Abstract
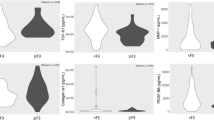
IFNL4 is linked to hepatitis C virus treatment response and type III interferons (IFNs). We studied the functional associations among hepatic expressions of IFNs and IFN-stimulated genes (ISGs), and treatment response to peginterferon and ribavirin. Type I IFNs (IFNA1, IFNB1), type II (IFNG), type III (IFNL1, IFNL2/3), IFNL4 and ISG hepatic expressions were measured by qPCR from in 65 chronic hepatitis C (CHC) patients whose IFNL4-associated rs368234815 and IFNL3-associated rs12989760 genotype were determined. There was a robust correlation of hepatic expression within type I and type III IFNs and between type III IFNs and IFNL4 but no correlation between other IFN types. Expression of ISGs correlated with type III IFNs and IFNL4 but not with type I IFNs. Levels of ISGs and IFNL2/3 mRNAs were lower in IFNL3 rs12979860 CC patients compared with non-CC patients, and in treatment responders, compared with nonresponders. IFNL4-ΔG genotype was associated with high ISG levels and nonresponse. Hepatic levels of ISGs in CHC are associated with IFNL2/3 and IFNL4 expression, suggesting that IFNLs, not other types of IFNs, drive ISG expression. Hepatic IFNL2/3 expression is functionally linked to IFNL4 and IFNL3 polymorphisms, potentially explaining the tight association among ISG expression and treatment response.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Seeff LB . The history of the "natural history" of hepatitis C (1968-2009). Liver Int 2009; 29 (Suppl 1): 89–99.
Ghany MG, Strader DB, Thomas DL, Seeff LB . Diagnosis, management, and treatment of hepatitis C: an update. Hepatology 2009; 49: 1335–1374.
Liang TJ, Ghany MG . Current and future therapies for hepatitis C virus infection. N Engl J Med 2013; 368: 1907–1917.
Liang TJ, Ghany MG . Therapy of Hepatitis C - Back to the Future. N Engl J Med 2014; 370: 2043–2047.
Meissner EG, Wu D, Osinusi A, Bon D, Virtaneva K, Sturdevant D et al. Endogenous intrahepatic IFNs and association with IFN-free HCV treatment outcome. J Clin Invest 2014; 124: 3352–3363.
Meissner EG, Bon D, Prokunina-Olsson L, Tang W, Masur H, O'Brien TR et al. IFNL4-DeltaG genotype is associated with slower viral clearance in hepatitis C, genotype-1 patients treated with sofosbuvir and ribavirin. J Infect Dis 2014; 209: 1700–1704.
Thomas E, Gonzalez VD, Li Q, Modi AA, Chen W, Noureddin M et al. HCV infection induces a unique hepatic innate immune response associated with robust production of type III interferons. Gastroenterology 2012; 142: 978–988.
Sarasin-Filipowicz M, Oakeley EJ, Duong FH, Christen V, Terracciano L, Filipowicz W et al. Interferon signaling and treatment outcome in chronic hepatitis C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008; 105: 7034–7039.
Chen L, Borozan I, Feld J, Sun J, Tannis LL, Coltescu C et al. Hepatic gene expression discriminates responders and nonresponders in treatment of chronic hepatitis C viral infection. Gastroenterology 2005; 128: 1437–1444.
Ge D, Fellay J, Thompson AJ, Simon JS, Shianna KV, Urban TJ et al. Genetic variation in IL28B predicts hepatitis C treatment-induced viral clearance. Nature 2009; 461: 399–401.
Tanaka Y, Nishida N, Sugiyama M, Kurosaki M, Matsuura K, Sakamoto N et al. Genome-wide association of IL28B with response to pegylated interferon-alpha and ribavirin therapy for chronic hepatitis C. Nat Genet 2009; 41: 1105–1109.
Suppiah V, Moldovan M, Ahlenstiel G, Berg T, Weltman M, Abate ML et al. IL28B is associated with response to chronic hepatitis C interferon-alpha and ribavirin therapy. Nat Genet 2009; 41: 1100–1104.
Thomas DL, Thio CL, Martin MP, Qi Y, Ge D, O'Huigin C et al. Genetic variation in IL28B and spontaneous clearance of hepatitis C virus. Nature 2009; 461: 798–801.
Rauch A, Kutalik Z, Descombes P, Cai T, Di Iulio J, Mueller T et al. Genetic variation in IL28B is associated with chronic hepatitis C and treatment failure: a genome-wide association study. Gastroenterology 2010; 138: 1338–1345 45 e1-7.
Prokunina-Olsson L, Muchmore B, Tang W, Pfeiffer RM, Park H, Dickensheets H et al. A variant upstream of IFNL3 (IL28B) creating a new interferon gene IFNL4 is associated with impaired clearance of hepatitis C virus. Nat Genet 2013; 45: 164–171.
Bibert S, Roger T, Calandra T, Bochud M, Cerny A, Semmo N et al. IL28B expression depends on a novel TT/-G polymorphism which improves HCV clearance prediction. J Exp Med 2013; 210: 1109–1116.
McFarland AP, Horner SM, Jarret A, Joslyn RC, Bindewald E, Shapiro BA et al. The favorable IFNL3 genotype escapes mRNA decay mediated by AU-rich elements and hepatitis C virus-induced microRNAs. Nat Immunol 2014; 15: 72–79.
Balagopal A, Thomas DL, Thio CL . IL28B and the control of hepatitis C virus infection. Gastroenterology 2010; 139: 1865–1876.
Park H, Serti E, Eke O, Muchmore B, Prokunina-Olsson L, Capone S et al. IL-29 is the dominant type III interferon produced by hepatocytes during acute hepatitis C virus infection. Hepatology 2012; 56: 2060–2070.
Honda M, Sakai A, Yamashita T, Nakamoto Y, Mizukoshi E, Sakai Y et al. Hepatic ISG expression is associated with genetic variation in interleukin 28B and the outcome of IFN therapy for chronic hepatitis C. Gastroenterology 2010; 139: 499–509.
Dill MT, Duong FH, Vogt JE, Bibert S, Bochud PY, Terracciano L et al. Interferon-induced gene expression is a stronger predictor of treatment response than IL28B genotype in patients with hepatitis C. Gastroenterology 2011; 140: 1021–1031.
Abe H, Hayes CN, Ochi H, Maekawa T, Tsuge M, Miki D et al. IL28 variation affects expression of interferon stimulated genes and peg-interferon and ribavirin therapy. J Hepatol 2011; 54: 1094–1101.
Abe H, Hayes CN, Ochi H, Tsuge M, Miki D, Hiraga N et al. Inverse association of IL28B genotype and liver mRNA expression of genes promoting or suppressing antiviral state. J Med Virol 2011; 83: 1597–1607.
Asahina Y, Tsuchiya K, Muraoka M, Tanaka K, Suzuki Y, Tamaki N et al. Association of gene expression involving innate immunity and genetic variation in interleukin 28B with antiviral response. Hepatology 2012; 55: 20–29.
Urban TJ, Thompson AJ, Bradrick SS, Fellay J, Schuppan D, Cronin KD et al. IL28B genotype is associated with differential expression of intrahepatic interferon-stimulated genes in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2010; 52: 1888–1896.
Noureddin M, Wright EC, Alter HJ, Clark S, Thomas E, Chen R et al. Association of IL28B genotype with fibrosis progression and clinical outcomes in patients with chronic hepatitis C: a longitudinal analysis. Hepatology 2013; 58: 1548–1557.
Rotman Y, Noureddin M, Feld JJ, Guedj J, Witthaus M, Han H et al. Effect of ribavirin on viral kinetics and liver gene expression in chronic hepatitis C. Gut 2014; 63: 161–169.
Suppiah V, Moldovan M, Ahlenstiel G, Berg T, Weltman M, Abate ML et al. IL28B is associated with response to chronic hepatitis C interferon-alpha and ribavirin therapy. Nat Genet 2009; 41: 1100–1104.
Meier V, Mihm S, Ramadori G . Interferon-alpha therapy does not modulate hepatic expression of classical type I interferon inducible genes. J Med Virol 2008; 80: 1912–1918.
Sarasin-Filipowicz M, Wang X, Yan M, Duong FH, Poli V, Hilton DJ et al. Alpha interferon induces long-lasting refractoriness of JAK-STAT signaling in the mouse liver through induction of USP18/UBP43. Mol Cell Biol 2009; 29: 4841–4851.
Lanford RE, Guerra B, Lee H, Chavez D, Brasky KM, Bigger CB . Genomic response to interferon-alpha in chimpanzees: implications of rapid downregulation for hepatitis C kinetics. Hepatology 2006; 43: 961–972.
Fujiwara D, Hino K, Yamaguchi Y, Kubo Y, Yamashita S, Uchida K et al. Type I interferon receptor and response to interferon therapy in chronic hepatitis C patients: a prospective study. J Viral Hepat 2004; 11: 136–140.
Marcello T, Grakoui A, Barba-Spaeth G, Machlin ES, Kotenko SV, MacDonald MR et al. Interferons alpha and lambda inhibit hepatitis C virus replication with distinct signal transduction and gene regulation kinetics. Gastroenterology 2006; 131: 1887–1898.
Duong FH, Trincucci G, Boldanova T, Calabrese D, Campana B, Krol I et al. IFN-lambda receptor 1 expression is induced in chronic hepatitis C and correlates with the IFN-lambda3 genotype and with nonresponsiveness to IFN-alpha therapies. J Exp Med 2014; 211: 857–868.
Feld JJ, Nanda S, Huang Y, Chen W, Cam M, Pusek SN et al. Hepatic gene expression during treatment with peginterferon and ribavirin: Identifying molecular pathways for treatment response. Hepatology 2007; 46: 1548–1563.
Randall G, Chen L, Panis M, Fischer AK, Lindenbach BD, Sun J et al. Silencing of USP18 potentiates the antiviral activity of interferon against hepatitis C virus infection. Gastroenterology 2006; 131: 1584–1591.
Amanzada A, Kopp W, Spengler U, Ramadori G, Mihm S . Interferon-lambda4 (IFNL4) transcript expression in human liver tissue samples. PloS One 2013; 8: e84026.
Petta S, Cabibbo G, Enea M, Macaluso FS, Plaia A, Bruno R et al. Cost-effectiveness of sofosbuvir-based triple therapy for untreated patients with genotype 1 chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2014; 59: 1692–1705.
Geiss GK, Bumgarner RE, Birditt B, Dahl T, Dowidar N, Dunaway DL et al. Direct multiplexed measurement of gene expression with color-coded probe pairs. Nat Biotechnol 2008; 26: 317–325.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Intramural Research Program of the NIDDK, NIH.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on Genes and Immunity website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Noureddin, M., Rotman, Y., Zhang, F. et al. Hepatic expression levels of interferons and interferon-stimulated genes in patients with chronic hepatitis C: A phenotype–genotype correlation study. Genes Immun 16, 321–329 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2015.11
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2015.11
This article is cited by
-
Possible relationship between IL28B rs12979860 and TLR2 -196 to -174 del/ins polymorphisms and the liver fibrosis stage in hepatitis C patients
Archives of Virology (2022)
-
Interferon lambda4 polymorphism is not associated with human papillomavirus infection outcome
Virus Genes (2018)
-
IFN-λ4 potently blocks IFN-α signalling by ISG15 and USP18 in hepatitis C virus infection
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Gene–disease association with human IFNL locus polymorphisms extends beyond hepatitis C virus infections
Genes & Immunity (2016)
-
IFN-stimulated gene expression is independent of the IFNL4 genotype in chronic HIV-1 infection
Archives of Virology (2016)