Abstract
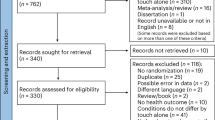
Breathlessness on exertion is common in people with obesity. Assessments of breathlessness may include sensation (intensity, sensory quality or unpleasantness) and/ or the behavioral/emotional consequences of the sensation (respiratory-related functional impairment, disability or quality of life). This systematic review of primary studies published since 2005 evaluated how has the sensation of breathlessness been assessed in adults with increased adiposity. A total of 41 articles were retained from the systematic search strategy resulting in 20 instruments. The Modified Borg Scale (perceived exertion-intensity), the Medical Research Council (MRC) Scale and Baseline Dyspnea Index (BDI; both assess respiratory-related functional impairment) were, respectively, the most frequently reported instruments. Few instruments had been tested for reliability and validity in people with increased adiposity. Visual Analog Scale, Modified Borg Scale, descriptors of sensory quality, MRC and BDI can be recommended as instruments based on their psychometric properties (reliability (correlations >0.8) and concurrent validity (correlation with severity of airways obstruction and walking distance)). A greater number of instruments were identified that assessed the consequences of the breathlessness rather than breathlessness as a sensation. If sensation drives behavior, comprehensive data on the sensation of breathlessness might assist in understanding the behavioral consequences of interventions.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gibson GJ . Obesity, respiratory function and breathlessness. Chest 1998; 114: 1372–1377.
Sin DD, Jones RL, Man SF . Obesity is a risk factor for dyspnea but not for airflow obstruction. Arch Intern Med 2002; 162: 1477–1481.
Guenette JA, Jensen D, O’Donnell DE . Respiratory function and the obesity paradox. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 2010; 13: 618–624.
Scano G, Innocenti-Bruni G, Stendardi L . Do obstructive and restrictive lung diseases share common underlying mechanism of breathlessness? Resp Med 2010; 104: 925–933.
Steele RM, Finucane FM, Griffin SJ, Wareham NJ, Ekelund U . Obesity is associated with altered lung function independently of physical activity and fitness. Obesity 2009; 17: 578–580.
Gabrielsen AM, Lund MB, Kongerud J, Viken KE, Roislien J, Hjelmesaeth J . The relationship between anthropometric measures, blood gases and lung function in morbidly obese white subjects. Obes Surg 2011; 21: 485–491.
Bowden JA, To THM, Aberthethy AP, Currow DC . Predictors of chronic breathlessness: a large population study. BMC Public Health 2011; 11: 33–43.
American Thoracic Society. Dyspnea-mechanisms, assessment, and management: a consensus statement. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1999; 159: 321–340.
O’Donnell DE, Banzett BB, Carrieri-Kohlman V . Pathophysiology of dyspnea in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. A roundtable. Proc Am Thorac Soc 2007; 4: 145–168.
Lansing R, Gracely R, Banzett R . The multiple dimensions of dyspnea: Review and hypothesis. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 2009; 167: 53–60.
Scano G, Innocenti-Bruni G, Stendardi L . Do obstructive and restrictive lung diseases share common underlying mechanism of breathlessness? Resp Med 2010; 104: 925–933.
Ofir D, Laveneziana P, Webb KA, O’Donnell DE . Ventilatory and perceptual responses to cycle exercise in obese women. Appl Physiol 2007; 1102: 2217–2226.
JensenD Ofir D, O’Donnell DE . Effects of pregnancy, obesity and aging on the intensity of perceived breathlessness during exercise in healthy humans. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 2009; 167: 87–100.
Nishino T . Dyspnea: underlying mechanism and treatment. Br J Anaesth 2011; 106: 463–474.
Herigstad M, Hayen A, Wiech K, Pattinson KTS . Dyspnea and the brain. Respir Med 2011; 105: 809–817.
Portney L, Watkins M . Foundations of Clinical Research: Applications to Practice, 3rd edn. Prentice Hall: New Jersey, USA, 2009.
Terwee CB, SDM Bott, de Boer MR, van der Windt DAWM, Knol DL, Dekker J et al. Quality criteria were proposed for measurement properties of health status questionnaires. Clin Epidemiol 2007; 60: 34–42.
Babb G, Ranasinghe KG, Comeau LA, Semon TL, Schwartz B . Dyspnea on exertion in obese women, association with an increased oxygen cost of breathing. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2008; 178: 116–123.
Park SJ, Cho KI, Jung SU, Choi SW, Chio JW, Lee DW et al. N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide in overweight and obese patients with and without diabetes: an analysis based on body mass index and left ventricular geometry. Korean Circ J 2009; 39: 538–544.
Cocco G, Pandolfi S, Rousson V . Sufficient weight reduction decreases cardiovascular complications in diabetic patients with the metabolic syndrome. Heartdrug 2005; 5: 68–74.
Ramachandran K, McCusker C, Connors M, ZuWallack R, Lahiri B . The influence of obesity on pulmonary rehabilitation outcomes in patients with COPD. Chron Respir Dis 2008; 5: 205–209.
Ghroubi S, Elleuch H, Hikh I, Kaffel N, ABid M, Elleuch MH . Physical training combined with dietary measures in the treatment of adult obesity. A comparison of two protocols. Ann Phys Rehabil Med 2009; 52: 394–413.
El-Gamal H, Khayat A, Shikora S, Unterborn JN . Relationship of dyspnea to respiratory drive and pulmonary function tests in obese patients before and after weight loss. Chest 2005; 128: 3870–3874.
Chuang ML, Lee CH, Lin IF . Using the oxygen-cost diagram in ramp-slope selection for dyspneic patient. Intern Med 2010; 49: 1325–1332.
Balaravi B, Miller TD, Hodge DO, Gibbons RJ . The value of stress single photon emission computed tomography in patients without known coronary artery disease presenting with dyspnea. Am Heart J 2006; 152: 551–557.
Daniel LB, Clopton P, Bhalla V, Krishnaswamy P, Nowak RM, McCord J et al. How obesity affects the cut-points for B-type natriuretic peptide in the diagnosis of acute heart failure: results from the breathing not properly multinational study. Am Heart J 2006; 151: 999–1005.
Noveanu M, Breidthardt T, Cayir S, Potochi M, Laule K, Mueller C . B-type natriuretic peptide-guided management and outcome in patients with obesity and dyspnea-results from the BASEL study. Am Heart J 2009; 158: 488–495.
Alzamora MT, Rores R, Baena-Diez JM, Pera G, Toran P, Sorribes M et al. The peripheral arterial disease study: prevalence and risk factors in the general population. BMC Public Health 2010; 10: 38–49.
Rose A, Blackburn H . Cardiovascular Survey Methods 1968; 56 World Health Organization Monograph Series, WHO: Switzerland.
Sarna L, Cooley ME, Brown JK, Chernecky C, Padilla G, Danao L et al. Women with lung cancer: quality of life after thoracotomy. Cancer Nurs 2010; 33: 85–92.
Pedersen F, Mehlsen J, Raymond I, Atar D, Skijoldborg US, Hildebrandt PR . Evaluation of dyspnea in a sample of elderly subjects recruited from general practice. Int J Clin Pract 2007; 61: 1481–1491.
Fletcher CM . The clinical diagnosis of pulmonary emphysema–an experimental study. Proceedings of the Royal Society of Medicine 1952. pp 577–584.
Ferris BG . Epidemiology standardization project (American thoracic society). Am Rev Resp Dis 1978; 118: 1–120.
Olafsdttir IS, Gislason F, Thjodleifsson B, Olafsson I, Gislason D, Jogi R et al. C creative protein levels are increased in non-allergic but not allergic asthma: a multicentre epidemiological study. Thorax 2005; 60: 451–454.
Simon PM, Schwartzstein RM, Woodrow Weiss J, Fencl V, Teghtsoonian M, Weinberger SE . Distinguishable types of dyspnea in patients with shortness of breath. Am Rev Resp Dis 1990; 142: 1009–1014.
Steuten L, Creutzber E, Vrijhoef H, Wouters E . COPD as a multicomponent disease: inventory of dyspnea, underweight, obesity and fat free mass depletion in primary care. Prim Care Respir J 2006; 15: 84–91.
Herlitz J, Wognsen GB, Caidahl K, Hartford M, Karlson BW, Karlson T et al. Symptoms of chest pain and dyspnea and factors associated with chest pain and dyspnea 10 years after coronary artery bypass grafting. Am Heart J 2008; 156: 580–587.
Herlitz J, Wognsen GB, Evander MH, Caidahl K, Hartford M, Karlson BW et al. Symptoms of chest pain anddyspnea during a period of 15 years after coronary artery bypass grafting. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 2010; 37: 112–118.
Mahler DA, Weinberg DH, Well Ck, Feinstein AR . The measurement of dypnea: contents, interobserver agreement, and physiologic correlates of two new clinical index. Chest 1984; 85: 751–758.
Mahle DA, Wells CK . Evaluation of clinical methods for rating dyspnea. Chest 1988; 93: 580–586.
Powers J, Bennett SJ . Measurement of dyspnea in patients treated with mechanical ventilation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1999; 8: 254–261.
Goldman L, Hashimoto B, Cook EF, Loscalzo A . Comparative reproducibility and validity of systems for assessing cardiovascular functional class: advantage of a new specific activity scale. Circulation 1981; 64: 1227–1234.
Mahler D, Harver A, Lentine T, Scott J, Beck K, Schwartzstein R . Descriptors of breathlessness in cardiorespiratory disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1996; 154: 1357–1363.
Simon P, Schwartzstein RM, Weiss JW, Lahive K, Fencl V, Martha T et al. Distinguishable sensations of breathlessness induced in normal volunteers. Am Rev Respir Dis 1989; 140: 1021–1027.
O’Donnell DE, Hong HH, Webb KA . Respiratory sensation during chest wall restriction and dead space loading in exercising men. J Appl Physiol 2000; 88: 1859–1869.
Werge-Kolmert U, Wisen A, Wohlfart B . Repeatability of measurements of oxygen consumption, heart rate and Borg’s scale in men during ergometer cycling. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging 2002; 22: 261–265.
Burney PG, Chinn S, Britton JR, Tattersfield AE, Papacosta AO . What symptoms predict the bronchial response to histamine? Evaluation in a community survey of the Bronchial Symptoms Questionnaire (1984) of the International Union against Tuberculosis and Lung Disease. Int J Epidemiol 1984; 18: 165–173.
Ahmed AA . Propensity matched study of New York Heart Association class and natural history end points in heart failure. Am J Cardiol 2007; 99: 549–553.
Ozalevli S, Ucan ES . The comparison of different dyspnea scales in patients with COPD. J Eval Clin Pract 2006; 12: 532–538.
Camago L, Pereira C . Dyspnea in COPD: beyond the modified Medical Research Council scale. J Bras Pneumol 2010; 36: 571–578.
Whaley M, Brubaker P, Leonard K, Miller C . Validity of rating of perceived exertion during graded exercise testing in apparently healthy adults and cardiac patients. J Cardiopulm Rehabil 1997; 17: 261–267.
Eakin EG, Sassi-Dambron DE, Al Ries, Kaplan RM . Reliability and validity of dyspnea measures in patients with obstructive lung disease. Int J Behav Med 1995; 2: 118–134.
Raphael C, Briscore C, Davies J, Whinnett Z, Manisty C, Sulton R et al. Limitations of the New York Heart Association functional classification system and self-reported walking distances in chronic heart failure. Heart 2007; 93: 476–482.
Cochrane AL, Chapman PJ, Oldham PD . Observers’ errors in taking medical histories. Lancet 1951; 1: 1007–1009.
Fletcher CM, Tinker CM . Chronic bronchitis: a further study of simple diagnostic methods in a working population. Br Med J 1961; 1: 1491–1498.
Wijkstra PJ, Em Vergert, Van Altena R, Postma DS, Kraan J, Koeter GH . Reliability and validity of the chronic respiratory questionnaire. Thorax 1994; 48: 465–467.
Williams JEA, Singh SJ, Swell L, Guyatt GH, Morgan MDL . Development of a self-reported chronic respiratory questionnaire (CRQ-SR). Thorax 2001; 56: 954–959.
Martin LL . Validity and reliability of a quality-of-life instrument: the chronic respiratory disease questionnaire. Clin Nurs Res 1994; 3: 146–156.
Mahler DA, Ward J, Waterman LA, McCusker C, ZuWallack R, Baird JC . Patient-reported dyspnea in COPD reliability and association with stage of disease. Chest 2009; 136: 1473–1479.
Burney PG, Laitinen LA, Perdrizet S, Huckauf H, Tattersfield AE, Chinn S et al. Validity and repeatability of the IUATLD (1984) Bronchial Symptoms Questionnaire: an international comparison. Eur Respir J 1984; 2: 940–945.
Rutten-van Molken M, Roos B, Van Noord JAV . AN empirical comparison of the St George’s respiratory questionnaire (SGRQ) and the chronic respiratory disease questionnaire (CRQ) in a clinical trial setting. Thorax 1999; 54: 995–1003.
Chhabra SK, Gupta AK, Khuma MZ . Evaluation of three scales of dyspnea in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Ann Thorac Med 2009; 4: 128–132.
Nguyen HQ, Altinger J, Carrieri-Kohlman V, Gormley JM, Paul S, Stulbarg MS . Factor analysis of laboratory and clinical measurements of dyspnea in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Pain Symptom Manage 2003; 25: 118–126.
Schunemann HJ, Goldstein R, Mador MJ, McKim D, Stahl E, Puhan M et al. A randomised trial to evaluate the self-administered standardised chronic respiratory questionnaire. Eur Respir J 2005; 25: 31–40.
Guyatt GH, Berman LB, Townsend M, So Pugsley, Chambers LW . A measure of quality of life for clinical trials in chronic lung disease. Thorax 1987; 42: 773–778.
Strassinig M, Brar JS, Ganguli R . Low cardiorespiratory fitness and physical functional capacity in obese patients with schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 2011; 126: 103–109.
Ariansen I, Edvardsen E, Borchsenius F, Abdelnoor M, Tveit A, Gjesdal K . Lung function and dyspnea in patients with permanent atrial fibrillation. Eur J Inter Med 2011; 22: 466–470.
MacDonald VM, Higgins I, Simpson JL, Gibson PG . The importance of clinical management problems in older people with COPD and asthma: do patients and physicians agree? Prim Care Respir J 2011; 20: 389–395.
Bowden JA, To TH, Abernethy AP, Currow DC . Predictors of chronic breathlessness: a large population study. BMC Public Health 2011; 11: 33.
Frank I, Briggs R, Spengler CM . Respiratory muscles, exercise performance, and health in overweight and obese subjects. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2011; 43: 714–727.
Villiot-Danger JC, Villiot-Danger E, Borel JC, Pepin JL, Wuyam B, Verges S . Respiratory muscle endurance training in obese patients. Int J Obesity 2011; 35: 692–699.
Pendharkar SR, Tsai WH, Eves ND, Ford GT, Davidson WJ . CPAP increases exercise tolerance in obese subjects with obstructive sleep apnea. Respir Med 2011; 105: 1565–1571.
Cecere LM, Littman AJ, Slatore CG, Udris EM, Bryson CL, Boyko EJ et al. Obesity and COPD: associated symptoms, health-related quality of life, and medication use. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis 2011; 8: 275–284.
Bernabeu-Wittel M, Baron-Franco B, Nurcia-Zaragoza J, Fuertes-Martin A, Ramos-Cantos C, Fernandez-Moyano A et al. A multi-institutional, hospital-based assessment of clinical, functional, sociofamilial and health-care characteristics of polypathological patients (PP). Arch Gerontol Geriatr 2011; 53: 284–291.
Affirm investigators Quality of life in Atrial Fibrillation: the Atrial Fibrillation Follow-up Investigation of Rhythm Management (AFFIRM) study. Am Heart J 2005; 149: 112–120.
Reynolds MR, Ellis E, Zimetbaum P . Quality of life in atrial fibrillation: measurement tools and impact of interventions. J Cardiovasc Electr 2008; 19: 762–768.
Von Leupoldt A, Dahme B . Differentiation between the sensory and affective dimension of dyspnea during resistive load breathing in normal subjects. Chest 2005; 128: 3345–3349.
Von Leupoldt A, Petersen S, Scheuchl S, Fullekrug K, Gerwin C, Reer R et al. Reliability of verbal descriptors of dypnoea and their relationship with perceived intensity and unpleasantness. G Ital Med Lav Erg 2006; 28: 83–88.
Williams MT, Cafarella P, Olds T, Petkov J, Frith P . Affective descriptors of the sensation of breathlessness are more highly associated with severity of impairment than physical descriptors in people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Chest 2010; 138: 315–322.
Yorke J, Moosavi SH, Shuldham C, Jones PW . Quantification of dyspnea using descriptors: development and initial testing of the Dyspnea-12. Thorax 2010; 65: 21–26.
Banzett R, Pedersen S, Schwartzstein R . Lansing RW. The affective dimension of laboratory dyspnea. Air hunger is more unpleasant than work/effort. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2008; 177: 1384–1390.
Currow DC, Abernethy AP . Therapeutic nihilism: The next hurdle in improving treatment of breathlessness. Curr Opin SUpp Palliat Care 2011; 5: 69–70.
Williams MT . Applicability and generalizability of palliative interventions for dyspnea: One size fits all, some or none? Curr Opin Supp Palliat Care 2011; 5: 92–100.
Mahler DA, Slecky PA, Harrod CG, Benditt JO, Carrieri-Kohlman V, Curtis JR et al. American College of Chest Physicians consensus statement on the management of dyspnea in patients with advanced lung disease. Chest 2010; 137: 674–691.
Johnson MJ, Oxberry SG, Cleland JGF, Clark AL . Measurement of breathlessness in clinical trials in patients with chronic heart failure; the need for a standardized approach: a systemic review. Eur J Heart Fail 2010; 12: 137–147.
Mularski RA, Campbell ML, Asch SM, Reeve BB, Basch E, Maxwell TL et al. A review of quality of care evaluation for the palliation of dyspnea. Am J Resp Crit Care Med 2010; 181: 534–538.
West RL, Hernandez AF, O’Connor CM, Starling RC, Califf RM . A review of dyspnea in acute heart failure syndromes. Am Heart J 2010; 160: 209–214.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on International Journal of Obesity website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gerlach, Y., Williams, M. & Coates, A. Weighing up the evidence–a systematic review of measures used for the sensation of breathlessness in obesity. Int J Obes 37, 341–349 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2012.49
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2012.49