Abstract
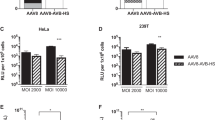
We have demonstrated the potential of random peptide libraries displayed on adeno-associated virus (AAV)2 to select for AAV2 vectors with improved efficiency for cell type-directed gene transfer. AAV9, however, may have advantages over AAV2 because of a lower prevalence of neutralizing antibodies in humans and more efficient gene transfer in vivo. Here we provide evidence that random peptide libraries can be displayed on AAV9 and can be utilized to select for AAV9 capsids redirected to the cell type of interest. We generated an AAV9 peptide display library, which ensures that the displayed peptides correspond to the packaged genomes and performed four consecutive selection rounds on human coronary artery endothelial cells in vitro. This screening yielded AAV9 library capsids with distinct peptide motifs enabling up to 40-fold improved transduction efficiencies compared with wild-type (wt) AAV9 vectors. Incorporating sequences selected from AAV9 libraries into AAV2 capsids could not increase transduction as efficiently as in the AAV9 context. To analyze the potential on endothelial cells in the intact natural vascular context, human umbilical veins were incubated with the selected AAV in situ and endothelial cells were isolated. Fluorescence-activated cell sorting analysis revealed a 200-fold improved transduction efficiency compared with wt AAV9 vectors. Furthermore, AAV9 vectors with targeting sequences selected from AAV9 libraries revealed an increased transduction efficiency in the presence of human intravenous immunoglobulins, suggesting a reduced immunogenicity. We conclude that our novel AAV9 peptide library is functional and can be used to select for vectors for future preclinical and clinical gene transfer applications.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Miller WH, Brosnan MJ, Graham D, Nicol CG, Morecroft I, Channon KM et al. Targeting endothelial cells with adenovirus expressing nitric oxide synthase prevents elevation of blood pressure in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats. Mol Ther 2005; 12: 321–327.
Xu Y, Gong B, Yang Y, Awasthi YC, Boor PJ . Adenovirus-mediated overexpression of glutathione-s-transferase mitigates transplant arteriosclerosis in rabbit carotid allografts. Transplantation 2010; 89: 409–416.
Gruchala M, Bhardwaj S, Pajusola K, Roy H, Rissanen TT, Kokina I et al. Gene transfer into rabbit arteries with adeno-associated virus and adenovirus vectors. J Gene Med 2004; 6: 545–554.
Sen S, Conroy S, Hynes SO, McMahon J, O’Doherty A, Bartlett JS et al. Gene delivery to the vasculature mediated by low-titre adeno-associated virus serotypes 1 and 5. J Gene Med 2008; 10: 143–151.
Denby L, Nicklin SA, Baker AH . Adeno-associated virus (AAV)-7 and -8 poorly transduce vascular endothelial cells and are sensitive to proteasomal degradation. Gene Therapy 2005; 12: 1534–1538.
Pajusola K, Gruchala M, Joch H, Luscher TF, Yla-Herttuala S, Bueler H . Cell-type-specific characteristics modulate the transduction efficiency of adeno-associated virus type 2 and restrain infection of endothelial cells. J Virol 2002; 76: 11530–11540.
Chen YH, Chang M, Davidson BL . Molecular signatures of disease brain endothelia provide new sites for CNS-directed enzyme therapy. Nat Med 2009; 15: 1215–1218.
Müller OJ, Kaul F, Weitzman MD, Pasqualini R, Arap W, Kleinschmidt JA et al. Random peptide libraries displayed on adeno-associated virus to select for targeted gene therapy vectors. Nat Biotechnol 2003; 21: 1040–1046.
Nicklin SA, Buening H, Dishart KL, de Alwis M, Girod A, Hacker U et al. Efficient and selective AAV2-mediated gene transfer directed to human vascular endothelial cells. Mol Ther 2001; 4: 174–181.
Waterkamp DA, Müller OJ, Ying Y, Trepel M, Kleinschmidt JA . Isolation of targeted AAV2 vectors from novel virus display libraries. J Gene Med 2006; 8: 1307–1319.
White K, Büning H, Kritz A, Janicki H, McVey J, Perabo L et al. Engineering adeno-associated virus 2 vectors for targeted gene delivery to atherosclerotic lesions. Gene Therapy 2008; 15: 443–451.
Work LM, Büning H, Hunt E, Nicklin SA, Denby L, Britton N et al. Vascular bed-targeted in vivo gene delivery using tropism-modified adeno-associated viruses. Mol Ther 2006; 13: 683–693.
White SJ, Nicklin SA, Büning H, Brosnan MJ, Leike K, Papadakis ED et al. Targeted gene delivery to vascular tissue in vivo by tropism-modified adeno-associated virus vectors. Circulation 2004; 109: 513–519.
Boutin S, Monteilhet V, Veron P, Leborgne C, Benveniste O, Montus MF et al. Prevalence of serum IgG and neutralizing factors against adeno-associated virus (AAV) types 1, 2, 5, 6, 8, and 9 in the healthy population: implications for gene therapy using AAV vectors. Hum Gene Ther 2010; 21: 704–712.
Calcedo R, Vandenberghe LH, Gao G, Lin J, Wilson JM . Worldwide epidemiology of neutralizing antibodies to adeno-associated viruses. J Infect Dis 2009; 199: 381–390.
Goehringer C, Rutschow D, Bauer R, Schinkel S, Weichenhan D, Bekeredjian R et al. Prevention of cardiomyopathy in delta-sarcoglycan knockout mice after systemic transfer of targeted adeno-associated viral vectors. Cardiovasc Res 2009; 82: 404–410.
Inagaki K, Fuess S, Storm TA, Gibson GA, McTiernan CF, Kay MA et al. Robust systemic transduction with AAV9 vectors in mice: efficient global cardiac gene transfer superior to that of AAV8. Mol Ther 2006; 14: 45–53.
Pacak CA, Mah CS, Thattaliyath BD, Conlon TJ, Lewis MA, Cloutier DE et al. Recombinant adeno-associated virus serotype 9 leads to preferential cardiac transduction in vivo. Circ Res 2006; 99: e3–e9.
Zincarelli C, Soltys S, Rengo G, Rabinowitz JE . Analysis of AAV serotypes 1-9 mediated gene expression and tropism in mice after systemic injection. Mol Ther 2008; 16: 1073–1080.
Grimm D, Lee JS, Wang L, Desai T, Akache B, Storm TA et al. In vitro and in vivo gene therapy vector evolution via multispecies interbreeding and retargeting of adeno-associated viruses. J Virol 2008; 82: 5887–5911.
Perabo L, Büning H, Kofler DM, Ried MU, Girod A, Wendtner CM et al. In vitro selection of viral vectors with modified tropism: the adeno-associated virus display. Mol Ther 2003; 8: 151–157.
Koerber JT, Maheshri N, Kaspar BK, Schaffer DV . Construction of diverse adeno-associated viral libraries for directed evolution of enhanced gene delivery vehicles. Nat Protoc 2006; 1: 701–706.
Maheshri N, Koerber JT, Kaspar BK, Schaffer DV . Directed evolution of adeno-associated virus yields enhanced gene delivery vectors. Nat Biotechnol 2006; 24: 198–204.
Perabo L, Endell J, King S, Lux K, Goldnau D, Hallek M et al. Combinatorial engineering of a gene therapy vector: directed evolution of adeno-associated virus. J Gene Med 2006; 8: 155–162.
Li W, Asokan A, Wu Z, Van Dyke T, DiPrimio N, Johnson JS et al. Engineering and selection of shuffled AAV genomes: a new strategy for producing targeted biological nanoparticles. Mol Ther 2008; 16: 1252–1260.
Yang L, Jiang J, Drouin LM, Agbandje-McKenna M, Chen C, Qiao C et al. A myocardium tropic adeno-associated virus (AAV) evolved by DNA shuffling and in vivo selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106: 3946–3951.
Kern A, Schmidt K, Leder C, Müller OJ, Wobus CE, Bettinger K et al. Identification of a heparin-binding peptide on adeno-associated virus type 2 capsids. J Virol 2003; 77: 11072–11081.
Opie SR, Warrington Jr KH, Agbandje-McKenna M, Zolotukhin S, Muzyczka N . Identification of amino acid residues in the capsid proteins of adeno-associated virus type 2 that contribute to heparan sulfate proteoglycan binding. J Virol 2003; 77: 6995–7006.
Xie Q, Bu W, Bhatia S, Hare J, Somasundaram T, Azzi A et al. The atomic structure of adeno-associated virus (AAV-2), a vector for human gene therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 10405–10410.
Summerford C, Samulski RJ . Membrane-associated heparan sulfate proteoglycan is a receptor for adeno-associated virus type 2 virions. J Virol 1998; 72: 1438–1445.
Mitchell M, Nam HJ, Carter A, McCall A, Rence C, Bennett A et al. Production, purification and preliminary X-ray crystallographic studies of adeno-associated virus serotype 9. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun 2009; 65: 715–718.
Lochrie MA, Tatsuno GP, Christie B, McDonnell JW, Zhou S, Surosky R et al. Mutations on the external surfaces of adeno-associated virus type 2 capsids that affect transduction and neutralization. J Virol 2006; 80: 821–834.
Gao G, Vandenberghe LH, Alvira MR, Lu Y, Calcedo R, Zhou X et al. Clades of Adeno-associated viruses are widely disseminated in human tissues. J Virol 2004; 78: 6381–6388.
Moskalenko M, Chen L, van Roey M, Donahue BA, Snyder RO, McArthur JG et al. Epitope mapping of human anti-adeno-associated virus type 2 neutralizing antibodies: implications for gene therapy and virus structure. J Virol 2000; 74: 1761–1766.
Wobus CE, Hugle-Dorr B, Girod A, Petersen G, Hallek M, Kleinschmidt JA . Monoclonal antibodies against the adeno-associated virus type 2 (AAV-2) capsid: epitope mapping and identification of capsid domains involved in AAV-2-cell interaction and neutralization of AAV-2 infection. J Virol 2000; 74: 9281–9293.
Huttner NA, Girod A, Perabo L, Edbauer D, Kleinschmidt JA, Büning H et al. Genetic modifications of the adeno-associated virus type 2 capsid reduce the affinity and the neutralizing effects of human serum antibodies. Gene Therapy 2003; 10: 2139–2147.
Bessis N, Garcia-Cozar FJ, Boissier MC . Immune responses to gene therapy vectors: influence on vector function and effector mechanisms. Gene Therapy 2004; 11 (Suppl 1): S10–S17.
Ruoslahti E . RGD and other recognition sequences for integrins. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 1996; 12: 697–715.
Asokan A, Hamra JB, Govindasamy L, Agbandje-McKenna M, Samulski RJ . Adeno-associated virus type 2 contains an integrin alpha5beta1 binding domain essential for viral cell entry. J Virol 2006; 80: 8961–8969.
Akache B, Grimm D, Pandey K, Yant SR, Xu H, Kay MA . The 37/67-kilodalton laminin receptor is a receptor for adeno-associated virus serotypes 8, 2, 3, and 9. J Virol 2006; 80: 9831–9836.
Dubielzig R, King JA, Weger S, Kern A, Kleinschmidt JA . Adeno-associated virus type 2 protein interactions: formation of pre-encapsidation complexes. J Virol 1999; 73: 8989–8998.
Wang Z, Ma HI, Li J, Sun L, Zhang J, Xiao X . Rapid and highly efficient transduction by double-stranded adeno-associated virus vectors in vitro and in vivo. Gene Therapy 2003; 10: 2105–2111.
Grimm D, Kay MA, Kleinschmidt JA . Helper virus-free, optically controllable, and two-plasmid-based production of adeno-associated virus vectors of serotypes 1 to 6. Mol Ther 2003; 7: 839–850.
Michelfelder S, Lee MK, deLima-Hahn E, Wilmes T, Kaul F, Müller O et al. Vectors selected from adeno-associated viral display peptide libraries for leukemia cell-targeted cytotoxic gene therapy. Exp Hematol 2007; 35: 1766–1776.
Gao GP, Alvira MR, Wang L, Calcedo R, Johnston J, Wilson JM . Novel adeno-associated viruses from rhesus monkeys as vectors for human gene therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 11854–11859.
Reed SE, Staley EM, Mayginnes JP, Pintel DJ, Tullis GE . Transfection of mammalian cells using linear polyethylenimine is a simple and effective means of producing recombinant adeno-associated virus vectors. J Virol Methods 2006; 138: 85–98.
Hauswirth WW, Lewin AS, Zolotukhin S, Muzyczka N . Production and purification of recombinant adeno-associated virus. Methods Enzymol 2000; 316: 743–761.
Samulski RJ, Chang LS, Shenk T . A recombinant plasmid from which an infectious adeno-associated virus genome can be excised in vitro and its use to study viral replication. J Virol 1987; 61: 3096–3101.
Veldwijk MR, Topaly J, Laufs S, Hengge UR, Wenz F, Zeller WJ et al. Development and optimization of a real-time quantitative PCR-based method for the titration of AAV-2 vector stocks. Mol Ther 2002; 6: 272–278.
Grimm D, Kern A, Rittner K, Kleinschmidt JA . Novel tools for production and purification of recombinant adenoassociated virus vectors. Hum Gene Ther 1998; 9: 2745–2760.
Acknowledgements
We thank Barbara Leuchs (VP and DU, the German Cancer Research Center, Heidelberg, Germany) and her team for excellent assistance in vector production and titration and Ender Serbest (Department of Physiology, University of Heidelberg, Heidelberg, Germany) for outstanding technical assistance related to processing of human umbilical cords. This work was supported by the German Research Foundation (1654/3-2 to JAK and OJM).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Gene Therapy website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Varadi, K., Michelfelder, S., Korff, T. et al. Novel random peptide libraries displayed on AAV serotype 9 for selection of endothelial cell-directed gene transfer vectors. Gene Ther 19, 800–809 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2011.143
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2011.143
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Cathepsin B S-nitrosylation promotes ADAR1-mediated editing of its own mRNA transcript via an ADD1/MATR3 regulatory axis
Cell Research (2023)
-
Development of a dual hybrid AAV vector for endothelial-targeted expression of von Willebrand factor
Gene Therapy (2023)
-
Vector engineering, strategies and targets in cancer gene therapy
Cancer Gene Therapy (2022)
-
Endothelial PDGF-BB/PDGFR-β signaling promotes osteoarthritis by enhancing angiogenesis-dependent abnormal subchondral bone formation
Bone Research (2022)
-
Gentherapie der Transplantatvaskulopathie
Zeitschrift für Herz-,Thorax- und Gefäßchirurgie (2022)