Abstract
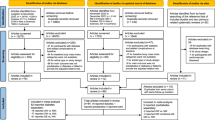
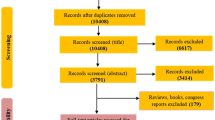
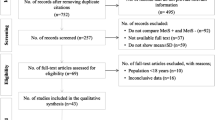
There are many recent observational studies on metabolic syndrome (MS) and the risk for ED, and it is still inconclusive whether MS increases the risk for ED. This meta-analysis aims to detect a relationship between MS and ED. We identified eligible studies by searching PubMed, Embase and the Cochrane Library for articles published before August 2013. Adjusted relative risks (RR) with 95% confidence interval (CI) were calculated using random-effects or fixed-effects models. A total of 10 studies involving 4092 participants were included in the meta-analysis. MS was associated with an increased incidence of ED (RR=1.60, 95% CI=1.27–2.02, P<0.001), with significant evidence of heterogeneity among these studies (P for heterogeneity <0.001, I2=92.9%). The subgroup and sensitivity analyses confirmed the stability of the results and no publication bias was detected. The present meta-analysis suggests that MS is significantly associated with the risk for ED. Large-scale and well-designed prospective studies are required to further investigate the association between MS and risk for ED.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dong JY, Zhang YH, Qin LQ . Erectile dysfunction and risk of cardiovascular disease: meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. J Am Coll Cardiol 2011; 58: 1378–1385.
Selvin E, Burnett AL, Platz EA . Prevalence and risk factors for erectile dysfunction in the US. Am J Med 2007; 120: 151–157.
Sullivan ME, Keoghane SR, Miller MA . Vascular risk factors and erectile dysfunction. Bju Int 2001; 87: 838–845.
Montorsi P, Ravagnani PM, Galli S, Rotatori F, Briganti A, Salonia A et al. Common grounds for erectile dysfunction and coronary artery disease. Curr Opin Urol 2004; 14: 361–365.
Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults. Executive Summary of The Third Report of The National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, And Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol In Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). JAMA 2001; 285: 2486–2497.
Alberti KG, Eckel RH, Grundy SM, Zimmet PZ, Cleeman JI, Donato KA et al. Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: a joint interim statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation 2009; 120: 1640–1645.
Roumeguere T, Wespes E, Carpentier Y, Hoffmann P, Schulman CC . Erectile dysfunction is associated with a high prevalence of hyperlipidemia and coronary heart disease risk. Eur Urol 2003; 44: 355–359.
Bansal TC, Guay AT, Jacobson J, Woods BO, Nesto RW . Incidence of metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance in a population with organic erectile dysfunction. J Sex Med 2005; 2: 96–103.
Mantel N, Haenszel W . Statistical aspects of the analysis of data from retrospective studies of disease. J Natl Cancer Inst 1959; 22: 719–748.
DerSimonian R, Laird N . Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials 1986; 7: 177–188.
Begg CB, Mazumdar M . Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics 1994; 50: 1088–1101.
Egger M, Davey SG, Schneider M, Minder C . Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 1997; 315: 629–634.
Esposito K, Giugliano F, Martedi E, Feola G, Marfella R, D'Armiento M et al. High proportions of erectile dysfunction in men with the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Care 2005; 28: 1201–1203.
Demir T, Demir O, Kefi A, Comlekci A, Yesil S, Esen A . Prevalence of erectile dysfunction in patients with metabolic syndrome. Int J Urol 2006; 13: 385–388.
Bal K, Oder M, Sahin AS, Karatas CT, Demir O, Can E et al. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome and its association with erectile dysfunction among urologic patients: metabolic backgrounds of erectile dysfunction. Urology 2007; 69: 356–360.
Heidler S, Temml C, Broessner C, Mock K, Rauchenwald M, Madersbacher S et al. Is the metabolic syndrome an independent risk factor for erectile dysfunction? J Urol 2007; 177: 651–654.
Lee YC, Liu CC, Huang CN, Li WM, Wu WJ, Yeh HC et al. The potential impact of metabolic syndrome on erectile dysfunction in aging Taiwanese males. J Sex Med 2010; 7: 3127–3134.
Zambon JP, Mendonca RR, Wroclawski ML, Karam JA, Santos RD, Carvalho JA et al. Cardiovascular and metabolic syndrome risk among men with and without erectile dysfunction: case-control study. Sao Paulo Med J 2010; 128: 137–140.
Lahoz-Garcia C, Arrabal-Polo M, Lopez-Carmona Pintado F, Merino-Salas S, Jimenez-Pacheco A, Palao-Yago F et al. Erectile dysfunction and metabolic syndrome: Two entities related to each other. Urology 2011; 78: S80–S81.
Pohjantahti-Maaroos H, Palomaki A, Hartikainen J . Erectile dysfunction, physical activity and metabolic syndrome: differences in markers of atherosclerosis. BMC Cardiovasc Disord 2011; 11: 36.
Arrabal-Polo MA, Arias-Santiago S, Lopez-Carmona PF, Merino-Salas S, Lahoz-Garcia C, Zuluaga-Gomez A et al. Metabolic syndrome, hormone levels, and inflammation in patients with erectile dysfunction. ScientificWorldJournal 2012; 2012: 272769.
Chao JK, Kuo WH, Chiang HS, Hwang TI, Chao IC, Chiang SK . Association of metabolic syndrome, atherosclerosis risk factors, sex hormones in ED in aboriginal Taiwanese. Int J Impot Res 2012; 24: 141–146.
Corona G, Mannucci E, Ricca V, Lotti F, Boddi V, Bandini E et al. The age-related decline of testosterone is associated with different specific symptoms and signs in patients with sexual dysfunction. Int J Androl 2009; 32: 720–728.
Reilly CM, Zamorano P, Stopper VS, Mills TM . Androgenic regulation of NO availability in rat penile erection. J Androl 1997; 18: 110–115.
Yassin AA, Saad F, Gooren LJ . Metabolic syndrome, testosterone deficiency and erectile dysfunction never come alone. Andrologia 2008; 40: 259–264.
Nehra A, Azadzoi KM, Moreland RB, Pabby A, Siroky MB, Krane RJ et al. Cavernosal expandability is an erectile tissue mechanical property which predicts trabecular histology in an animal model of vasculogenic erectile dysfunction. J Urol 1998; 159: 2229–2236.
Koca O, Caliskan S, Ozturk MI, Gunes M, Kilicoglu G, Karaman MI . Vasculogenic erectile dysfunction and metabolic syndrome. J Sex Med 2010; 7: 3997–4002.
Huang PL . A comprehensive definition for metabolic syndrome. Dis Model Mech 2009; 2: 231–237.
Corona G, Mannucci E, Forti G, Maggi M . Hypogonadism, ED, metabolic syndrome and obesity: a pathological link supporting cardiovascular diseases. Int J Androl 2009; 32: 587–598.
Esposito K, Giugliano F, Di Palo C, Giugliano G, Marfella R, D'Andrea F et al. Effect of lifestyle changes on erectile dysfunction in obese men: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2004; 291: 2978–2984.
Acknowledgements
We thank Professor An-Yang Wei for his excellent technical support. This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81170566) and Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (S2012010009091).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, L., Zhang, T., Zhang, Y. et al. Metabolic syndrome and risk for ED: a meta-analysis. Int J Impot Res 26, 196–200 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijir.2014.3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijir.2014.3
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Metabolic syndrome and erectile dysfunction: a systematic review and meta-analysis study
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation (2023)
-
Association of erectile dysfunction with diabetic foot and its outcomes in type 2 diabetic men
Hormones (2023)
-
Differences in the prevalence of erectile dysfunction between novel subgroups of recent-onset diabetes
Diabetologia (2022)
-
The intra-meatal application of alprostadil cream (Vitaros®) improves drug efficacy and patient’s satisfaction: results from a randomized, two-administration route, cross-over clinical trial
International Journal of Impotence Research (2019)