkova R, Fagard R, Germano G, et al. Management of Arterial Hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension et al. 2007 Guidelines for the Management of Arterial Hypertension: The Task Force for the Management of Arterial Hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). J Hypertens 2007; 25: 1105–1187.
Tsioufis C, Stefanadis C, Antoniadis D, Kallikazaros I, Zambaras P, Pitsavos C et al. Absence of any significant effects of circadian blood pressure variations on carotid artery elastic properties in essential hypertensive subjects. J Hum Hypertens 2000; 14: 813–818.
National Kidney Foundation. K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification and stratification. Am J Kidney Dis 2002; 39: S1–S246.
Schiller NB, Shah PM, Crawford M, DeMaria A, Devereux R, Feigenbaum H et al. Recommendations for quantitation of the left ventricular dimensions by two-dimensional echocardiography. American Society of Echocardiography Committee on standards, subcommittee on quantitation of the two-dimensional echocardiograms. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 1989; 2: 358–367.
Kielstein JT, Becker B, Graf S, Brabant G, Haller H, Fliser D . Increased resistin blood levels are not associated with insulin resistance in patients with renal disease. Am J Kidney Dis 2003; 42: 62–66.
Risch L, Saely C, Hoefle G, Rein P, Langer P, Gouya G et al. Relationship between glomerular filtration rate and the adipokines adiponectin, resistin and leptin in coronary patients with predominantly normal or mildly impaired renal function. Clin Chim Acta 2007; 376: 108–113.
Levey AS, Coresh J, Balk E, Kausz AT, Levin A, Steffes MW et al. National Kidney Foundation practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification, and stratification. Ann Intern Med 2003; 139: 137–147.
Perticone F, Maio R, Tripepi G, Zoccali C . Endothelial dysfunction and mild renal insufficiency in essential hypertension. Circulation 2004; 110: 821–825.
Waldmann TA, Strober W, Mogienlnicki RP . The renal handling of low molecular weight proteins. II. Disorders of serum protein catabolism in patients with tubular proteinuria, the nephrotic syndrome or uremia. J Clin Invest 1972; 51: 2162–2174.
Tsioufis C, Dimitriadis K, Chatzis D, Stougianos P, Kakavas A, Vlasseros I et al. Relation of microalbuminuria to adiponectin and augmented C-reactive protein levels in men with essential hypertension. Am J Cardiol 2005; 96: 946–951.
Tsioufis C, Dimitriadis K, Taxiarchou E, Vasiliadou C, Charzoulakis G, Tousoulis D et al. Diverse associations of microalbuminuria with C-reactive protein, interleukin-18 and soluble CD 40 ligand in male essential hypertensive subjects. Am J Hypertens 2006; 19: 462–466.
Bokarewa M, Nagaev I, Dahlberg L, Smith U, Tarkowski A . Resistin, an adipokine with potent proinflammatory properties. J Immunol 2005; 174: 5789–5795.
Reilly MP, Lehrke M, Wolfe ML, Rohatgi A, Lazar MA, Rader DJ . Resistin is an inflammatory marker of atherosclerosis in humans. Circulation 2005; 111: 932–939.
Jung HS, Park KH, Cho YM, Chung SS, Cho HJ, Cho SY et al. Resistin is secreted from macrophages in atheromas and promotes atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc Res 2006; 69: 76–85.
Verdecchia P, Schillaci G, Borgioni C, Giucci A, Pede S, Porcellati C . Ambulatory pulse pressure: a potent predictor of total cardiovascular risk in hypertension. Hypertension 1998; 32: 983–988.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dimitriadis, K., Tsioufis, C., Selima, M. et al. Independent association of circulating resistin with glomerular filtration rate in the early stages of essential hypertension. J Hum Hypertens 23, 668–673 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2009.12
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2009.12
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Association between resistin and fibroblast growth factor 23 in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 as a potential protective factor for renal insufficiency in Japanese subjects with heart failure: a pilot study
Journal of Human Hypertension (2014)
-
Association of resistin and adiponectin with different clinical blood pressure phenotypes
Journal of Human Hypertension (2011)
-
Association of Resistin With Urinary Albumin Excretion in Nondiabetic Patients With Essential Hypertension
American Journal of Hypertension (2010)