Abstract
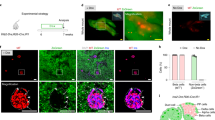
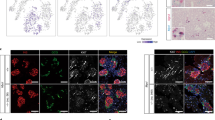
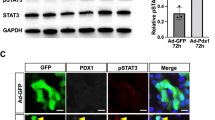
With the long-term aim of developing a new type of therapy for diabetes, we have investigated the reprogramming of liver cells in normal mice toward a pancreatic phenotype using the gene combination Pdx1, Ngn3, MafA. CD1 mice were rendered diabetic with streptozotocin and given a single dose of Ad-PNM, an adenoviral vector containing all three genes. Ad-PNM induced hepatocytes of the liver to produce insulin, and the blood glucose became normalized. But over several weeks, the insulin-positive cells were lost and the blood glucose rose back to diabetic levels. Simultaneous administration of a peroxisome-proliferator-activated receptor agonist, WY14643, caused remission of diabetes at a lower dose of Ad-PNM and also caused the appearance of a population of insulin-secreting ductal structures in the liver. The insulin-positive ducts were stable and were able to relieve diabetes in the long term. We show that the effect of WY14643 is associated with the promotion of cell division of the ductal cells, which may increase their susceptibility to being reprogrammed toward a beta cell fate.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferber S, Halkin A, Cohen H, Ber I, Einav Y, Goldberg I et al. Pancreatic and duodenal homeobox gene 1 induces expression of insulin genes in liver and ameliorates streptozotocin-induced hyperglycemia. Nat Med 2000; 6: 568–572.
Ber I, Shternhall K, Perl S, Ohanuna Z, Goldberg I, Barshack I et al. Functional, persistent, and extended liver to pancreas transdifferentiation. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 31950–31957.
Miyatsuka T, Kaneto H, Kajimoto Y, Hirota S, Arakawa Y, Fujitani Y et al. Ectopically expressed PDX-1 in liver initiates endocrine and exocrine pancreas differentiation but causes dysmorphogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 2003; 310: 1017–1025.
Kojima H, Fujimiya M, Matsumura K, Younan P, Imaeda H, Maeda M et al. NeuroD-betacellulin gene therapy induces islet neogenesis in the liver and reverses diabetes in mice. Nat Med 2003; 9: 596–603.
Kaneto H, Nakatani Y, Miyatsuka T, Matsuoka T, Matsuhisa M, Hori M et al. PDX-1/VP16 fusion protein, together with NeuroD or Ngn3, markedly induces insulin gene transcription and ameliorates glucose tolerance. Diabetes 2005; 54: 1009–1022.
Yechoor V, Liu V, Espiritu C, Paul A, Oka K, Kojima H et al. Neurogenin3 Is sufficient for transdetermination of hepatic progenitor cells into neo-islets in vivo but not transdifferentiation of hepatocytes. Dev Cell 2009; 16: 358–373.
Wang AY, Ehrhardt A, Xu H, Kay MA . Adenovirus transduction is required for the correction of diabetes using Pdx-1 or Neurogenin-3 in the liver. Mol The 2007; 15: 255–263.
Banga A, Akinci E, Greder LV, Dutton JR, Slack JMW . In vivo reprogramming of Sox9+ cells in the liver to insulin-secreting ducts. Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci USA 2012; 109: 15336–15341.
Zhou Q, Brown J, Kanarek A, Rajagopal J, Melton DA . In vivo reprogramming of adult pancreatic exocrine cells to beta-cells. Nature 2008; 455: 627–632.
Gittes GK . Developmental biology of the pancreas: a comprehensive review. Dev. Biol. 2009; 326: 4–35.
Yang Y, Nunes FA, Berencsi K, Furth EE, Gönczöl E, Wilson JM . Cellular immunity to viral antigens limits E1-deleted adenoviruses for gene therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci 1994; 91: 4407–4411.
Devchand PR, Keller H, Peters JM, Vazquez M, Gonzalez FJ, Wahli W . The PPAR alpha-leukotriene B-4 pathway to inflammation control. Nature 1996; 384: 39–43.
Lehmann JM, Lenhard JM, Oliver BB, Ringold GM, Kliewer SA . Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors alpha and gamma are activated by indomethacin and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. J Biol Chem 1997; 272: 3406–3410.
Cohen AJ, Grasso P . Review of the hepatic response to hypolipidaemic drugs in rodents and assessment of its toxicological significance to man. Food Cosmet Toxicol 1981; 19: 585–605.
Ledwith BJ, Johnson TE, Wagner LK, Pauley CJ, Manam S, Galloway SM et al. Growth regulation by peroxisome proliferators: opposing activities in early and late G(1). Cancer Res 1996; 56: 3257–3264.
Austyn JM, Gordon S . F4/80, a monoclonal antibody directed specifically against the mouse macrophage. Eur J Immunol 1981; 11: 805–815.
McGuckin MA, Linden SK, Sutton P, Florin TH . Mucin dynamics and enteric pathogens. Nat Rev Microbiol 2011; 9: 265–278.
Shiojiri N, Lemire JM, Fausto N . Cell lineages and oval cell progenitors in rat liver development. Cancer Res 1991; 51: 2611–2620.
Wang X, Foster M, Al-Dhalimy M, Lagasse E, Finegold M, Grompe M . The origin and liver repopulating capacity of murine oval cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003; 100: 11881–11888.
Duncan AW, Dorrell C, Grompe M . Stem cells and liver regeneration. Gastroenterology 2009; 137: 466–481.
Roskams T, De Vos R, Van Eyken P, Myazaki H, Van Damme B, Desmet V . Hepatic OV-6 expression in human liver disease and rat experiments: evidence for hepatic progenitor cells in man. J Hepatol 1998; 29: 455–463.
Kojima H, Fujimiya M, Matsumura K, Nakahara T, Hara M, Chan L . Extrahepatic insulin-producing cells in multiple organs in diabetes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 2458–2463.
Meivar-Levy I, Sapir T, Gefen-Halevi S, Aviv V, Barshack I, Onaca N et al. Pancreatic and duodenal homeobox gene 1 induces hepatic dedifferentiation by suppressing the expression of CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein β. Hepatology 2007; 46: 898–905.
Li WC, Ralphs KL, Slack JMW, Tosh D . Keratinocyte serum free medium maintains long-term liver gene expression and function in cultured rat hepatocytes by preventing the loss of liver-enriched transcription factors. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2007; 39: 541–554.
Horb ME, Shen CN, Tosh D, Slack JMW . Experimental conversion of liver to pancreas. Curr Biol 2003; 13: 105–115.
Kyrmizi I, Hatzis P, Katrakili N, Tronche F, Gonzalez FJ, Talianidis I . Plasticity and expanding complexity of the hepatic transcription factor network during liver development. Genes Dev 2006; 20: 2293–2305.
Dorrell C, Erker L, Schug J, Kopp JL, Canaday PS, Fox AJ et al. Prospective isolation of a bipotential clonogenic liver progenitor cell in adult mice. Genes Dev 2011; 25: 1193–1203.
Shin S, Walton G, Aoki R, Brondell K, Schug J, Fox A et al. Foxl1-Cre-marked adult hepatic progenitors have clonogenic and bilineage differentiation potential. Genes Dev 2011; 25: 1185–1192.
Andersson O, Adams BA, Yoo D, Ellis GC, Gut P, Anderson RM et al. Adenosine signaling promotes regeneration of pancreatic β cells in vivo. Cell Metab 2012; 15: 885–894.
Haumaitre C, Lenoir O, Scharfmann R . Histone deacetylase inhibitors modify pancreatic cell fate determination and amplify endocrine progenitors. Mol Cell Biol 2008; 28: 6373–6383.
Kubicek S, O'Sullivan RJ, August EM, Hickey ER, Zhang Q, Teodoro ML et al. Reversal of H3K9Me2 by a small-molecule inhibitor for the G9a histone methyltransferase. Mol Cell Biol 2007; 25: 473–481.
Shi Y, Desponts C, Do JT, Hahm HS, Scholer HR, Ding S . Induction of Pluripotent Stem Cells from Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts by Oct4 and Klf4 with Small-Molecule Compounds. Cell Stem Cell 2008; 3: 568–574.
Singhal N, Graumann J, Wu G, Arauzo-Bravo MJ, Han DW, Greber B et al. Chromatin-remodeling components of the BAF complex facilitate reprogramming. Cell 2010; 141: 943–955.
Hirai H, Tani T, Katoku-Kikyo N, Kellner S, Karian P, Firpo M et al. Radical acceleration of nuclear reprogramming by chromatin remodeling with the transactivation domain of MyoD. Stem Cells 2011; 29: 1349–1361.
Hasnain SZ, Gallagher AL, Grencis RK, Thornton DJ . A new role for mucins in immunity: insights from gastrointestinal nematode infection. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2013; 45: 364–374.
Thornton DJ, Rousseau K, McGuckin MA . Structure and function of the polymeric mucins in airways mucus. Ann Rev Physiol 2008; 70: 459–486.
Kliewer SA, Xu HE, Lambert MH, Willson TM . Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors: from genes to physiology. Recent Prog Horm Res 2001; 56: 239–263.
Akinci E, Banga A, Greder LV, Dutton JR, Slack JMW . Reprogramming of pancreatic exocrine cells towards a beta cell character using Pdx1, Ngn3 and MafA. Biochem J 2012; 442: 539–550.
Dutton JR, Daughters RS, Chen Y, O’Neill KE, JMW Slack . Use of adenovirus for ectopic gene expression in xenopus. Dev Dyn 2009; 238: 1412–1421.
Rerup CC . Drugs producing diabetes through damage to the insulin secreting cells. Pharmacol Rev 1970; 22: 485–518.
Peters DH, Fitton A, Plosker GL, Faulds D . Tacrolimus—a review of its pharmacology, and therapeutic potential in hepatic and renal-transplantation. Drugs 1993; 46: 746–794.
Brazelton TR, Morris RE . Molecular mechanisms of action of new xenobiotic immunosuppressive drugs: Tacrolimus (FK506), sirolimus (rapamycin), mycophenolate mofetil and leflunomide. Curr Opin Immunol 1996; 8: 710–720.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Cliff Steer for introducing us to the compounds causing liver hyperplasia and for useful discussions. This work was supported by a grant from the University of Minnesota Academic Health Center TRG 08-12 and by NIH grant R01DK080747.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on Gene Therapy website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Banga, A., Greder, L., Dutton, J. et al. Stable insulin-secreting ducts formed by reprogramming of cells in the liver using a three-gene cocktail and a PPAR agonist. Gene Ther 21, 19–27 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2013.50
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2013.50
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Improvement of the therapeutic capacity of insulin-producing cells trans-differentiated from human liver cells using engineered cell sheet
Stem Cell Research & Therapy (2021)
-
Liver to Pancreas Transdifferentiation
Current Diabetes Reports (2019)
-
PDX1, Neurogenin-3, and MAFA: critical transcription regulators for beta cell development and regeneration
Stem Cell Research & Therapy (2017)
-
Regenerative medicine and cell-based approaches to restore pancreatic function
Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology (2017)