Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the success (glaucoma control) of latanoprost therapy of primary congenital glaucoma (PCG) and factors affecting the long-term outcome.
Methods
Patients with PCG treated with latanoprost were re-examined. At study visit and from clinical charts, we evaluated: intraocular pressure, length of glaucoma control with latanoprost, need of further medication or glaucoma surgery, systemic and topical side effects. Multivariate analysis was used to test factors related to the final outcome of the treatment.
Results
Eighty-one eyes of 44 patients with PCG, and 42 eyes of 29 patients with previous glaucoma surgery, had received latanoprost therapy. In the first group, a success (glaucoma control by latanoprost therapy) was found in 24 eyes (29.6%), whereas 57 eyes (70.4%) had received surgery (45 eyes (55.6%) in the first year); among the eyes with previous surgery, a success was found in 12 eyes (28.6%), 13 eyes (31%) required an additional therapy, and 17 eyes (40.5%) had received further glaucoma surgery. No patient discontinued the treatment because of side effects. Factors related to the failure of the latanoprost treatment were: the high score of severity of glaucoma (P=0.014) and low age at PCG presentation (P=0.042).
Conclusions
Long-term treatment with latanoprost is effective in about 30% of the eyes; factors related to failure were severe glaucomatous alterations, and young age at PCG presentation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Primary congenital glaucoma (PCG) is a rare disease (about 1 in 10 000 births), which often leads to severe visual disability:1 about 8% of blindness in childhood has been ascribed to this disease.2
According to the European Glaucoma Society, surgical treatment of PCG is often necessary, and medical therapy can be used while a decision is made on a surgical approach and in case of failed surgery while waiting for further options. In PCG, primary medical therapy is usually not advised due to low efficacy and the potential for systemic adverse events; this latter are related to the high haematic concentration after topical administration (children have relatively low blood volume and drug deactivation) and to the sensitivity to the drugs.3, 4
Latanoprost is a prostaglandin F2α derivative that increases the uveoscleral outflow.5 In adult patients, it decreases the intraocular pressure (IOP) by 20–35%, with good tolerability and safety. Side effects are mainly local, and include burning, stinging, foreign body sensation and itching, conjunctival hyperaemia, increased pigmentation of periocular skin and of the iris, and eyelash changes. Cystoid macular edema in aphakic or pseudophakic eyes, reactivation of herpes keratitis, and reactivation of anterior uveitis have been reported.6
Few case series have reported the use of latanoprost in paediatric age.7, 8, 9, 10 In these studies, a minority of patients were responders to latanoprost treatment (IOP decrease over 15%), mainly patients with juvenile onset glaucoma.
Recently, a 12-week, double-masked, parallel-group multicenter study, showed in 137 subjects aging less than 18 years (mean age 8.8±5.5 years) that latanoprost determined an IOP reduction greater than timolol (respectively, 7.2 and 5.7 mm Hg), with a rate of responder, respectively, of 60 and 52%; both treatments were well tolerated.11
The aim of this study was to evaluate the long-term efficacy of treatment with latanoprost in PCG glaucoma, and to identify the factors affecting the clinical outcome.
Materials and methods
From March to May 2013, at the Eye Clinic of the University of Catania (Italy), we recalled and re-examined a group of children affected by PCG monitored at the Glaucoma Centre who had been treated with latanoprost eyedrops after January 1997. We excluded patients with childhood glaucoma with ocular and/or systemic anomalies, juvenile open-angle glaucoma, and secondary acquired glaucoma. The study followed the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki, and was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the University of Catania. Before the inclusion in the study, patients or parents gave the informed consent after the aims and the possible risks of the study were fully explained.
At the study visit, and retrospectively from the clinical chart, we evaluated: demographics, age at the presentation, previous glaucoma therapy or surgery, age at the latanoprost treatment, IOP at the start of treatment with latanoprost.
The following information were collected: other treatments (medical or surgical) received; systemic and ocular side effects as recorded in clinical charts; IOP at the last visit; the duration of latanoprost treatment.
The final outcome was defined as: glaucoma controlled only by latanoprost therapy, need for additional medical therapy, or glaucoma surgery. In children treated with latanoprost at age lower than 1 year, a severity score of PCG was calculated according to Al-Hazmi et al.12
The diagnosis of glaucoma had been made at an outpatient visit and/or under anaesthesia. Outpatients received a biomicroscopic examination of the anterior segment, an IOP measurement with topical anaesthesia, with a Perkins MK2 applanation tonometer (Clement Clarke, Harlow, UK) and a small wire lid retractor, and an ophthalmoscopic examination of the fundus with evaluation of the optic nerve (asymmetry, cupping). If glaucoma was detected, patients received latanoprost treatment, and verification under anaesthesia was planned; if glaucoma could be excluded, an outpatient examination in a month was planned. Examination under anaesthesia consisted of measurement of corneal diameters with a caliper, anterior segment examination with an operating microscope, gonioscopic examination by Koeppe lens (Ocular Instruments, Bellevue, WA, USA), measurement of anteroposterior and laterolateral ocular diameters by A-scan standardized echography, and, if surgery was not required, dilated fundus examination with optic nerve head evaluation; more recently, central corneal thickness was determined. IOP was assessed by Perkins tonometer with a wire lid retractor. Anaesthesia was by sevoflurane (Sevorane, Abbott, Maidenhead, UK); IOP was determined during maintenance and before the recovery. If glaucoma was judged not controlled by latanoprost treatment (high IOP, progressive ocular diameter enlargement, increase in cup-disc ratio of 0.2 or more), surgery was performed.
In cooperative patients aged over 6 years, glaucoma was assessed in the standard way, with IOP measurement by Goldmann tonometer, visual field testing, and optic nerve head examination. The visual field was tested by automated computerized perimetry (24-2, Humphrey Field Analyzer; Carl Zeiss, Jena, Germany). More recently, optic nerve head morphologic has been assessed by Heidelberg retinal tomography and retinal nerve fibre layer measurement by optical coherence tomography.
After the treatment began, IOP was measured at the first month and then every 2–3 months, in relation to the IOP and the ocular conditions. In cases of uncontrolled glaucoma (high IOP, progressive ocular diameter enlargement, increase in cup-disc ratio of 0.2 or more, progression of visual field damage in older children), patients received surgery or, if not contraindicated by age, additional medical therapy.
Statistical analysis
Multivariate analysis was used to test the if gender, monocular or binocular PCG, age at presentation, glaucoma severity (high IOP, corneal edema, corneal diameter enlargement), could affect the final outcome and the duration of treatment. Kaplan–Meier survival analyses were applied to assess the long-term outcome in eyes with or without previous surgery. P values lower than 0.05 were considered statistically significant. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS v15.0 (SPSS Inc, Chicago, IL, USA).
Results
Eighty-one eyes of 44 children (25 male, 19 female) have been treated with latanoprost as primary treatment; 37 patients received treatment in both eyes and 7 in one eye. Age at the treatment ranged from 1 to 34 months (mean±SD: 10±7 months).
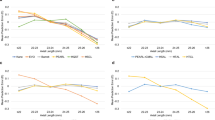
At the final visit, 57 eyes (70.4%) had received surgery: 45 eyes (55.6%) in the first year, 8 (9.9%) eyes in the following year, and 4 eyes during 2 further years (4.9%). Twenty-four eyes (29.6%) had glaucoma controlled by therapy with latanoprost; for three eyes (3.7%), latanoprost had been discontinued. In the eyes with PCG controlled by latanoprost, the mean IOP reduction was 8.5±1.8 mm Hg (35.6%; mean baseline IOP: 23.9±1.9 mm Hg, final IOP: 15.4±1.3 mm Hg, t-test P<0.001). Overall, the mean duration of glaucoma control with latanoprost was 18±22 months (range 1–94 months).
Forty-two eyes of 29 patients, which had previous surgery, received latanoprost when glaucoma was uncontrolled; time after surgery ranged from 7 to 83 months (mean 37±18 months); mean age at the start of the latanoprost treatment was 54±28 months (range 14–113 months). At the final visit, 17 eyes (40.5%) had received further glaucoma surgery, 13 eyes (31%) an additional therapy (latanoprost+timolol 0.5% fixed combination, or brinzolamide 1% bid), 12 eyes (28.6%) had glaucoma still controlled by latanoprost treatment. Overall, the mean duration of glaucoma control with latanoprost was 33±15 months (range 6–70 months; Figures 1 and 2).
None of the patients stopped latanoprost treatment because of side effects. The adverse events recorded were: in four eyes (9%) conjunctival hyperaemia; in one eye (of one patient with monocular glaucoma) increase of iris pigmentation and eyelash changes, which regressed 3 years after treatment discontinuation (because of low IOP). One patient had irritation of the upper airways that regressed with systematic manual nasolacrimal occlusion on instillation of drops.
Multivariate analysis showed that factors related to the failure of the latanoprost treatment were: high score of severity of glaucoma (P=0.014) and low age at PCG presentation (P=0.042).
Discussion
Glaucoma severity at the presentation is key factor in treatment efficacy; previously Al-Hazmi et al12 evaluated some clinical parameters (corneal diameter, corneal clarity, IOP) of PCG at the time of the treatment (surgery). They obtained good surgical results by using more aggressive techniques in cases with higher score. In our series, many patients with severe PCG at the presentation had no clinical response to latanoprost: more than 50% of the eyes received surgery within 1 year.
Also the age at presentation is related to the final outcome. Previous studies have found that responder to latanoprost (15% IOP reduction) had juvenile onset glaucoma, whereas less or no effect was found in eyes with PCG.8, 10, 11 The IOP reduction in a 12 weeks study ranged between 20 and 30%, and the rate of responders (IOP decrease>15% of baseline IOP) was greater in non-PCG than in PCG (75% vs 40%).13 Also in patients with Sturge–Weber syndrome, a significant IOP reduction was found in eyes with juvenile onset glaucoma (mean 8.8 mm Hg), but not in those affected with congenital onset glaucoma.7
Time of presentation affects the prognosis of PCG: the earlier in life the disease occurs the worse the prognosis, and higher the failure rate of surgery, caused by more severe alterations.14
Enyedi et al8 found, in patients with several forms of glaucoma (31 eyes) that after one year of treatment, IOP fell more than 15% in 6 eyes (19%; responders to treatment, with a mean IOP reduction of 8.5 mm Hg); IOP fell less than 15% in 34% of the eyes and did not change in the other eyes. The same group, in a 10-year survey of 63 patients affected with various types of glaucoma, found that 36% of the eyes were responders (mean reduction 7 mm Hg).10 Overall, most of the patients were not responders, but responders had varied IOP reduction.
We have used latanoprost in congenital glaucoma since May 1997: under an institutional review board-approved protocol, it was prescribed to a 2-month-old female patient with monocular glaucoma who could not be operated on because of anaesthesia problems. After this, latanoprost therapy was proposed for all patients with congenital glaucoma, at least during preparation for surgery. In a previous study with a mean follow-up of 12 months, we found in 22 eyes of 14 patients affected with congenital glaucoma, a mean IOP decrease of 7.1±7.2 mm Hg (28.3%). Five eyes (23%) with uncontrolled glaucoma underwent surgery.15 In the present study, we evaluated the long-term efficacy of latanoprost therapy in PCG and identified some factors related to the outcome.
In a series of 81 eyes with PCG that received latanoprost as primary treatment, we found that 24 eyes (29.6%) had glaucoma controlled by latanoprost treatment and 57 eyes (70.4%) had received surgery. For three eyes (3.7%), latanoprost had been discontinued. In the group of eyes with PCG with previous glaucoma surgery, latanoprost treatment was effective in glaucoma control in 28% of eyes; in such patients, because of the older age, it was possible to use an additional topical therapy, and surgery was performed in 40% of the eyes; surgery was the only available option in younger children.
In three eyes of two patients with stable low IOP values (<10 mm Hg), latanoprost was discontinued. Sporadic cases of spontaneous resolution of congenital glaucoma have been reported in past decades.16, 17 More recently, Nagao et al,18 in a retrospective analysis on 356 patients, reported a spontaneous resolution in 14 eyes of nine patients; all had larger corneas (10 eyes had Haab’s striae) and normal IOP, and a postnatal development of the angle structures in eyes with milder abnormalities was hypothesized.
We found infrequent mild and reversible topical side effects. Also, the above-mentioned studies have reported low side effects;7, 8, 9, 10 consistent with the experience in adults. Although conjunctival hyperaemia, eyelash changes, and increased pigmentation of periocular skin (removed by epidermal exfoliation) are reversible, increase of iris pigmentation, caused by an increase of the size of melanin granules in iris melanocytes, is considered irreversible.19, 20 In our case also this event regressed; however, increase of iris pigmentation has been shown with no ocular damage.
Even though the present study has some limitations such as sample size and no control group, we can conclude that the treatment with latanoprost allowed long-term control of PCG in about 30% of eyes; in eyes with previous glaucoma surgery, also because of a greater age, a control by latanoprost and latanoprost plus adjunctive medical therapy was obtained in 60% of the eyes. Factors related to failure, among others, were higher severity and early presentation of PCG.
References
European glaucoma society. Terminology and Guidelines for Glaucoma 3rd edn. Editrice Dogma: Savona, Italy, 2008 pp 93–94.
Dureau P . Congenital glaucoma and trabeculodysgenesis. Clinical and genetic aspects. J Fr Ophtalmol 2006; 29: 198–215.
Passo MS, Palmer EA, Van Buskirk EM . Plasma timolol in glaucoma patients. Ophthalmology 1984; 91: 1361–1363.
Levy Y, Zadok D . Systemic side effects of ophthalmic drops. Clin Pediatr 2004; 43: 99–101.
Bucolo C, Salomone S, Drago F, Reibaldi M, Longo A, Uva MG . Pharmacological management of ocular hypertension: current approaches and future prospective. Curr Opin Pharmacol 2013; 13: 50–55.
European glaucoma society. Terminology and Guidelines for Glaucoma 3rd edn. Editrice Dogma: Savona, Italy, 2008 pp 136–138.
Yang CB, Freedman SF, Myers JS, Buckley EG, Herndon LW, Allingham RR . Use of latanoprost in the treatment of glaucoma associated with Sturge-Weber syndrome. Am J Ophthalmol 1998; 126: 600–602.
Enyedi LB, Freedman SF, Buckley EG . The effectiveness of latanoprost for the treatment of pediatric glaucoma. J AAPOS 1999; 3: 33–39.
Enyedi LB, Freedman SF . Latanoprost for the treatment of pediatric glaucoma. Surv Ophthalmol 2002; 47: 129–132.
Black AC, Jones S, Yanovitch TL, Enyedi LB, Stinnett SS, Freedman SF . Latanoprost in pediatric glaucoma—pediatric exposure over a decade. J AAPOS 2009; 13: 558–562.
Maeda-Chubachi T, Chi-Burris K, Simons BD, Freedman SF, Khaw PT, Wirostko B et al. A6111137 Study Group. Comparison of latanoprost and timolol in pediatric glaucoma: a phase 3, 12-week, randomized, double-masked multicenter study. Ophthalmology 2011; 118: 2014–2021.
Al-Hazmi A, Awad A, Zwaan J, Al-Mesfer SA, Al-Jadaan I, Al-Mohammed A . Correlation between surgical success rate and severity of congenital glaucoma. Br J Ophthalmol 2005; 89: 449–453.
Maeda-Chubachi T, Chi-Burris K, Simons B, Brémond-Gignac D, Freedman S, Khaw PT et alA6111137 Study Group. Impact of age, diagnosis, and history of glaucoma surgery on outcomes in pediatric patients treated with latanoprost. J Glaucoma 2013; 22: 614–619.
Dureau P, Dollfus H, Cassegrain C, Dufier JL . Long-term results of trabeculectomy for congenital glaucoma. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus 1998; 35: 198–202.
Uva MG, Longo A, Cannemi V, Reibaldi A . Efficacy and Safety of Latanoprost in Congenital Glaucoma. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2003; 44, E-Abstract 2163.
Le Rebeller MJ, Lagoutte F . Spontaneous resolution of a case of congenital glaucoma. Bull Soc Ophtalmol Fr 1975; 75: 555–559.
Lockie P, Elder J . Spontaneous resolution of primary congenital glaucoma. Aust N Z J Ophthalmol 1989; 17: 75–77.
Nagao K, Noël LP, Noël ME, Walton DS . The spontaneous resolution of primary congenital glaucoma. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus 2009; 46: 139–143.
Alm A, Grierson I, Shields MB. . Side effects associated with prostaglandin analog therapy. Surv Ophthalmol 2008; 53 (suppl 1): S93–105.
Albert DM, Gangnon RE, Grossniklaus HE, Green WR, Darjatmoko S, Kulkarni AD . A study of histopathological features of latanoprost-treated irides with or without darkening compared with non-latanoprost-treated irides. Arch Ophthalmol 2008; 126: 626–631.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uva, M., Avitabile, T., Reibaldi, M. et al. Long-term efficacy of latanoprost in primary congenital glaucoma. Eye 28, 53–57 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/eye.2013.232
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/eye.2013.232
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Pediatric Glaucoma: Pharmacotherapeutic Options
Pediatric Drugs (2016)
-
Latanoprost and Dorzolamide for the Treatment of Pediatric Glaucoma: The Glaucoma Italian Pediatric Study (Gipsy), Design and Baseline Characteristics
Advances in Therapy (2016)
-
Evolving Perspectives on Congenital Glaucoma
Current Ophthalmology Reports (2015)
-
Latanoprost
Reactions Weekly (2014)