Abstract
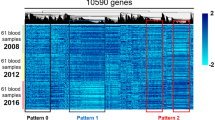
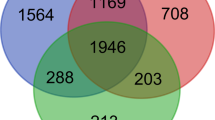
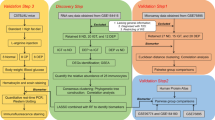
Understanding the pathogenesis of type-I diabetes (T1D) is hindered in humans by the long autoimmune process occurring before clinical onset and by the difficulty to study the pancreas directly. Alternatively, exploring body fluids and particularly peripheral blood can provide some insights. Indeed, circulating cells can function as ‘sentinels’, with subtle changes in gene expression occurring in association with disease. Therefore, we investigated the gene expression profiles of circulating blood cells using Affymetrix microarrays. Whole-blood samples from 20 first-degree relatives of T1D children with autoimmune diabetes-related antibodies, 19 children immediately after the onset of clinical T1D and 20 age- and sex-matched healthy controls were collected in PAXgene tubes. A global gene expression analysis with MDS approach allowed the discrimination of pre-diabetic subjects, diabetic patients and healthy controls. Univariate statistical analysis highlighted 107 distinct genes differently expressed between these three groups. Two major gene expression profiles were characterized, including type-I IFN-regulated genes and genes associated with biosynthesis and oxidative phosphorylation. Our results showed the presence of early functional modifications associated with T1D, which could help to understand the disease and suggest possible avenues for therapeutic interventions.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bach JF . Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus as an autoimmune disease. Endocr Rev 1994; 15: 516–542.
Bach JF . Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus as a beta-cell targeted disease of immunoregulation. J Autoimmun 1995; 8: 439–463.
Atkinson MA, Leiter EH . The NOD mouse model of type 1 diabetes: as good as it gets? Nat Med 1999; 5: 601–604.
Meier JJ, Bhushan A, Butler AE, Rizza RA, Butler PC . Sustained beta cell apoptosis in patients with long-standing type 1 diabetes: indirect evidence for islet regeneration? Diabetologia 2005; 48: 2221–2228.
Achenbach P, Warncke K, Reiter J, Naserke HE, Williams AJ, Bingley PJ et al. Stratification of type 1 diabetes risk on the basis of islet autoantibody characteristics. Diabetes 2004; 53: 384–392.
Bingley PJ, Gale EA . Progression to type 1 diabetes in islet cell antibody-positive relatives in the European nicotinamide diabetes intervention trial: the role of additional immune, genetic and metabolic markers of risk. Diabetologia 2006; 49: 881–890.
Wang X, Jia S, Geoffrey R, Alemzadeh R, Ghosh S, Hessner MJ . Identification of a molecular signature in human type 1 diabetes mellitus using serum and functional genomics. J Immunol 2008; 180: 1929–1937.
Kaizer EC, Glaser CL, Chaussabel D, Banchereau J, Pascual V, White PC . Gene expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from children with diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2007; 92: 3705–3711.
Liew CC, Ma J, Tang HC, Zheng R, Dempsey AA . The peripheral blood transcriptome dynamically reflects system wide biology: a potential diagnostic tool. J Lab Clin Med 2006; 147: 126–132.
Maas K, Chan S, Parker J, Slater A, Moore J, Olsen N et al. Cutting edge: molecular portrait of human autoimmune disease. J Immunol 2002; 169: 5–9.
Batliwalla FM, Li W, Ritchlin CT, Xiao X, Brenner M, Laragione T et al. Microarray analyses of peripheral blood cells identifies unique gene expression signature in psoriatic arthritis. Mol Med 2005; 11: 21–29.
Li D, Butt A, Clarke S, Swaminathana R . Real-time quantitative PCR measurement of thyroglobulin mRNA in peripheral blood of thyroid cancer patients and healthy subjects. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2004; 1022: 147–151.
Pachot A, Lepape A, Vey S, Bienvenu J, Mougin B, Monneret G . Systemic transcriptional analysis in survivor and non-survivor septic shock patients: a preliminary study. Immunol Lett 2006; 106: 63–71.
Thach DC, Lin B, Walter E, Kruzelock R, Rowley RK, Tibbetts C et al. Assessment of two methods for handling blood in collection tubes with RNA stabilizing agent for surveillance of gene expression profiles with high density microarrays. J Immunol Methods 2003; 283: 269–279.
Rainen L, Oelmueller U, Jurgensen S, Wyrich R, Ballas C, Schram J et al. Stabilization of mRNA expression in whole blood samples. Clin Chem 2002; 48: 1883–1890.
Hartel C, Bein G, Muller-Steinhardt M, Kluter H . Ex vivo induction of cytokine mRNA expression in human blood samples. J Immunol Methods 2001; 249: 63–71.
Baccala R, Kono DH, Theofilopoulos AN . Interferons as pathogenic effectors in autoimmunity. Immunol Rev 2005; 204: 9–26.
Baechler EC, Batliwalla FM, Karypis G, Gaffney PM, Ortmann WA, Espe KJ et al. Interferon-inducible gene expression signature in peripheral blood cells of patients with severe lupus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003; 100: 2610–2615.
Kirou KA, Lee C, George S, Louca K, Peterson MG, Crow MK . Activation of the interferon-alpha pathway identifies a subgroup of systemic lupus erythematosus patients with distinct serologic features and active disease. Arthritis Rheum 2005; 52: 1491–1503.
Baechler EC, Bauer JW, Slattery CA, Ortmann WA, Espe KJ, Novitzke J et al. An interferon signature in the peripheral blood of dermatomyositis patients is associated with disease activity. Mol Med 2007; 13: 59–68.
Tan FK, Zhou X, Mayes MD, Gourh P, Guo X, Marcum C et al. Signatures of differentially regulated interferon gene expression and vasculotrophism in the peripheral blood cells of systemic sclerosis patients. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2006; 45: 694–702.
van Baarsen LG, van der Pouw Kraan TC, Kragt JJ, Baggen JM, Rustenburg F, Hooper T et al. A subtype of multiple sclerosis defined by an activated immune defense program. Genes Immun 2006; 7: 522–531.
van der Pouw Kraan TC, Wijbrandts CA, van Baarsen LG, Voskuyl AE, Rustenburg F, Baggen JM et al. Rheumatoid arthritis subtypes identified by genomic profiling of peripheral blood cells: assignment of a type I interferon signature in a subpopulation of patients. Ann Rheum Dis 2007; 66: 1008–1014.
Li Q, Xu B, Michie SA, Rubins KH, Schreriber RD, McDevitt HO . Interferon-alpha initiates type 1 diabetes in nonobese diabetic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 12439–12444.
Huang X, Yuang J, Goddard A, Foulis A, James RF, Lernmark A et al. Interferon expression in the pancreases of patients with type I diabetes. Diabetes 1995; 44: 658–664.
Foulis AK, Farquharson MA, Meager A . Immunoreactive alpha-interferon in insulin-secreting beta cells in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Lancet 1987; 2: 1423–1427.
Blanco P, Palucka AK, Gill M, Pascual V, Banchereau J . Induction of dendritic cell differentiation by IFN-alpha in systemic lupus erythematosus. Science 2001; 294: 1540–1543.
Wallace J, Petri M, Olsen N, Kirou K, Dennis G, Yao Y et al. Abstract 1315: MEDI-545, an anti-interferon alpha monoclonal antibody, shows evidence of clinical activity in systemic lupus erythematosus (ACR 71st annual scientific meeting). Arthritis Rheum 2007; 56 (9 suppl): S526.
Lang KS, Weigert C, Braedel S, Fillon S, Palmada M, Schleicher E et al. Inhibition of interferon-gamma expression by osmotic shrinkage of peripheral blood lymphocytes. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2003; 284: 200–208.
Yeshao W, Gu J, Peng X, Nairn AC, Nadler JL . Elevated glucose activates protein synthesis in cultured cardiac myocytes. Metabolism 2005; 54: 1453–1460.
Yin Z, Wilson S, Hauser NC, Tournu H, Hoheisel JD, Brown AJ . Glucose triggers different global responses in yeast, depending on the strength of the signal, and transiently stabilizes ribosomal protein mRNAs. Mol Microbiol 2003; 48: 713–724.
Nair KS, Halliday D, Garrow JS . Increased energy expenditure in poorly controlled type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetic patients. Diabetologia 1984; 27: 13–16.
Charlton MR, Nair KS . Role of hyperglucagonemia in catabolism associated with type 1 diabetes: effects on leucine metabolism and the resting metabolic rate. Diabetes 1998; 47: 1748–1756.
Peakman M, Tree TI, Endl J, van Endert P, Atkinson MA, Roep BO . Characterization of preparations of GAD65, proinsulin, and the islet tyrosine phosphatase IA-2 for use in detection of autoreactive T-cells in type 1 diabetes: report of phase II of the second international immunology of diabetes society workshop for standardization of T-cell assays in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 2001; 50: 1749–1754.
van Halteren AG, Kardol MJ, Mulder A, Roep BO . Homing of human autoreactive T cells into pancreatic tissue of NOD–scid mice. Diabetologia 2005; 48: 75–82.
Monks SA, Leonardson A, Zhu H, Cundiff P, Pietrusiak P, Edwards S et al. Genetic inheritance of gene expression in human cell lines. Am J Hum Genet 2004; 75: 1094–1105.
Morley M, Molony CM, Weber TM, Devlin JL, Ewens KG, Spielman RS et al. Genetic analysis of genome-wide variation in human gene expression. Nature 2004; 430: 743–747.
Schroeder A, Mueller O, Stocker S, Salowsky R, Leiber M, Gassmann M et al. The RIN: an RNA integrity number for assigning integrity values to RNA measurements. BMC Mol Biol 2006; 7: 3.
Irizarry RA, Hobbs B, Collin F, Beazer-Barclay YD, Antonellis KJ, Scherf U et al. Exploration, normalization, and summaries of high density oligonucleotide array probe level data. Biostatistics 2003; 4: 249–264.
Bolstad BM, Irizarry RA, Astrand M, Speed TP . A comparison of normalization methods for high density oligonucleotide array data based on variance and bias. Bioinformatics 2003; 19: 185–193.
Tusher VG, Tibshirani R, Chu G . Significance analysis of microarrays applied to the ionizing radiation response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001; 98: 5116–5121.
Lee ML, Whitmore GA . Power and sample size for DNA microarray studies. Stat Med 2002; 21: 3543–3570.
Valentini G . Clusterv: a tool for assessing the reliability of clusters discovered in DNA microarray data. Bioinformatics 2006; 22: 369–370.
Dennis Jr G, Sherman BT, Hosack DA, Yang J, Gao W, Lane HC et al. DAVID: database for annotation, visualization, and integrated discovery. Genome Biol 2003; 4: P3.
Hosack DA, Dennis Jr G, Sherman BT, Lane HC, Lempicki RA . Identifying biological themes within lists of genes with EASE. Genome Biol 2003; 4: R70.
Huang da W, Sherman BT, Tan Q, Kir J, Liu D, Bryant D et al. DAVID bioinformatics resources: expanded annotation database and novel algorithms to better extract biology from large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res 2007; 35 (Web Server issue): W169–W175.
Calvano SE, Xiao W, Richards DR, Felciano RM, Baker HV, Cho RJ et al. A network-based analysis of systemic inflammation in humans. Nature 2005; 437: 1032–1037.
Pachot A, Blond JL, Mougin B, Miossec P . Peptidylpropyl isomerase B (PPIB): a suitable reference gene for mRNA quantification in peripheral whole blood. J Biotechnol 2004; 114: 121–124.
Acknowledgements
We thank Professors H Dodat, R Kohler and P Mouriquand, and Dr CL Gay (Hospices Civils de Lyon), Dr P Pelissier (CHU de St Etienne) and Dr C Bony (CH d’Annonay) for their contribution to the study. This work was supported by bioMérieux and grants from the ‘Association Nationale de la Recherche Technique’ (ANRT) and the ‘Association Française des diabétiques’ (AFD).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Genes and Immunity website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reynier, F., Pachot, A., Paye, M. et al. Specific gene expression signature associated with development of autoimmune type-I diabetes using whole-blood microarray analysis. Genes Immun 11, 269–278 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2009.112
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2009.112
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Persistent coxsackievirus B infection and pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes mellitus
Nature Reviews Endocrinology (2022)
-
SARS-CoV-2 infects and replicates in cells of the human endocrine and exocrine pancreas
Nature Metabolism (2021)
-
Common functional alterations identified in blood transcriptome of autoimmune cholestatic liver and inflammatory bowel diseases
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Impact of blood collection and processing on peripheral blood gene expression profiling in type 1 diabetes
BMC Genomics (2017)
-
Investigation of coordination and order in transcription regulation of innate and adaptive immunity genes in type 1 diabetes
BMC Medical Genomics (2017)